After a last-minute failure by the Senate to pass the Terrorism Risk Insurance Act (TRIA) in December, the bill was overwhelmingly passed by the Senate on Jan. 8, with a vote of 93 to 4. The House of Representatives had voted 416 to 5 to pass TRIA in December. The bill now awaits President Obama’s signature.
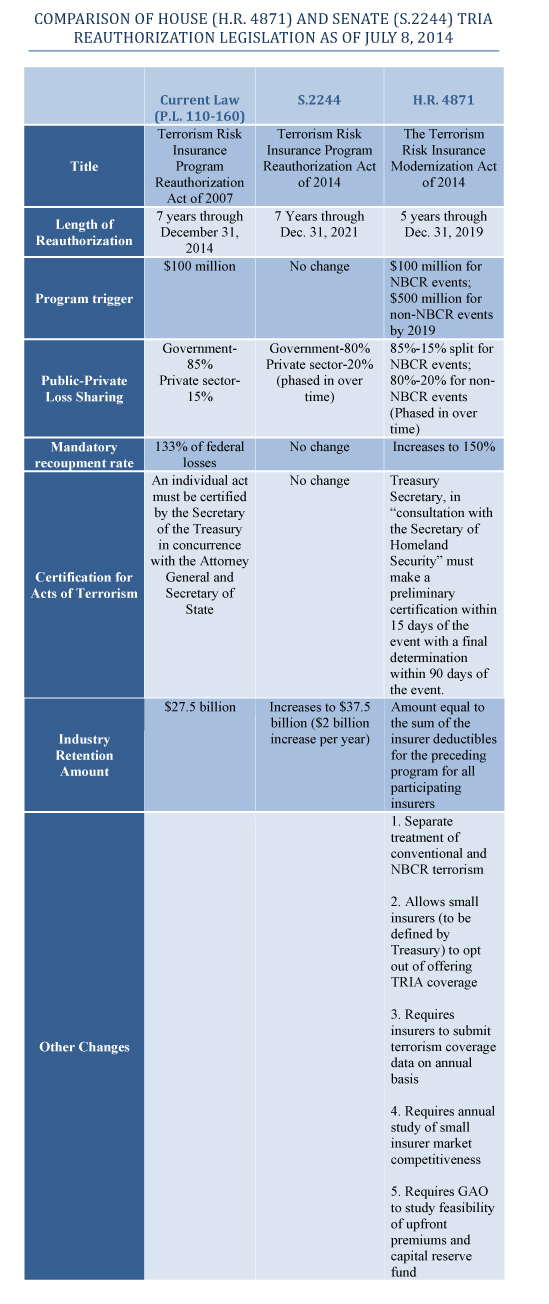
H.R. 26, which is the same as last year’s amended S. 2244, reauthorizes TRIA through the end of 2020. Under the six-year extension, starting in 2016, there will be phased-in increases to the program’s trigger, raising it from $100 million to $200 million in annual aggregate insured losses, and the insurer co-share will be raised from 15% to 20%. The bill also phases in an increase in the aggregate amount of insured terrorism losses that must be borne by the private sector from the current $27.5 billion to $37.5 billion. Taxpayer dollars to fund those losses would be recouped post-event.
Several industries were quick to praise TRIA’s passage, as the Senate’s failure to reauthorize the Terrorism Risk Insurance Act in December left insurance buyers facing renewals on terrorism coverage with unanswered questions.
The Commercial Real Estate Development Association (NAIOP) praised the bill’s passage, saying, “This is sound policy because it enables insurers and private sector capital to provide coverage for losses that otherwise would fall upon the taxpayer. This vital security blanket could help save billions of dollars that would otherwise be spent in the aftermath of a terrorist attack. Renewing TRIA for six years represents a major victory for the commercial real estate industry and the millions of jobs and economic growth it supports. Today’s vote gives developers the peace of mind to invest in an industry that contributed $376 billion to GDP last year, supported 2.8 million jobs, and produced $120 billion in personal earnings.”
The Coalition to Insure Against Terrorism (CIAT) said in a statement, “CIAT members are pleased the Senate has acted quickly to approve TRIA reauthorization as one of the first orders of business in the new Congress. We commend Majority Leader McConnell and Minority Leader Reid for their leadership in seeing this critical legislation through to completion, and are encouraged by the strong bipartisan support for reauthorization in both chambers.”
Marsh & McLennan said it “applauds the new Congress for its swift reauthorization of this critically important public-private partnership, which will help to ensure a reliable marketplace for terrorism coverage in the event of attack. We are pleased that TRIPRA directs the Treasury Department to review the protocols for certification which would help to protect the nation’s economic security in the event of a terrorist attack.”
Leigh Ann Pusey, president and CEO of the American Insurance Association (AIA), said in a statement that the “terrorism risk insurance program will remain in place protecting our nation’s economy, policyholders and taxpayers. Congress’ timely reauthorization of TRIA will preserve a well-functioning private terrorism insurance marketplace.” She added, “As with previous TRIA reauthorizations, the primary responsibility for financial recovery is placed on the private sector in all but the most catastrophic of events.
“Congress’ bipartisan action on TRIA this week will help ensure the continued availability of terrorism risk insurance, providing stability for the broad range of businesses of all sizes that depend on this essential coverage,” noted the National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts (NAREIT). “We strongly urge President Obama to sign this legislation into law at the earliest opportunity.”
ISO announced that it is filing revised terrorism forms in response to passage of the act. The revised forms will be for insurer use in most states shortly after President Obama signs the bill, known as the Terrorism Risk Insurance Program Reauthorization Act of 2015.