LAS VEGAS—At Black Hat 2015, Charlie Miller and Chris Valasek gave one of the most highly anticipated and best-attended presentations, even far beyond the elite infosecurity experts gathered here this week. The already notable duo of hackers made international headlines two weeks ago when they demonstrated more than a year’s worth of work figuring out how to hack into and remotely control unaltered cars—and used Wired reporter Andy Greenberg as their test driver.
Greenberg’s article and video of the test paint a compelling portrait of just what Miller and Valasek’s hack means in practice. “As the two hackers remotely toyed with the air-conditioning, radio, and windshield wipers, I mentally congratulated myself on my courage under pressure. That’s when they cut the transmission,” Greenberg wrote. “Immediately my accelerator stopped working. As I frantically pressed the pedal and watched the RPMs climb, the Jeep lost half its speed, then slowed down to a crawl.
This occurred just as I reached a long overpass, with no shoulder to offer an escape. The experiment had ceased to be fun.”
From a couch in Miller’s basement 10 miles away, they were able to seize control of the Jeep, and their methods could be applied to any car operating the same technology: Uconnect, an internet-connected computer feature in hundreds of thousands of cars that controls the entertainment and navigation systems, enables phone calls and, with a subscription purchase, offers a Wi-Fi hotspot. The hackers’ exploit can also be used for surveillance, using the Jeep’s GPS to track location to measure speed, and even drops pins on a map at regular intervals to trace its route. And, because of the system’s cellular connection, this can be done on any car from anywhere with access to the same cellular network (Sprint) as long as hackers know the car’s IP address.
In the wake of the Wired article, Sprint has blocked the kind of phone to car traffic and car to car traffic that facilitates remote hacking. What’s more, Fiat Chrysler announced the recall of 1.
4 million cars and trucks that could be vulnerable to hacking—more than three times as many as the pair originally estimated may be at risk.
Miller and Valasek approached the company with their findings as early as 2014, and said the automaker was responsive to their report. Unauthorized remote access was blocked with a network-level improvement, the company announced shortly after Greenberg’s article went to print. In addition to the recall to update software in the infotainment system, affected customers will receive a USB device to upgrade vehicles’ software with internal safety features.
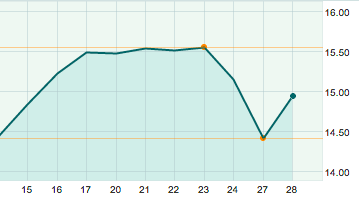
And lest anyone still question the impact hackers can have on a business’s bottom line, as they were only too happy to point out, here’s a look at Chrysler’s stock from a week before to a week after the Wired story:
Part of their aim was to increase consumer awareness and provoke greater scrutiny of technology they are being told is safe. “If consumers don’t realize this is an issue, they should, and they should start complaining to carmakers,” Miller told Wired. “This might be the kind of software bug most likely to kill someone.” Their research has already effected concrete change beyond the cars recalled. Partially spurred by the team’s earlier demonstrations in the arena, Senators Edward Markey of Massachusetts and Richard Blumenthal of Connecticut introduced legislation on July 21 that would direct the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration and the Federal Trade Commission to establish rules to secure cars and protect consumer privacy. The bill would also establish a rating system to inform owners about how secure their vehicles are beyond any minimum federal requirements, Bloomberg reported. “Controlled demonstrations show how frightening it would be to have a hacker take over controls of a car,” Markey said in a statement to Wired. “Drivers shouldn’t have to choose between being connected and being protected…We need clear rules of the road that protect cars from hackers and American families from data trackers.”
Miller and Valasek have done a lot more than present a frightening demonstration of just how vulnerable so many cars are, and it involves everyone here at Black Hat. In their presentation, Valasek opened with a blunt public service announcement: Please stop saying anything is “unhackable,” because you are wrong and you are just going to look silly. Proving that took more than a year of meticulous work, much of which could not be easily reproduced and applied any time soon, but they did prove it, and in doing so, they prompted the first formal safety campaign in response to a cybersecurity threat. That may be the biggest impact, he told the audience: “Hackers did something, fiscal change happened and it wasn’t in infosec—it was in the real world.”