 Activity from the Kilauea volcano on the island of Hawaii, in Lava Zones 1 and 2—deemed the most dangerous of the island’s nine zones—continues into its third week. As previously reported, aftershocks, lava flow and lingering hazardous fumes in Lanipuna spilled into nearby areas. About 1,800 people living in surrounding neighborhoods were ordered to be evacuated earlier this month by Hawaii County. The one serious injury reported was of a man sitting on this front porch, who sustained a leg injury caused by lava splatter.
Activity from the Kilauea volcano on the island of Hawaii, in Lava Zones 1 and 2—deemed the most dangerous of the island’s nine zones—continues into its third week. As previously reported, aftershocks, lava flow and lingering hazardous fumes in Lanipuna spilled into nearby areas. About 1,800 people living in surrounding neighborhoods were ordered to be evacuated earlier this month by Hawaii County. The one serious injury reported was of a man sitting on this front porch, who sustained a leg injury caused by lava splatter.
Experts warn that more powerful explosions may follow the 30,000-foot ash cloud that engulfed the sky on May 17. Since then, breathing masks have been distributed to local residents and workers.
On May 18, the Hawaii Tourism Authority (HTA) issued a press release aiming to quell fears about safety on other parts of the island. The statement explained that the only affected region is “a remote area along the Lower East Rift Zone on the island, Kilauea Summit and surrounding areas.” The steam and ash outbursts from Halema’uma’u crater are occurring in Hawaii Volcanoes National Park, which is about 40 miles from the Lower East Rift Zone. This is a natural occurrence as rocks fall into the crater and magma interacts with groundwater.
An “aviation red alert” was issued last week due to the potential that aircraft routes could be impacted by the ash, but flights and normal operations have apparently not been impacted and the HTA maintained that there is “no reason for visitors planning a trip to the Hawaiian Islands to change or alter their leisure or business travel plans.”
Reports indicate, however, that as of last week, cancellations from May through July added up to at least $5 million and bookings for hotels and other outdoors activities have declined by 50%.
And while the tourism and transportation industries are integral to the state’s economy, the risk to its ecology is becoming more evident and immediate. In addition to the falling ashes, air near the site contains sulfur dioxide, which some breathing masks cannot protect against.
Several fissures combined created two lava flows that have entered the ocean off Highway 137 near MacKenzie State Park, according to the Island of Hawaii’s Civil Defense. Highway 137 is a critical stretch along the coast that is the site of several problems for residents. A two-story lava wall emerged on parts of the highway, essentially cutting off a portion of the escape and evacuation route. Authorities have since opened an alternate escape route via Highway 11, which was blocked by almost a mile of lava in 2014.
The lava oozing into the Pacific Ocean has short- and long-term effects on the local ecology. While it is certain to harm or repel marine life, the chemical reaction when mixed with water also affects the air.
A Hawaii county spokesman said recently:
“The lava has entered the ocean. Be aware of the laze (lava haze) hazard and stay away from any ocean plume. Laze is formed when hot lava hits the ocean sending hydrochloric acid and steam with fine glass particles into the air.
As one can imagine, since the laze is in the air, lungs, eyes and skin are particularly susceptible to irritation and it can change direction quickly since it travels with the wind.”
Information on ash hazards and how to prepare for ashfall can be found here.
Although the K volcano has been active for decades, this most recent surge in activity could be attributed to the 6.9-magnitude earthquake on May 4, the strongest quake to hit Hawaii in more than 40 years. The earthquake was one of hundreds to be felt recently on the Big Island, although none of them caused any notable threat to life or property.


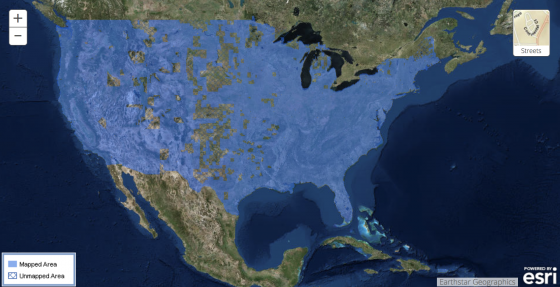 Across the vast geography of the United States, flood is no stranger to any of the states. From the March 2018 Nor’Easters that slammed the East Coast to the numerous storms and hurricanes that have swept across the country, both coastal and non-coastal regions are all at risk of flood.
Across the vast geography of the United States, flood is no stranger to any of the states. From the March 2018 Nor’Easters that slammed the East Coast to the numerous storms and hurricanes that have swept across the country, both coastal and non-coastal regions are all at risk of flood.