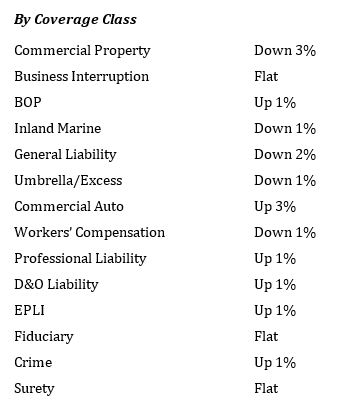
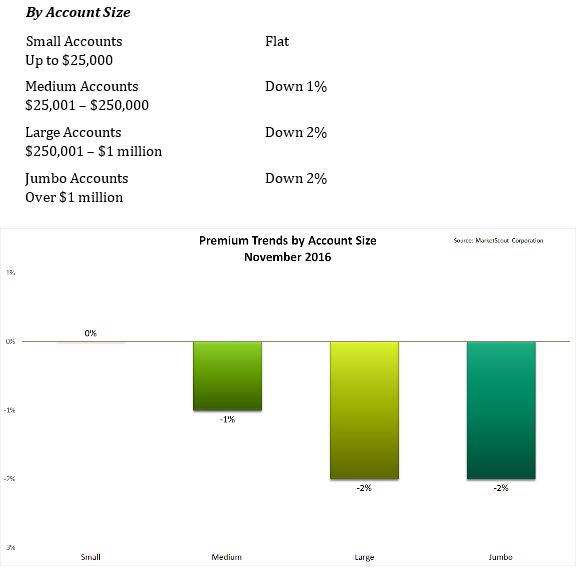
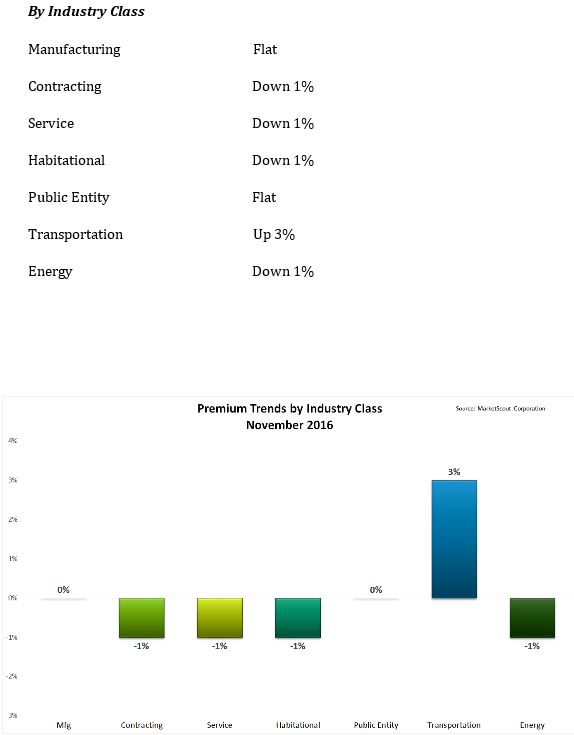
According to Beazley’s recent Risk & Resilience Geopolitical Report, inflation is a key area of concern for business leaders and they expect economic uncertainty to remain high through to the end of this year. High inflation impacts multiple aspects of corporate decision making, from the changing value of stock to rising employee wages and cost of borrowing. It is interesting to note that worries about inflation differ internationally; in the US, 42% of companies rated it their biggest concern, while only 33% of business leaders in the UK had it at the top of their list. Even more striking is the lack of perceived resilience to inflationary pressure, with 65% of business leaders in the U.S. and 55% globally feeling unprepared to meet the challenge.
US business leaders’ concerns about the impending impacts of inflation are justified, as financial market volatility and losses are currently driving the greatest run-up in prices that the U.S. has seen in four decades. The S&P 500 officially entered a bear market and is down more than 20% since the beginning of the year, and the prevailing sentiment in the U.S. is an expectation that inflation is only going to get worse. U.S. retail sales fell in May as supply chain challenges drove a decrease in major purchases like vehicles, and record high gas prices pulled spending away from other goods. The Federal Reserve raised interest rates to try and reduce inflation, but businesses face a long road ahead as rising prices for everything from groceries to housing influence consumers’ buying power and economic confidence for the foreseeable future.
Inflation’s Impact on the Insurance Market
In light of current economic conditions, the directors and officers (D&O) insurance market is now facing several notable inflationary risks. Inflation and supply chain constraints led to higher costs of goods sold, including both raw materials and transportation/freight costs. If a company cannot or is not willing to pass the price on to the consumer, the margins will be impacted, leading to softer financial results. At the same time, as consumer prices increase due to inflation, companies (especially those in the retail and hospitality industries) may face a market with significantly less discretionary spending, leading to lower volume sales or lower sales overall.
Amid these challenges, there are several signs pointing to a potential U.S. and, likely, global recession. While unemployment rates have been improving since the all-time highs during the peak of COVID, analysts warn of future mass layoffs. With high unemployment and higher costs, this also poses a risk to employment practices liability (EPL) insurers. Workers may look to recover lost wages through whatever means available, including bringing suits against their employer. A strong EPL policy and relationship with insurance carrier and broker can help during this time where unemployment may swing back the other way.
Wage and labor inflation also remain a challenge in a tight (though softening) labor market as companies either cannot fully staff their businesses or are spending more to attract and retain talent. Both impact the bottom line. The insurance industry has already seen several supply chain and inflation-driven Security Class Action claims. Various companies have made claims as a result of challenged financials in the wake of strong inflationary and supply chain/labor impact. These were driven by everything from a shortage of staff to deal with consumer demand to slowed production as a result of supply chain constraints, and these cases are just the beginning.
In other lines of business, as inflation continues to rise and products become harder to get, we can expect to see increased crime activity, with higher value attributed to stolen goods due to shortages and inflation encouraging more employee theft. In the cyber market, larger ransom payouts are becoming regular and the costs to buy insurance, negotiate ransomware, and rebuild after a breach are all rising, but the need for more experts is also likely to present challenges as wage inflation rises.
Claims teams are seeing social inflation across most lines of business today, most prominently in bodily injury, wrongful death, EPL, and sexual abuse/molestation liability. This trend is driven largely by the plaintiff’s bar, which has been increasingly emboldened to tap into consumer unrest about everything that is happening in the world today. Jurors’ distrust of larger corporations and their empathy for impacted individuals are increasingly factors that the plaintiff’s bar is leveraging to return higher settlements.
Increasing Complexity of Corporate Insurance Buying
The conflict in Ukraine was already an inflection point for the insurance markets, with hardening rates and capacity changes anticipated in some specific classes as a result. Now, the wider impact of inflationary pressure is likely to push costs (and, in turn, premiums) higher across all classes. This is bad news for insurers, and ultimately even worse news for the business owners who are insurance buyers.
Inflation brings uncertainty and demonstrates the increasing criticality of insurance in certain key areas. For those trading internationally, trade credit insurance becomes essential. With rising business pressure, D&O and EPL insurance-related risks also rise. Business interruption also becomes more likely in a world where energy supply and supply chains are both less certain. As pricing goes up, whether due to supply chain constraints or wage increases, this cannot help but impact companies’ overall performance, leaving them open to potential litigation from shareholders. In a land of rising costs and rising risks, many business owners may consider protecting their business operations as a continued priority, no matter what happens to cost.
Key Action Steps for Risk Managers
One of the most important things that risk managers can be doing in this landscape is proactively seeking to understand what is happening in the world. This includes considering not only the risks that are present, but also what is happening as a result of the inflation and social inflation trends we are seeing—namely higher costs and more pressure from the plaintiff’s bar.
With this understanding in hand, risk managers are then well-advised to call upon trusted experts, including brokers, insurance partners and third-party vendors who are available to test systems and table-top strategies. The priority should always be to find the best vendors and build long-standing relationships with them. This is the time to leverage that trust.
It is essential to be proactive when it comes to risk management. Do not wait for a crisis to come in the door and then behave reactively. Rather, prepare yourself with education and resources and then, after identifying risks unique to your business, proactively seek to mitigate them.
As inflationary risks look to be with us for the immediate future, it is critical for organizations to have a plan. Use your enterprise risk management strategies to develop responses to potential economic and geopolitical events. Communicate regularly and conservatively with shareholders. Consider diversifying your supply chain, as working with different suppliers can add to the confidence level of meeting demand levels. It is also important for businesses to demonstrate empathy for the suffering and hardships that employees and customers may be experiencing.
Many of today’s senior business leadership have not dealt with inflation, unlike the previous generation of leaders who endured double-digit inflation in the 1970s and early 1980s. Use data and rely on the experience of management that survived the Great Recession of 2008 to 2011 to help navigate these new concerns. And of course, work with your carrier partner to ensure that you are properly covered for the road ahead. If COVID-19 has taught us anything, it is that companies must be prepared and plan for the unexpected. This adage will continue to prove true as we weather the coming period of inflation-driven challenges.

 revealed, ending at $9.75 in 2017. The main drivers were declines in liability costs (8%), by decreases in property, liability, workers compensation, management liability, and professional liability costs, as well as overall risk management administration costs. TCOR is defined in the survey as the cost of insurance, plus the costs of the losses retained and the administrative costs of the risk management department.
revealed, ending at $9.75 in 2017. The main drivers were declines in liability costs (8%), by decreases in property, liability, workers compensation, management liability, and professional liability costs, as well as overall risk management administration costs. TCOR is defined in the survey as the cost of insurance, plus the costs of the losses retained and the administrative costs of the risk management department.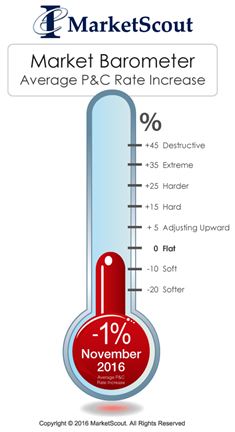 according to MarketScout.
according to MarketScout.