According to an April New York Times article, “Uber’s core company values included making bold bets, being “obsessed” with the customer, and to “always be hustling.” The company emphasized meritocracy, setting employees up as rivals and overlooking transgressions of its high performers.
At its worst, Uber maintained an “unrestrained culture” that has since resulted in several allegations of harassment. A published blog post by engineer Susan Fowler, indicated that “the culture was stoked—and even fostered—by those at the top of the company.”
Adoption of a strong risk culture
An effective risk culture is not a matter of risk assessment or level of compliance; it is a matter of “conviction” – a corporate state of mind where human beings can take well-informed risk decisions because they want to, not because they have to.—@RiskCultureBuilder on Twitter
The “tone at the top” describes the climate and overall philosophy set by the board of directors and executive team to drive the culture and behaviors of all employees. In companies ranging from Uber to small businesses, this tone permeates the enterprise in a number of ways, including executive communications and onboarding and learning programs, as well as the policies and procedures designed to empower and/or control employee decision-making. The right tone stresses a high standard of ethics and a culture of compliance, but should be balanced with a message that empowers managers to take risks—appropriately—in the pursuit of short- and long-term rewards for the business.
Translating the tone into a strong risk culture requires reinforcement to employees defining how their decisions and actions affect the broader mission of the company.
buy azithromycin online https://galenapharm.com/pharmacy/azithromycin.html no prescription
Then, through change management and strong accountability, culture and risk management can be aligned to keep everyone “rowing in the same direction.”
Drivers of risk culture
Many companies today have defined a “culture statement,” put it down on paper, and socialized it to employees. This is only the first step in driving employees to make the right risk management decisions, however. Consider a few of the levers that companies can pull to drive behaviors towards a stronger risk culture:
- Performance management and compensation – Are corporate and employee goals tied to desired risk management outcomes?
- Corporate governance – From the board of directors down, are enough questions being asked? Is there too much reliance on historical data?
buy oseltamivir online pelmeds.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/jpg/oseltamivir.html no prescription pharmacy
- Management reporting – Is attention to certain metrics—often short-term in nature—driving decisions that could cannibalize long-term outcomes?
- Investor Relations – Are reasonable expectations being set with a company’s shareholders when it comes to risk versus reward?
While company leaders can help drive the desired corporate culture, this alone will not guarantee good risk management decisions every day. All employees must be taught risk management techniques, and relevant risk management skills should be built into the company’s overarching competency model. A risk culture that positions employees as an integral part of risk management will drive more successful and predictable business outcomes.
During his keynote presentation at the 2016 TMG Executive Summit, cybersecurity expert Brian Krebs reinforced this point when referring to the risk culture needed to deal with cyber risk: “…layers of technology are not enough to stop a data breach…security is only as effective as the people managing it.” Although achieving a strong risk culture is no small undertaking, the benefits will be significant as more and more risks are mitigated before impact.

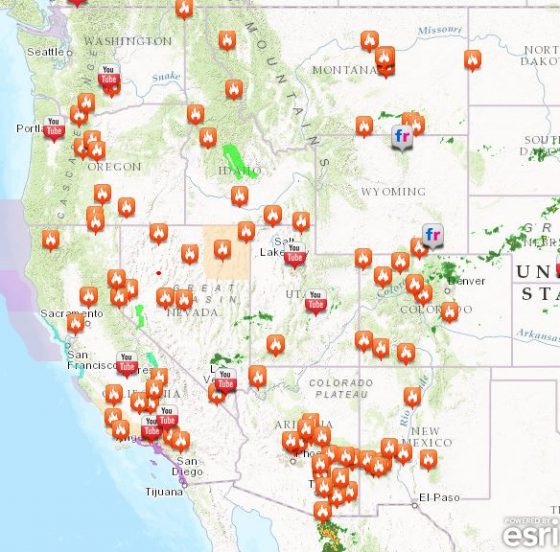 Western Canada is also seeing its share of wildfires. Evacuations are in effect for up to 10,000 residents in British Columbia, as 17 fires burn.
Western Canada is also seeing its share of wildfires. Evacuations are in effect for up to 10,000 residents in British Columbia, as 17 fires burn.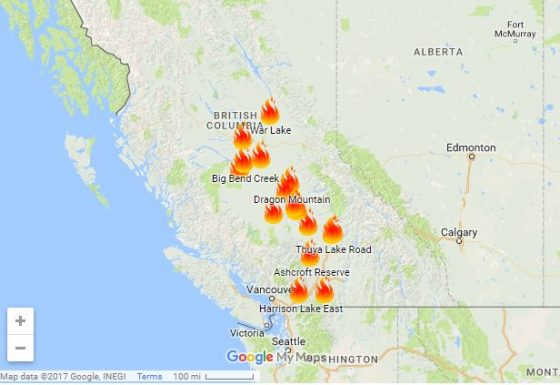 Residents of Fort McMurray, Canada, who saw
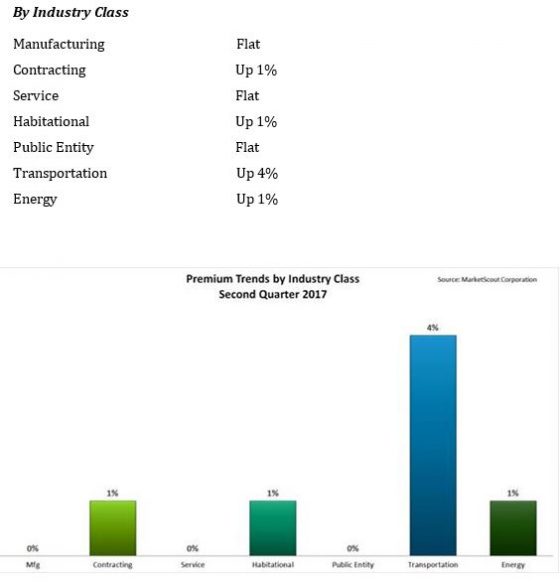
Residents of Fort McMurray, Canada, who saw 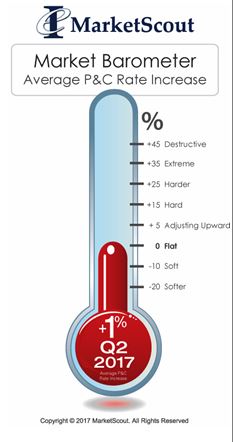 transportation sector, most notably auto-related exposures, is seeing the highest increases, up to 4%, according to a report released today by MarketScout.
transportation sector, most notably auto-related exposures, is seeing the highest increases, up to 4%, according to a report released today by MarketScout.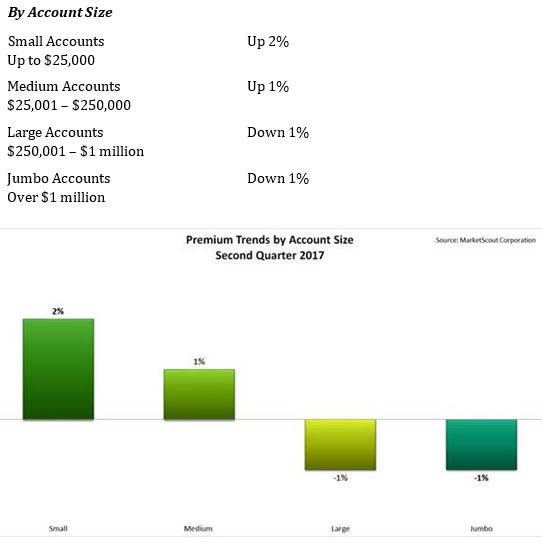 By coverage class, commercial property and inland marine adjusted from down 1% in the first quarter, to up 1% in the second quarter. Commercial auto rates rose from up 3% to up 4%. EPLI also went from up 1% to up 2%. Fiduciary adjusted downward to flat or no increase compared to up 1% in the prior quarter. All other coverage classifications were unchanged from the previous quarter, according to the report.
By coverage class, commercial property and inland marine adjusted from down 1% in the first quarter, to up 1% in the second quarter. Commercial auto rates rose from up 3% to up 4%. EPLI also went from up 1% to up 2%. Fiduciary adjusted downward to flat or no increase compared to up 1% in the prior quarter. All other coverage classifications were unchanged from the previous quarter, according to the report.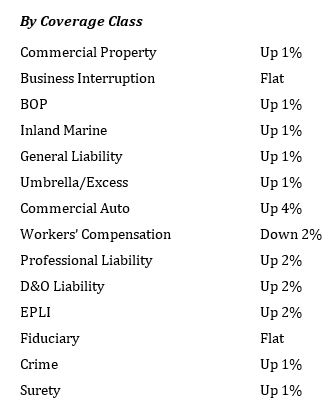 By industry class, public entity rates moderated from up 1% to flat.
By industry class, public entity rates moderated from up 1% to flat.