Workforce use of illicit drugs across the board—including cocaine, marijuana and methamphetamine—remains at its highest rate in a decade, a new study by Quest Diagnostics found.
Overall positivity in urine drug testing among the combined U.S. workforce in 2017 continued to hold at 4.2%, which is still 0.7% higher than the positivity rate from 2012, which represented a 30-year low. The findings were made from analysis of more than 10 million workforce drug test results.
“It’s unfortunate that we mark 30 years of the Drug-Free Workplace Act with clear evidence that drugs continue to invade the country’s workplaces. Not only have declines appeared to have bottomed out, but also in some drug classes and areas of the country drug positivity rates are increasing,” Barry Sample, senior director of science and technology at Quest Diagnostics, said in a statement.
“These changing patterns and geographical variations may challenge the ability of employers to anticipate the ‘drug of choice’ for their workforce or where to best focus their drug prevention efforts to ensure a safe and healthy work environment.”
The new data indicates shifting patterns of drug use, with cocaine and amphetamines positivity surging in some areas of the country and marijuana positivity rising sharply in states with newer recreational use statutes.
Opioids
The one bit of good news is that prescription opiate positivity rates declined dramatically on a national basis. Quest reported that the positivity rate for opiates in the general U.S. workforce in urine drug testing declined 17% between 2016 and 2017 (0.47% versus 0.39%). More notably, oxycodones (oxycodone and/or oxymorphone) positivity declined 12% between 2016 and 2017 (0.69% vs. 0.61%), hydrocodone positivity declined 17% (0.81% vs. 0.67%); and hydromorphone positivity declined 22% (0.59% vs. 0.46%). Opiates other than codeine were at their lowest positivity rate in more than a decade.
This data is supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which shows that the overall national opioid prescribing rate in 2017 fell to the lowest it had been in more than 10 years, although rates vary by state and are high in some areas of the country.
The topic was explored during an educational session at RIMS 2018, where it was noted that the decrease in opioid use may be attributed to corporate initiatives like prescription drug monitoring policies (PDMP), which can limit employees’ ability to refill scripts, in addition to states that had comprehensive reforms.
“This shows that the more queries there are, the bigger the drop in opioid prescribing,” said John Ruser, president and CEO of the Workers Compensation Research Institute (WCRI), last month in San Antonio. He said WCRI used Kentucky as an example of a successful PDMP. Kentucky’s HB1 law mandated the use of the PDMP and between 2011 and 2013, WCRI information indicated a 10% decline in prescriptions in the state, whereas prescription levels were flat in others that did not have similar reforms.
Methamphetamine
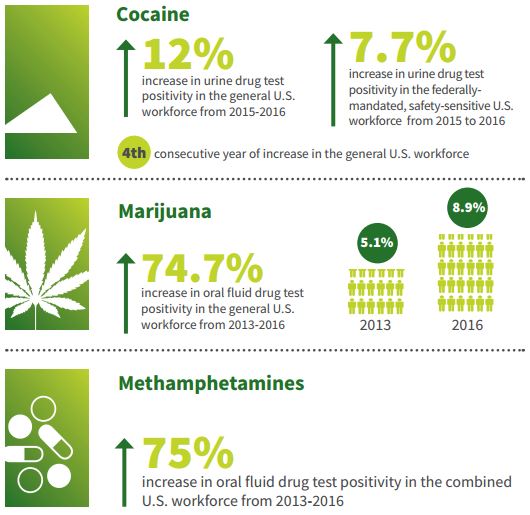
Methamphetamine positivity, however, is increasing. An analysis of trends in the general U.S. workforce based on the four U.S. Census regions identified large increases of methamphetamine positivity rates. Between 2013 and 2017, methamphetamine positivity increased: 167% in the East North Central division of the Midwest (Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, Wisconsin); 160% in the East South Central division of the South (Alabama, Kentucky, Mississippi, Tennessee); 150% in the Middle Atlantic division of the Northeast (New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania); and 140% in the South Atlantic division of the South (Delaware, District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, West Virginia). The percentage increase in these four divisions ranged between 9% and 25% between 2016 and 2017.
Marijuana
Overall, marijuana positivity continued its five-year upward climb for both the general U.S. workforce and the federally-mandated, safety-sensitive workforce. Marijuana positivity increased 4% in the general U.S. workforce (2.5% in 2016 versus 2.6% in 2017) and nearly 8% in the safety-sensitive workforce (0.78% versus 0.84%).
Increases in positivity rates for marijuana were most striking in states that have enacted recreational use statues since 2016. Those states include: Nevada (43%), Massachusetts (14%) and California (11%). These three states also saw significant increases in marijuana positivity in federally-mandated, safety-sensitive workers: Nevada (39%), California (20%), and Massachusetts (11%). Federally-mandated, safety-sensitive workers include pilots, rail, bus and truck drivers, and workers in nuclear power plants, for whom routine drug testing is required by the Department of Transportation.
“These increases are similar to the increases we observed after recreational marijuana use statues were passed in Washington and Colorado,” Sample said. “While it is too early to tell if this is a trend, our data suggest that the recreational use of marijuana is spilling into the workforce, including among individuals most responsible for keeping our communities safe.”