
Supertyphoon Haiyan hit the Philippines on Friday, leaving at least 10,000 residents dead and hundreds of thousands without reliable food, shelter or water. One of the strongest storms ever recorded, Haiyan’s winds surpassed 140 miles per hour, bringing record storm surges. The full extent of the damage remains uncertain, with communication and transportation severely restricted.
The World Bank has called the Philippines one of the most hazard-prone countries in the world. Closed roads and airports restricted aid efforts after Supertyphoon Haiyan, and communication failures posed some of the greatest challenges to both assessing and recovering from damage.
“Under normal circumstances, even in a typhoon, you’d have some local infrastructure up and some businesses with which you can contract,” Praveen Agrawal, the World Food Program’s Philippines representative and country director, told the New York Times. “Being as strong as it was, it was very much like a tsunami. It wiped out everything. It’s like starting from scratch” in terms of delivering the aid, he said.
The United Nations has set aside over $300 million to help with the country’s recovery from Haiyan over the next six months, and three dozen individual nations and international organizations have pledged financial and humanitarian assistance. The United States recalled thousands of sailors from shore leave back to the USS George Washington, a massive aircraft carrier currently docked in Hong Kong, to use its 80 aircraft to help deliver supplies and evacuate victims in the Philippines’ hardest-hit islands.
Yet with the broad scope of damage to critical infrastructure, the process has been slow. In the major city of Tacloban, for example, the traffic control tower at one of the country’s biggest airports was destroyed, forcing all aircraft to land by sight, further slowing distribution of food and water. Officials opened smaller airstrips, focusing on safely reopening transportation routes as the hundreds of thousands of evacuees continue to face extreme water shortage. This shortage further compounds the dangers authorities face in recovery, as health officials grow more concerned about water-borne diseases. Most notably, the lack of clean drinking and bathing water in crowded evacuation centers brings risk of diarrhea, leptospirosis and dengue.
Officials are looking forward while managing the catastrophic fallout. According to the Wall Street Journal:
Finance Secretary Cesar Purisima acknowledged that the destruction wrought by the disaster on an area that contributes 12.5% to gross domestic product could shave off as much as a full percentage point to economic growth next year, when the government targets GDP expansion of at least 6.5%. He is hopeful that the adverse effect on growth will be cushioned, if not offset, by the reconstruction spending.
“From a fiscal standpoint, we do have fiscal space to spend for reconstruction. The estimates are preliminary, but we need to invest significantly on infrastructure,” Mr. Purisima said.
The New York Times reported:
HSBC Global Research said that the typhoon probably destroyed half the sugar cane production areas in Leyte Province, and that all told, 3.5 percent of the nation’s sugar cane output was probably lost. It also warned of inflationary shocks to the Philippine economy in the coming months, as supply chains are disrupted.
But given the general health of the Philippine economy and the fact that the typhoon affected geographic areas and sectors like agriculture that are not major drivers of the nation’s output, HSBC said, “The economic impact will be limited.”
Citi Research estimated that infrastructure damage will probably run into billions of pesos, exceeding $70 million.
In Warsaw on Monday, some delegates at United Nations talks on a global climate treaty suggested that global warming was responsible for making Haiyan such a devastating storm. Naderev Saño, the chief representative of the Philippines at the conference, told the New York Times, “What my country is going through as a result of this extreme climate event is madness; the climate crisis is madness.”
Scientists cannot be certain of the overall impact of climate change on severe weather like hurricanes and typhoons, but have noted that more powerful storms will continue as the climate changes. With winds of at least 140 miles an hour, Typhoon Haiyan is considered one of the strongest storms to make landfall. “As you warm the climate, you basically raise the speed limit on hurricanes,” said M.I.T. atmospheric scientist Kerry A. Emanuel.
The powerful storm surges recorded are also likely part of a new reality in major storms. “When you strip everything else away, we’re seeing a general rise in sea level,” James P. Kossin, atmospheric scientist at the National Climatic Data Center, told the Times. “There’s no question that storm surge is going to be compounded.”
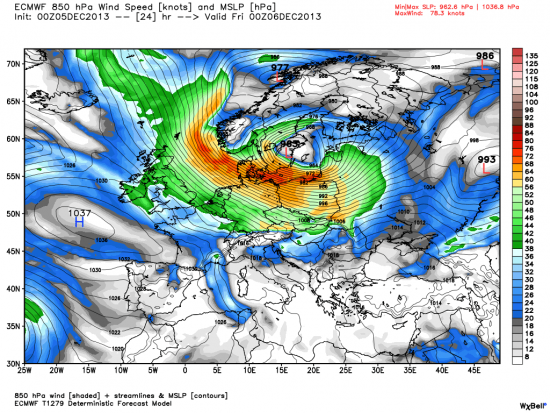 Windstorm Xaver: Model shows a large area of high winds in the lower atmosphere pushing waters of the North Sea into the coasts around western Europe.
Windstorm Xaver: Model shows a large area of high winds in the lower atmosphere pushing waters of the North Sea into the coasts around western Europe.

