In Deloitte’s 2019 State of Inclusion Survey, 86% of respondents said they felt comfortable being themselves all or most of the time at work, including 85% of women, 87% of Hispanic respondents, 86% of African American respondents, 87% of Asian respondents, 80% of respondents with a disability and 87% of LGBT respondents. But other questions in the company’s survey show a more troubling, less inclusive and productive office environment, and may indicate that simply implementing inclusion initiatives is not enough to prevent workplace bias.
While more than three-fourths of those surveyed also said that they believed their company “fostered an inclusive workplace,” many reported experiencing or witnessing bias (defined as “an unfair prejudice or judgment in favor or against a person or group based on preconceived notions”) in the workplace. In fact, 64% said that they “had experienced bias in their workplaces during the last year” and “also felt they had witnessed bias at work” in the same time frame. A sizable number of respondents—including 56% of LGBT respondents, 54% of respondents with disabilities and 53% of those with military status—also said they had experienced bias at least once a month.
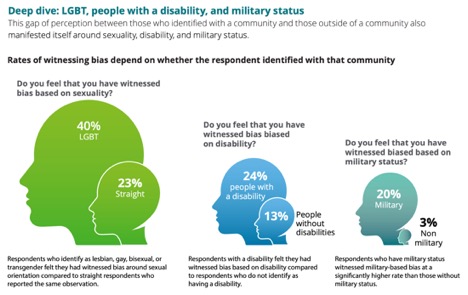
Listening to those who say they have witnessed or experienced bias is especially important. When asked to more specifically categorize the bias they experienced and/or witnessed in the past year, 83% said that the bias in those incidents was indirect and subtle (also called “microaggression”), and therefore less easily identified and addressed. Also, the study found that those employees who belonged to certain communities were more likely to report witnessing bias against those communities than those outside them. For example, 48% of Hispanic respondents, 60% of Asian respondents, and 63% of African American respondents reported witnessing bias based on race or ethnicity, as opposed to only 34% of White, non-Hispanic respondents. Additionally, 40% of LGBT respondents reported witnessing bias based on sexuality, compared to only 23% of straight respondents.
While inclusion initiatives have not eliminated bias, Deloitte stresses that these programs are important and should remain. As Risk Management previously reported in the article “The Benefits of Diversity & Inclusion Initiatives,” not only can fostering diversity and inclusion be beneficial for workers of all backgrounds, it can also encourage employees to share ideas for innovations that can help the company, keep employees from leaving, and insulate the company from accusations of discrimination and reputational damage.
But building a more diverse workforce is only the first step, and does not guarantee that diverse voices are heard or that bias will not occur. Clearly, encouraging inclusion is not enough and more can be done to curtail workplace bias. And employees seeing or experiencing bias at work has serious ramifications for businesses. According to the survey, bias may impact productivity—68% of respondents experiencing or witnessing bias stated that bias negatively affected their productivity, and 70% say bias “has negatively impacted how engaged they feel at work.”
Deloitte says that modeling inclusion and anti-bias behavior in the workplace is essential, stressing the concept of “allyship,” which includes, “supporting others even if your personal identity is not impacted by a specific challenge or is not called upon in a specific situation.” This would include employees or managers listening to their colleagues when they express concerns about bias and addressing incidents of bias when they occur, even if that bias is not apparent to them or directly affecting them or their identity specifically.
According to the survey, 73% of respondents reported feeling comfortable talking about workplace bias, but “when faced with bias, nearly one in three said they ignored bias that they witnessed or experienced.” If businesses foster workplaces where people feel comfortable listening to and engaging honestly with colleagues of different backgrounds, create opportunities for diversity on teams and projects, and most importantly, address bias whenever it occurs, they can move towards a healthier, more productive work environment.

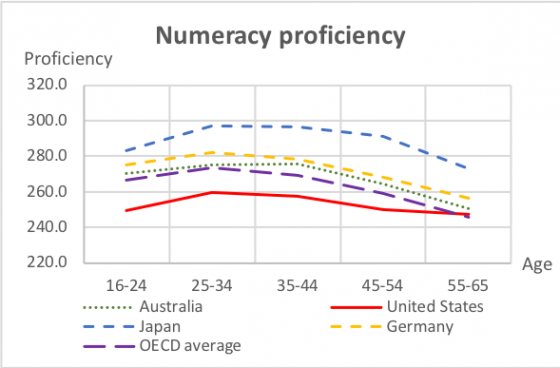
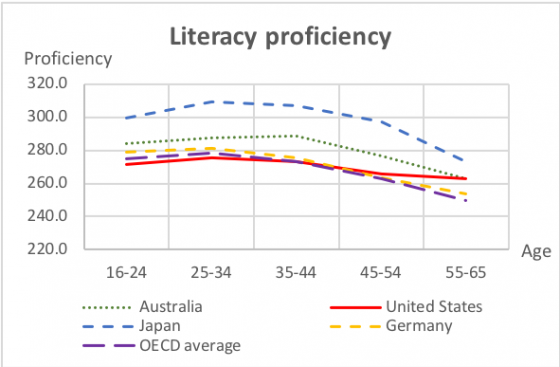
 People are living and working longer today than in the agricultural and industrial ages. The growth in the number and percentage of individuals over 60 and 80 years of age is already having a global impact.
People are living and working longer today than in the agricultural and industrial ages. The growth in the number and percentage of individuals over 60 and 80 years of age is already having a global impact.