SAN FRANCISCO—Information security executives are telling boards what they want to hear, not what they need to hear, and boards are frequently not asking the right questions or understanding the responses, according to a report released today by Bay Dynamics at the RSA Conference.
“The report reveals that both the board and security professionals are not doing their jobs when it comes to security reporting,” said Feris Rifai, co-founder and CEO at Bay Dynamics. “The board isn’t holding IT and security executives accountable for providing accurate, traceable and actionable information and security executives are failing to report information that is accurate, traceable and actionable. Both parties must do better if they want to make the right decisions that minimize their cyberrisk”.
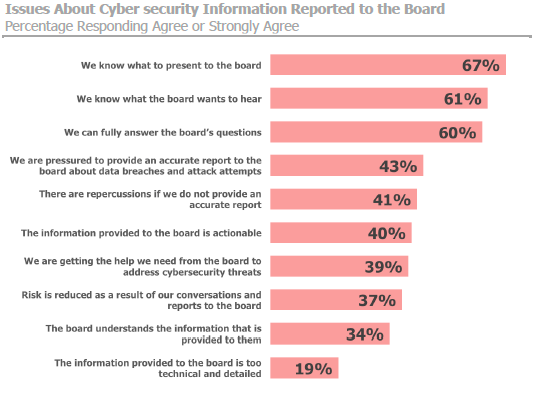
While the majority surveyed say they know what to present to the board, only two in five IT and security executives feel that the information they provide to the board is actionable, and even fewer believe they are getting the help they need from the board to address cyber security threats. This may be in part because of the ongoing struggle to fully understand and measure cyberrisk exposure and the costs of failure.
Just over half of boards expressed a strong preference for qualitative information, while 38% have a preference for quantitative data. To truly make appropriate decisions, however, the board must focus more on quantitative information in context, meaning qualitative information must be wrapped around quantitative information, the report explained.
Regardless of what information they provide, only a third of IT and security executives believe the board understands the information they are given about cyber threats. In turn, only 39% think they are getting the support they need from the board to address threats. Some other major issues these executives identified in their reporting included:
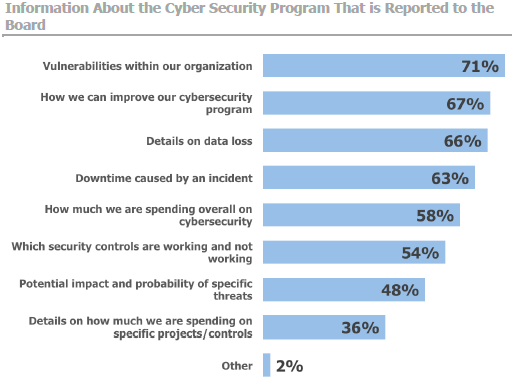
While 36% of boards want recommendations for additional spending and 34% want recommendations to reduce cybersecurity spending, boards are getting little data about the specifics of information security investments. The most common type of information reported about cybersecurity issues is known vulnerabilities within the organizational systems, followed by recommendations about cybersecurity program improvements and specific details on data loss incidents, Bay reported, while information about the cost of cybersecurity programs and details about expenditures on specific projects or controls are not as commonly reported.
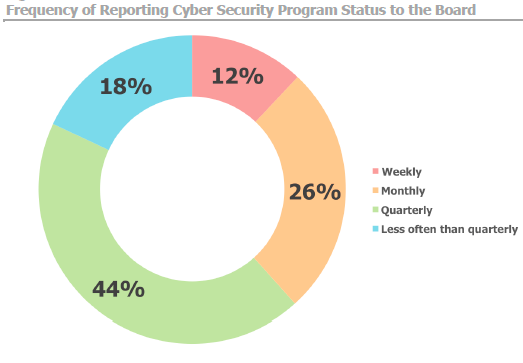
Reporting is also relatively infrequent for such a rapidly evolving high-risk exposure, with most executives only presenting to the board quarterly, and 18% even less frequently.
Looking forward, Bay Dynamics had the following suggestions for how both boards and IT and security executives can improve:
Issues the board must address:
- The board is not doing its job when it comes to effectively managing cyberrisk.
- Boards of directors must hold IT and security executives accountable for providing accurate, actionable information about their cyberrisk to help the board make effective decisions about their cybersecurity programs.
buy mobic online familyvoicesal.org/resources/images/jpg/mobic.html no prescription pharmacyBoards cannot make decisions about what they consider acceptable risk if they don’t have actionable information.
buy tenormin online familyvoicesal.org/resources/images/jpg/tenormin.html no prescription pharmacy- Boards must demand actionable information from IT and security executives about their cyberrisk since the board is responsible for the company’s risk appetite. Strengthening their cyberrisk program begins with the board.
Issues IT and security executives must address:
- IT and security executives must communicate to their boards more effectively and more completely using quantitative and qualitative information. They should communicate the value of data at risk using numbers that explain what it is and how to take action to protect it.
- Given that board members in many organizations are typically less technical than the IT and security executives reporting to them, the latter must contextualize the information in order to make it both understandable and actionable.