Reports of fraud have risen in the past year. In fact, incidences of every type of fraud have reached double-digit levels, according to the Kroll Global Fraud & Risk Report 2016/2017. Overall, 82% of executives reported falling victim to at least one instance of fraud in the past year, up from 75% in 2015.
Theft of physical assets remained the most prevalent type of fraud in the last year, reported by 29% of respondents, up 7 percentage points from 22% of respondents in the last survey. Kroll reported that vendor, supplier, or procurement fraud (26%) and information theft, loss, or attack (24%) were the next two most common types of fraud cited, each up 9 percentage points year-over-year.
Kroll found that most threats come from within an organization, with current and ex-employees being the most frequently cited perpetrators of fraud, cyber, and security incidents over the past 12 months. External parties were also identified as active perpetrators.
In the United States:
• On the complexity of fraud risks, the majority (60%) of executives who reported suffering fraud incidents identified some combination of perpetrators, including current employees, ex-employees, and third parties, with almost half (49%) involving all three groups.
• Almost four in 10 respondents (39%) who were victims experienced fraud perpetrated by a junior employee, 30% by senior or middle management, 27% by ex-employees, and 27% by freelance/temporary employees. Agents and/or intermediaries were also cited by 27% of respondents as involved in carrying out fraud.
• Insiders were cited as the main perpetrators of fraud, and also identified as the most likely to discover it. Almost half (44%) of respondents said that recent fraud had been discovered through a whistleblowing system and 39% said it had been detected through an internal audit.
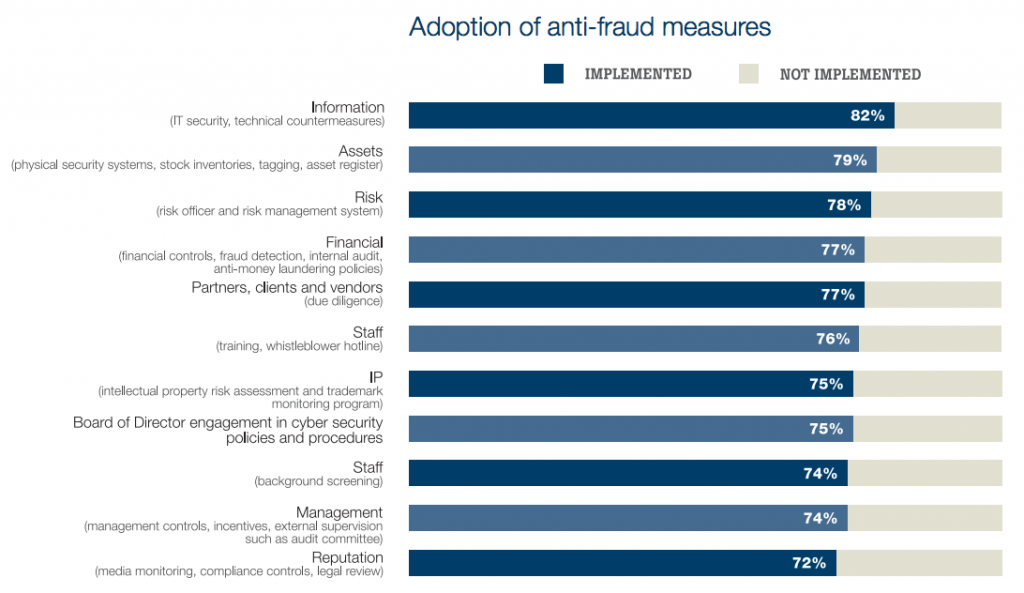
Among anti-fraud measures, the widest adoption—reported by 82% of executives surveyed—focused on information, such as IT security and technical countermeasures. The converse of the finding is concerning: nearly one out of five respondents (18%) have not adopted such protections.
According to the report:
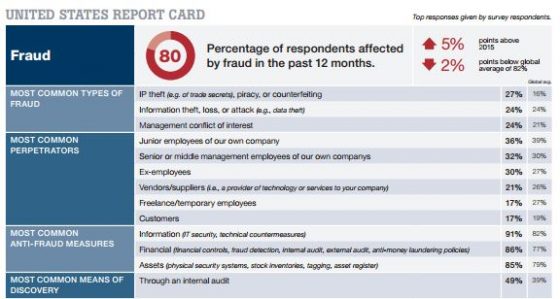
80% of respondents in the U.S. experienced fraud in the past 12 months, an increase of 5 percentage points on the previous year. This figure is 2 percentage points below the reported global average of 82%. Intellectual property (IP) theft, piracy, or counterfeiting is a clear threat to companies in the U.S., which was reported by just over a quarter (27%) of U.S. participants, almost twice the reported global average. The U.S. was the only country where IP theft was the most common type of fraud reported. Information theft, loss, or attack was the second most mentioned type of fraud impacting companies in the U.S., followed by conflicts of interest in the management team. The main perpetrators of fraud were reported to be insiders. Where fraud had been discovered, 36% of executives in the U.S. reported that junior employees were responsible, and 32% named senior or middle management. Respondents in the U.S. were most likely to have adopted IT security measures, followed by financial controls and asset security as their top three ways to mitigate fraud risk. In the U.S., the most common way fraud was detected was not through a whistle-blower, as it was for most of the other countries surveyed, but through an internal audit. Nearly half (49%) of U.S. participants said it was the most common detection mechanism.
