With the official opening of 2017 Atlantic hurricane season fast approaching, researchers appear cautiously optimistic the relatively quiet streak will continue.
Today, Colorado State University’s Tropical Meteorology Project released the extended range forecast of 2017 Atlantic seasonal hurricane activity, predicting slightly below-average activity in the Atlantic basin, with a forecast of 11 named storms, four hurricanes, and two major hurricanes.
The probability of at least one major (Category 3+) hurricane making landfall on the entire U.S. coastline is 42%, compared to an average of 52% over the past century. The probability of such a storm hitting the East Coast, including peninsula Florida is 24%, compared to an average of 31%. Thus, CSU noted, the estimated probability of a major hurricane making landfall in the U.S. this season is approximately 80% of the long-period average.
Hurricane activity may not be as critical a determinant for how insurers and property-owners will fare, however. Aon Benfield’s Global Catastrophe Recap reports have consistently noted the rising toll of economic and insured losses due to severe weather events including severe thunderstorms, hailstorms, and flash flooding. In Texas alone, for example, Aon Benfield reports the state incurred record thunderstorm-related losses for the year, with insurers citing costs exceeding $8.0 billion.
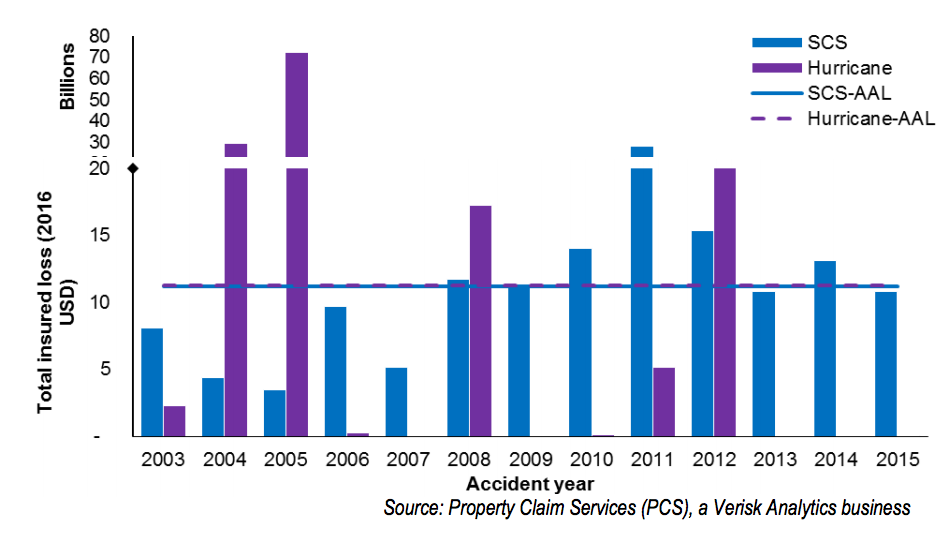
Other recent studies support this trend. In the Willis Re and Columbia University report Managing Severe Thunderstorm Risk, researchers found the risk to U.S. property from thunderstorms is just as high as from hurricanes. Their review of Verisk Analytics loss statistics for 2003 to 2015 found the average annual loss from severe convective storms including tornadoes and hailstorms was $11.23 billion, compared to $11.28 billion from hurricanes. Considering the past decade alone, severe convective storms posed the largest annual aggregated risk peril to the insurance industry.