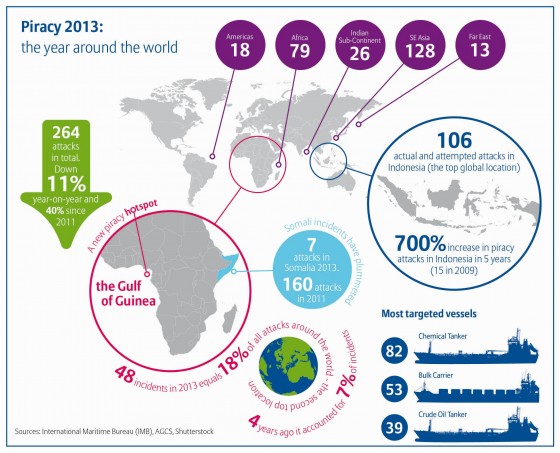
Steps taken by the international maritime community have paid off, reducing the threat of piracy in the Arabian Sea’s Gulf of Aden, according to the Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty Safety and Shipping Review 2014. The number of ships seized and hostages taken was down significantly in 2013. According to the International Maritime Bureau (IMB), piracy at sea is at the lowest level in six years—264 attacks were recorded worldwide in 2013, a 40% drop since Somali piracy peaked in 2011. There were 15 incidents reported off Somalia in 2013, including Gulf of Aden and Red Sea incidents—down from 75 in 2012, and 237 in 2011 (including attacks attributed to Somali pirates in the Gulf of Aden, Red Sea and Oman).
But while the number of incidents in this region has gone down, piracy attacks in other areas have increased in frequency, notably Indonesia and off the west coast of Africa. While most of these Indonesian attacks remain local, low level opportunistic thefts carried out by small bands of individuals, a third of the incidents in these waters were reported in the last quarter of 2013, meaning there is potential for such attacks to escalate into a more organized piracy model unless they are controlled.
The Gulf of Guinea region accounted for 48 of the 264 incidents in 2013. Of these, Nigerian pirates and armed robbers were responsible for 31 incidents, including two hijackings, 13 vessel boardings and 13 vessels fired upon. One crew member was killed and 36 kidnapped—the highest number of Nigerian kidnappings for five years, according to the IMB.