With more visibility and vulnerability in today’s business landscape due to social media, online commerce and doing business through mobile devices, it only makes sense that there would be more potential risks to a company’s reputation and brand. In fact, now more than ever, executives are attempting to protect their brands from these security threats by being more proactive and looking for blindspots in their risk management program. That’s according to findings from the “2012 IBM Global Reputational Risk and IT Study,” conducted by the Economist Intelligence Unit, which analyzed responses from 427 senior executives from around the world, representing nearly all industries.
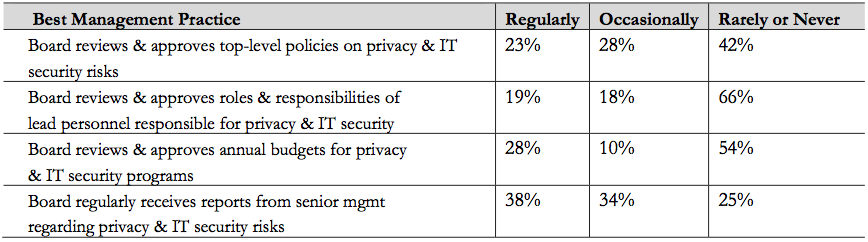
Respondents indicated that cybercrime is more of a reputational threat than systems failure — a finding that clearly illustrates how cybersecurity is a growing concern among executives, as shown in the following graph from the report.
What’s more, 64% say their company will put additional effort into managing its reputation in the future while 75% of respondents say their IT budget will grow over the next 12 months due to reputational concerns. “Underestimating the cost of reputational risk greatly exceeds the cost of protection,” said one U.S.-based study participant. “Being proactive is preferable to being reactive.”
As the report states:
Going forward, assessing potential blind spots and new technologies will likely be accelerated through the use of case studies and scenario analysis rather than waiting for direct experience. “To use new technologies like cloud you need trust,” says Andrea MacIntosh, director of quality with Alpha Technologies in British Columbia, Canada. “How do you build trust? Either by demonstrating performance or through looking at comparable organizations that are using it with good success. I think there’s a lot of referential data for companies like ours, but as with any new technology, you’ve got to be cautious.”
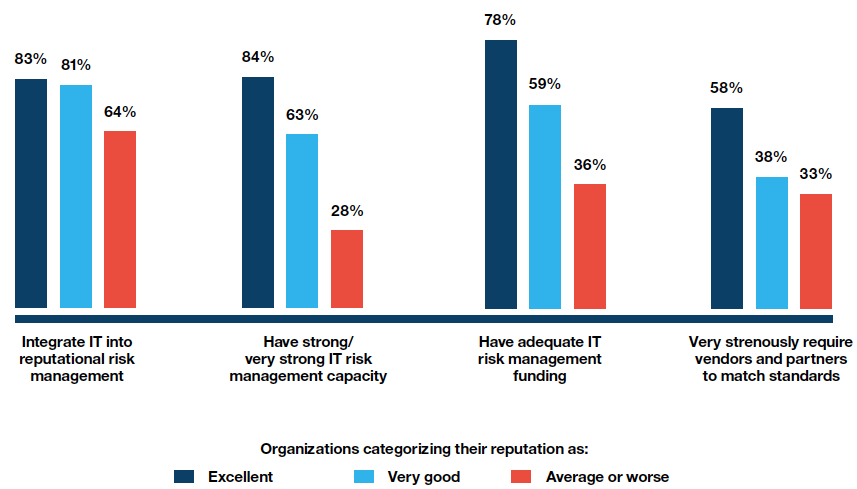
So how does a company avoid data breaches and strengthen the public’s trust in its brand? The respondents feel that integrating IT into reputational risk management, along with having a strong IT risk management capacity, is the best bet.
Gone are the days when a customer inherently trusts that a company’s IT capabilities are sufficient. In fact, customers are taking a more proactive approach when it comes to understanding a current or potential business partner’s IT infrastructure. “We’re seeing more requests from our customers for details of our IT infrastructure and security, along with on-site audits, as part of the supplier qualification process,” said MacIntosh.
Organizations of all sizes across all industries are devoting more time and attention to potential cyber threats that could harm their reputation. “This concern is reflected in more integrated, enterprise-wide approaches to risk management led from the C-suite and increased attention being paid to the direct reputational impacts of IT risks,” the report states. This study, along with many others, point to the conclusion that cyber and data security has earned top billing in the list of biggest risks posed to businesses. How is your company responding?