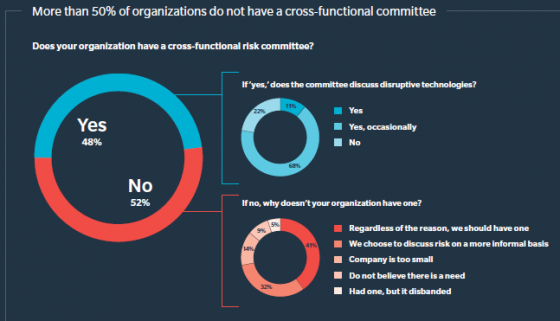
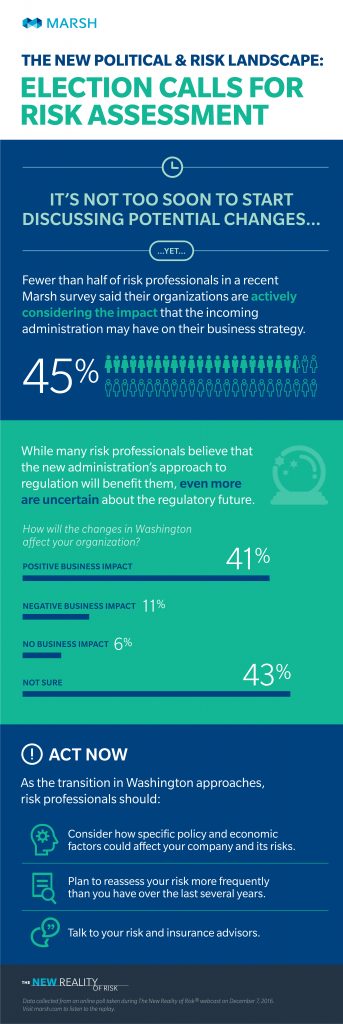
Businesses in India expressed an overwhelming desire to approach risk management more strategically in this year’s Excellence in Risk Management India report, with 68% of respondents deeming “integrating risk management into strategic planning” their top priority. Today, managing risk intelligently is everyone’s responsibility—not just the company’s executives—and the question of how to enable risk management at the front line of defense (FLoD) was a key theme for Marsh’s “Enabling the First Line of Defense” panel discussion at the RIMS Risk Forum India 2019. Consistently taking the initiative is key to risk management, and panelists discussed a number of proactive strategies for enabling front-line employees to address risk.
Enabling the First Line of Defense
As risk responsibilities move to the front line, organizations will need to review how their risk framework can be adapted. To equip everyone to confidently handle risk, risk management needs to be more intuitive. Data and analytics can also play a significant role in making the process more collaborative, measurable and strategic. Backed by technology, many firms are now not only able to prevent downside risks, but have capitalized on new markets, opportunities and changes in demand.
Panelists expressed that risk management was not a priority for frontline staff like sales executives, who are more likely to be encouraged to meet sales KPIs. Reflecting on his time within financial services, panelist Sudip Basu, Hinduja’s group head of risk, said that during peak times, risk was not an important consideration, and rarely outweighed more immediate profit and success motivations. Of course, self-examination happens during down-turns, which the sector has experienced over several tumultuous decades, both in India and globally. Basu said that this was definitely the case after the global financial crisis.
Bake Risk Management into KRAs
One key activity that the panelists flagged was baking risk management into key responsibility areas (KRAs) so that risk management messaging cascades down to the front line and into business activities. However, the panelists also expressed concern about the level of monitoring being implemented alongside these KRAs, stressing the need for follow-through on good intentions and highlighting this as an area of development needed for success.
Celebrate Successes
Celebrating success is far from an unfamiliar concept, though firms may need to address how success is measured and at what level. According to panelist Jyotsna Sharma, Bridgestone India’s chief financial officer and head of IT, firms are very good at celebrating risk management successes at the senior levels, but not as good at recognizing it for front-line teams. Sharma said that it would be beneficial to build in small acknowledgements for front-line teams and employees who have done exceptional work, have been proactive or have demonstrated risk management best practices.
Acknowledge Incremental Gains
The panelists also stressed the importance of incremental gains. A change in the front line’s perception of risk management is not likely to happen overnight. If only key milestones or large events are recognized, it could be harder to gain buy-in and ongoing support from teams on the ground. Much like celebrating wins achieved by the FLoD, acknowledging incremental gains helps the team to view the journey to success as a process, and could help FLoD initiatives to more easily gain momentum.
While the FLoD is traditionally associated with operational management, as risks grow increasingly complex and interrelated, risk management is no longer only the purview of control functions, particularly when major influences from regulatory and broader economic environment exist. Ensuring that there is adequate awareness of risks—while rewarding successes across various levels of the organization—is critical for organizations to cope with risk in the current business environment.

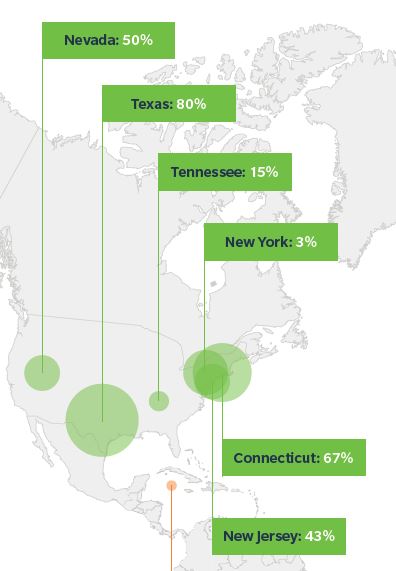 As organizations’ exposures increase in number, complexity and severity, shareholder funds generated by captives are becoming more important. According to Marsh:
As organizations’ exposures increase in number, complexity and severity, shareholder funds generated by captives are becoming more important. According to Marsh: “We expect to see a continued increase, driven in part by companies that are already strong captive users and by those that may have difficulty insuring their professional liability risks,” Marsh said.
“We expect to see a continued increase, driven in part by companies that are already strong captive users and by those that may have difficulty insuring their professional liability risks,” Marsh said.