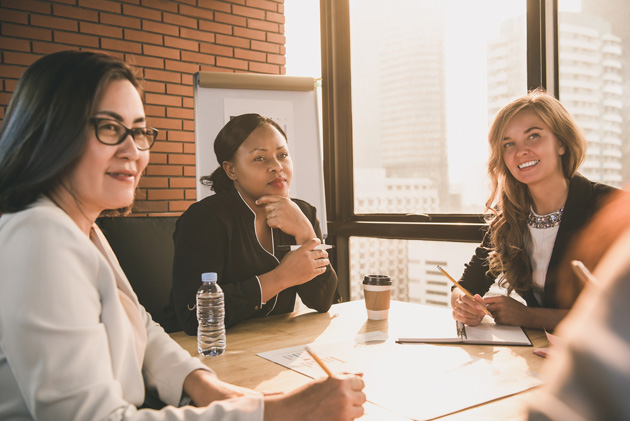
“There are more and more courageous conversations happening in business about gender parity and barriers for women in business,” said Tina Gardiner, manager of risk management services for Regional Municipality of York, Canada, and member of the RIMS board of directors. “While women are still underrepresented at the executive level largely due to gender bias, I am pleased to see changes happening at a rate much faster than ever before.”
Indeed, significant challenges remain in gaining true equity and eliminating the gender gap in risk and insurance, but there are also more resources, momentum and mentors than ever before.
“One of the biggest barriers I faced as a young woman starting a career in risk management was operating in an environment where there wasn’t really the benefit of high-level female role models or mentors,” said Carrie Cannataro, senior vice president of client services at Gallagher Bassett, noting the dramatic evolution since she entered the space in the mid-’80s. As more women have earned senior leadership roles, female risk professionals are increasingly strengthening both the risk profession itself and the prospects of other women fighting for a seat at the table. As Cannataro noted, “We can only be successful if we immerse ourselves within a network of collaborative and positive influences.”
To that end, I recently put out a call on social media asking women in risk to share their best advice for others who are trying to advance in the risk profession and who identify as female. Originally, the goal was to celebrate Women’s History Month by spotlighting women in risk and insurance in March, and it has been wonderful to see initiatives to highlight and advocate for women across the industry for the past 31 days. Equity and excellence from half the population should span far more than a month, however.
In that spirit, here’s some of the valuable insight of women advancing risk management year-round, and their advice to fellow female risk professionals looking to advance their careers in risk:
“There are tremendous opportunities for women in risk management. However, to reach your potential and really excel in this field, women can’t be afraid to speak up. We must ask for the resources we need and seek out opportunities that might take us out of our comfort zones but that also offer a platform for us to share our knowledge and expertise.”
– Kristen D. Peed, CPCU, RPLU, CRM, AIC, ARM-E, corporate director of risk management and insurance at CBIZ, Inc. and member of the RIMS board of directors
“In my experience I have found women in risk management are strong in their support and encouragement of each other through networking, mentoring, celebrating and sharing stories about career journeys. We need to keep investing in each other by pushing boundaries and comfort zones in the positions we apply for, the salary levels we expect, the credentials we earn and the workplace environment we demand. We need to actively engage in the socialization of gender equality, inclusivity, combating imposter syndrome and workplace flexibility for shared family responsibilities. The future we want and deserve is ours to create for each other.”
– Tina Gardiner, B.Sc., CRM, CIP, manager of risk management services for the Regional Municipality of York
“I’m committed to supporting women in the workplace and believe it’s crucial that we pave the way for future generations. I’d offer the following advice: 1) Own your development and invest in yourself. 2) Establish a personal growth/career goals, including strategies and tactics on how to achieve them and timelines. Review regularly to monitor progress and celebrate wins. 3) Create a personal board of directors and mentors, and seek feedback from them. 4) Give back and gain valuable experience via joining a non-profit board. 5) Network, network, network.”
– Soraya Wright, RIMS-CRMP, vice president of strategic initiatives at RIMS, and founder and chief risk officer of SMW Risk Management Consulting LLC
“Women have been the cornerstone of this profession since its inception. I applaud all of those who came before us and laid a foundation for us to grow and succeed, as well as those inspiring women who are determined to leave their own mark on this profession. For women to succeed in risk management, we must support each other. We must create opportunities for others to demonstrate their knowledge and capabilities, achieve their goals and advance professionally.”
– Penni L. Chambers, CPRM, CIC, CRM, ARM, vice president of risk management for Hillwood, a Perot Company, and member of the RIMS board of directors
“One of my biggest pieces of advice for women working in risk is that working hard by yourself is not the answer. We need to seek out relationships that inform and support our advancement. Whether it’s a mentor, coach or other professional network, there are plenty of ways we can seek help in defining rewarding and realistic career opportunities and put those opportunities within our reach.”
– Carrie Cannataro, senior vice president of client services at Gallagher Bassett
“Persistence and communication. Not everyone hears information the same way. Think about your audience as you communicate fact-based information and gut instincts. If you’re not heard the first time, don’t give up! You may need to change your wording, timing, or examples in order to get your point across.”
– Katherine Gledhill, MBA, vice president of finance and accounting at RIMS and CFO of Spencer Educational Foundation
“Growth and comfort do not always happen at the same time. You have to get comfortable doing things that are out of your comfort zone. This is where you’ll really grow, when you challenge yourself beyond what you think is possible. As women, we must build each other up and constantly look for ways to learn from and support one another. I’d also strongly encourage women to consistently assess their values and take the time to prioritize them throughout their careers. This will lead to sustainable happiness and success in both your personal and professional life.”
– Grace Grant, executive director at Gamma Iota Sigma
“Pick an area that interests you and become an expert. Being an expert takes time, but once you have this knowledge, no one can take it away. You must always continue to learn and expand your knowledge base. A solid foundation will support and allow you to take chances that a generalist cannot. You can gain this expertise by moving within one company/industry, one line of business, or geographically—just be clear on what your focus is. Women are often undermined or challenged on technical issues. However, if you have developed the needed expertise, you are more likely to challenge confidently with fact and figures. As you build your career, you will learn that people trust and respect experts, as experts understand their business better and can predict trends and drive the business more effectively.”
– Ciara Brady, global head of liability for Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty