Millions of workers in a number of industries are exposed to chemicals every day. While many of these chemicals may be harmful, only a small number are regulated in the workplace.
Because of this, employees suffer more than 190,000 illnesses and 50,000 deaths annually—all related to chemical exposures. Workplace chemical exposures have been linked to cancers as well as lung, kidney, skin, heart, stomach, brain, nerve and reproductive diseases, according to the United States Department of Labor.
An effective system for managing chemicals in the workplace is important. Ideally, a program would go beyond basic Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA) standards for compliance and would attempt to reduce or eliminate chemical hazards at the source through informed substitution.
An online toolkit, provided by OSHA, can help businesses improve the safety of their workers by eliminating or reducing hazardous chemicals. Other benefits are also created, including:
- Cost Savings—reduced expenses and future risks.
- Efficiency—improved performance.
- Industry Leadership—innovation helps a company stay competitive.
- Corporate Stewardship—Advancing socially responsible practices.
Considering safer alternatives to hazardous chemicals is not new, but a good program allows employers, workers and decision-makers to identify solutions rather than continuing to focus on the problem. This approach can also reduce costs and keep businesses competitive. On the other hand, continuing to assess the problem has no economic benefit, according to OSHA.
“Informed substitution,” or replacing hazardous substances with safer alternatives, is the goal of a solutions-oriented approach to chemical management, OSHA said. It involves identifying alternatives and evaluating safety hazards, any potential trade-offs, and their technical and economic feasibility. A “safer alternative” is an option that is less hazardous for workers than the existing method or solution used. This could mean choosing not to continue an activity altogether. It also might include using chemical substitutes, products or process redesigns that eliminate the need for specific hazardous chemicals.
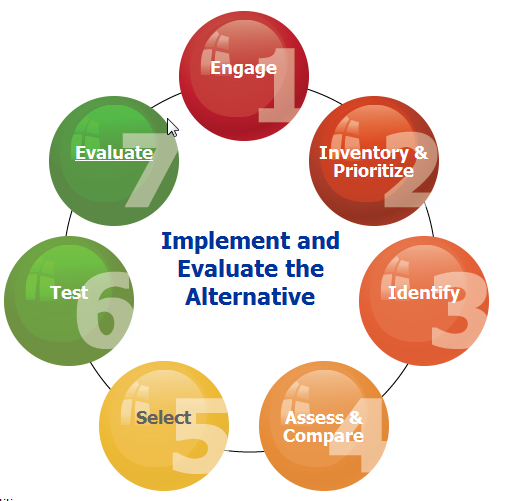
Seven Step Process
To help with the process, OSHA has developed a seven-step procedure to give employers and workers the information and guidance needed for informed substitution in the workplace.
In step 1, “engage,” for example, OSHA offers these considerations for developing a plan:
Key Questions
- How will workers be involved in the team and throughout the planning process?
- Who should be involved in developing the work plan and setting goals for transitioning to safer chemicals—managers, supply chain partners, customers, marketers, health and safety committee members, occupational health nurse or physician, occupational health consultant?
- What goals should be included in the plan? Consider specific goals such as eliminate carcinogens, reduce the use of hazardous chemicals by a certain percentage in a set number of years, substitute chemicals of concern from government or sector lists, etc.
- What policies, tasks, responsibilities, deadlines should be included in the plan?
- What particular drivers should you be aware of in developing the plan (existing or new laws, consumer pressures, new science)?
- How will external stakeholders be involved?
To read more and access OSHA’s seven-step plan and toolkit go to: