The earthquake in Japan earlier this month has impacted the supply chain of General Motors, causing four plants in North America to close temporarily because of a shortage of parts from Japan, the company reported.
GM said in a statement that its manufacturing operations are expected to be down for two weeks beginning April 25 in Spring Hill, Tennessee; Lordstown, Ohio; Fairfax, Kansas and the Oshawa Flex Assembly in Canada.
the Oshawa Flex Assembly in Canada.
The temporary adjustment is not expected to have “any material impact on GM’s full-year production plans in North America,” GM said. In addition, the company “does not expect a material impact to its second quarter or full-year financial results for GM North America.”
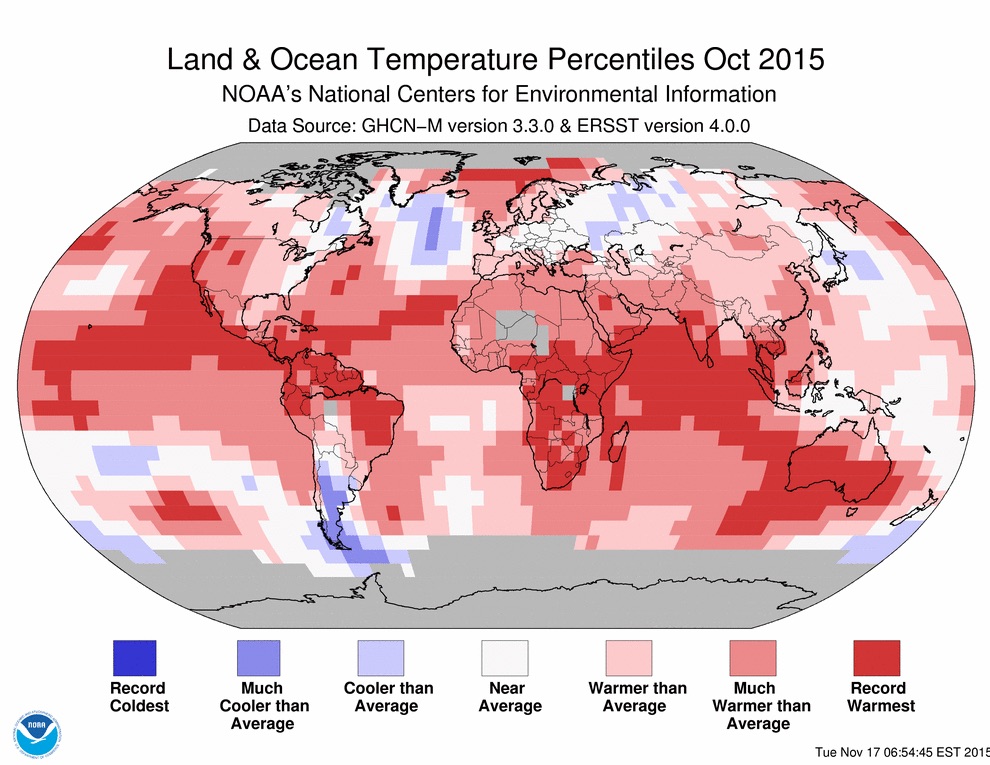
Japan’s Kyushu Island was rocked by a 7.0 temblor on April 16, killing 58 people and injuring about 900, according to AIR Worldwide. The quake was the strongest to strike Japan since 2011, when a massive 9.0-magnitude offshore earthquake unleashed a tsunami that killed 18,000 people in the country’s northeast and triggered meltdowns at a nuclear power plant in Fukushima, the New York Times reported.
AIR said the earthquake is expected to result in insured losses between $1.7 billion and $2.9 billion. Those losses only reflect insured physical damage to onshore property (residential, commercial/industrial, mutual), both structures and their contents, from ground shaking, fire-following and liquefaction, AIR said.
The Japan Fire and Disaster Management Agency (FDMA) estimates that more than 3,900 residences and 120 non-residential buildings were damaged or destroyed, a number of mudslides resulted, and 14 fires were attributed to the temblors.
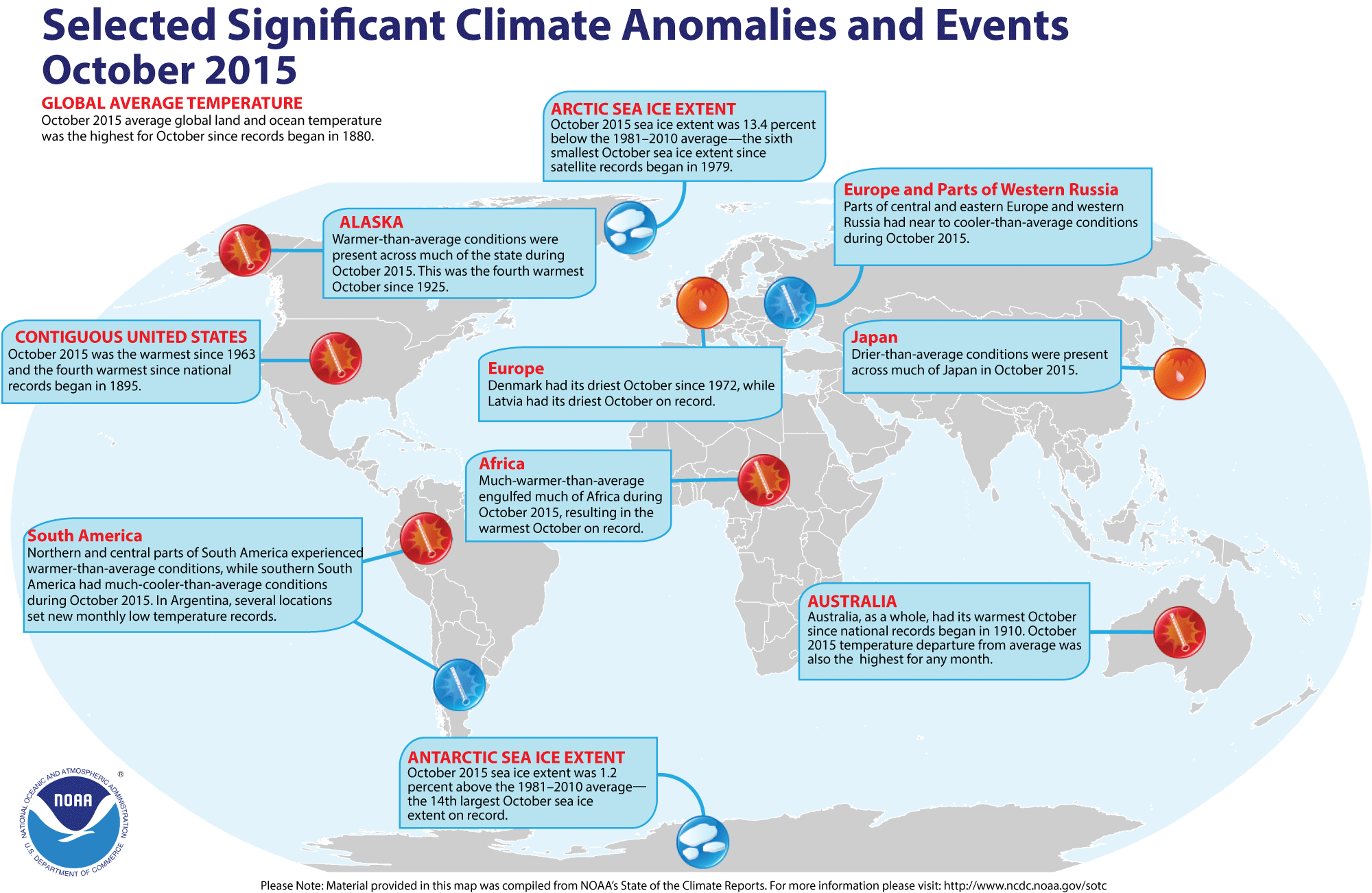
On the same day, April 16, a 7.
8 earthquake struck the central coast of Ecuador, killing 570 people and injuring more than 4,700. AIR estimates losses from that quake between $325 million and $850 million. More than 1,100 buildings are reported to have been destroyed and more than 800 damaged.
Even though they happened just hours apart, the two quakes are not related. The Times reported:
Are the two somehow related?
No. The two quakes occurred about 9,000 miles apart. That’s far too distant for there to be any connection between them.
Large earthquakes can, and usually do, lead to more quakes — but only in the same region, along or near the same fault. These are called aftershocks. Sometimes a large quake can be linked to a smaller quake that occurred earlier, called a foreshock. In the case of the Japanese quake, seismologists believe that several magnitude-6 quakes in the same region on the previous day were foreshocks to the Saturday event.