Iman H. Al-Gharabally is responsible for the enterprise risk management program at Kuwait Petroleum Corporation (KPC) and its subsidiaries since 2004. She is the team  leader, coordinator and project manager for the ERM program and its strategic implementation across the Kuwait oil sector. Al-Gharabally, a speaker at RIMS’ Middle East Risk Forum 2016, taking place Dec. 13 and 14 in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, discusses the implementation strategies and successes of KPC’s ERM program.
leader, coordinator and project manager for the ERM program and its strategic implementation across the Kuwait oil sector. Al-Gharabally, a speaker at RIMS’ Middle East Risk Forum 2016, taking place Dec. 13 and 14 in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, discusses the implementation strategies and successes of KPC’s ERM program.
RIMS: How did you begin the process of building KPC’s ERM program?
Al-Gharabally: In 2002 the KPC managing directors at the time recognized there was a serious need to look into and have in place a consolidated view of potential risks and a consolidated risk management format of those risks facing the organization. Hence the ERM initiative was introduced as a way to instill this unified format of consolidated risk management mainly through the insurance section. In 2004 the ERM initiative was introduced and in 2006 the ISO 31000 was launched.
RIMS: How did you develop your ERM structure?
Al-Gharabally: Initially I had no prior knowledge of what ERM stood for. I was recruited in April 2004 from Kuwait Oil Company (a subsidiary to KPC) to project manage and lead this new ERM initiative. I studied the topic extensively and slowly had to lay down the foundation for a dynamic ERM program for KPC and its subsidiaries. We started at the very top, first in the corporate office looking at the strategy of the corporation and what the corporate objectives aimed to achieve in the coming five years from 2004 to 2009. We then looked at the potential risks that would prevent the corporation from achieving those objectives and started the communication lines across the subsidiaries to initiate awareness on these potential risks and put forth mitigation options to ensure the corporation was well prepared and to increase our abilities to deliver on our strategic objectives.
It was imperative at the very beginning to ensure that we worked hand-in-hand with the various planning, HSE and marketing units across the entire value chain. The idea was to start the conversations early and brainstorm unilaterally for solutions to be placed to counteract any potential risks emerging that would hinder our 2020 strategic business goals.
Over the first few months in 2004, we managed to convince CEOs across the group to create and assign a focal point to be internally responsible for ERM and coordinate and liaise with us at the corporate head office on all ERM related matters. It took 10-12 months before having each subsidiary assign a dedicated ERM focal point. Once there were dedicated individuals to communicate with and be internally responsible for monitoring and reporting on all risk-related matters, the next phase of setting up an ERM framework and governance structure was initiated. In 2007 the ISO 31000 framework was launched across the group for implementation.
KPC’s ERM structure is that of a hybrid matrix in which central ERM policies, procedures and key performance measures are set, while subsidiaries and ERM units across the group are free to implement according to their individual company’s needs and business model.
RIMS: How did you make ERM a success?
Al-Gharabally: It was not an easy task, to be honest. KPC is the corporate head office to eight other companies from upstream to downstream. The nature of their business is quite complex and diversified. So to lead ERM initiatives and have them fully incorporated and periodically monitor and report on the progress is a challenging full time task. The key is to be well integrated.
From the very start of our initiative in 2004 we made certain that the corporate head office ERM unit was well integrated with each and every single subsidiary ERM unit. We put in place a platform establishing a community of ERM best practice and there are means to discuss, troubleshoot and share various topics to ensure the benefit is widely absorbed across the entire oil sector. We conduct periodic risk culture surveys and benchmark ourselves not only internally across the group, but also against international financial and oil corporations with advanced risk management programs.
RIMS: What is unique about KPC’s approach to ERM?
Al-Gharabally: Having an ERM program in place in an oil corporation is in itself unique. To take that further and have a single unified ERM strategy and shared initiatives across multi discipline functions and across eight subsidiaries elevates the uniqueness. Having delivered a successful fully functioning ERM program over the past 13 years in close collaboration with the corporation’s strategic planning, financial and marketing departments sets KPC’s ERM program apart.
RIMS: What tools/resources have been the most helpful on this journey?
Al-Gharabally: From a risk culture perspective, establishing a community of best practices for ERM individuals to have a platform to share and collaborate various ideas, trouble-shoot implementation issues or integrate objectives on unilateral ERM implementation plans is critical to the success of our program. Having a risk operating committee chaired by the CFO and reporting to the corporation’s risk and audit committee was also a critical success factor to KPC’s ERM initiative. Subsidiaries learned early on that having a dedicated ERM unit reporting directly to the CEO, with no conflicts of interest of shared ownership of risks in the reporting line, was a critical success factor to KPC’s ERM structure. From a technical perspective, establishing a clear ERM framework, policy and procedure as well as systematic reporting of risks in a unified ERM information system, and linking the reporting to the corporations was a critical success factor.
Rims: How can ERM best inform strategy?
Al-Gharabally: KPC’s decision to maximize transparency and work closely with strategy marketing and finance was a key aspect in making our ERM program successful. To be able to look at leading risk indicators and have in place the appropriate mitigation options for improving the corporation’s performance in meeting its strategic objectives is an invaluable resource.
RIMS: What advice can you give those embarking on building a world-class ERM program?
Al-Gharabally: Communication, communication, communication! Had we not lobbied, or brainstormed across various business functions early in our journey in 2004, or not ensured that we had the full support of planning and finance on board for our ERM initiatives, our program most likely would have flopped!

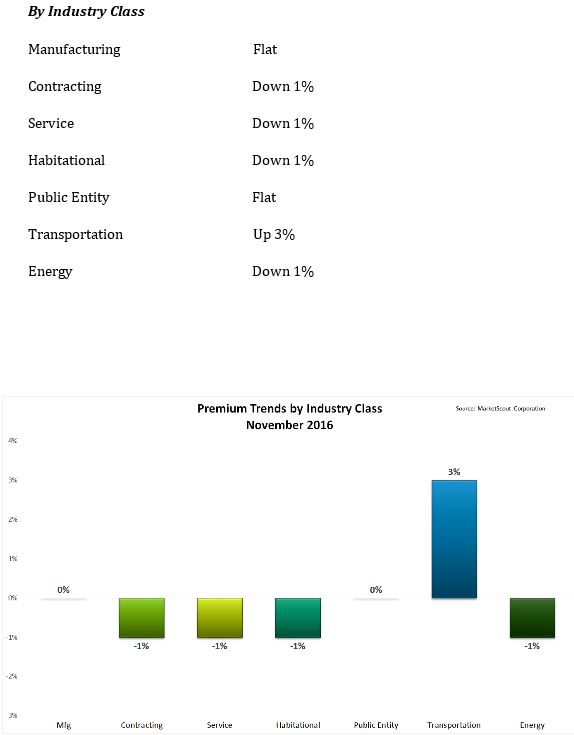
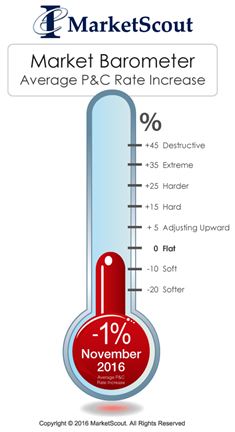 according to MarketScout.
according to MarketScout.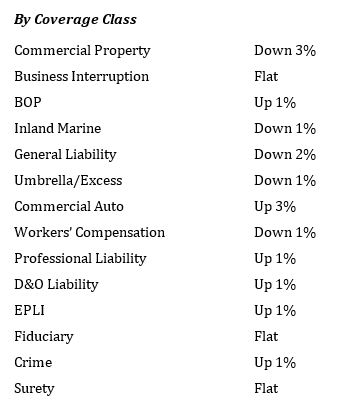
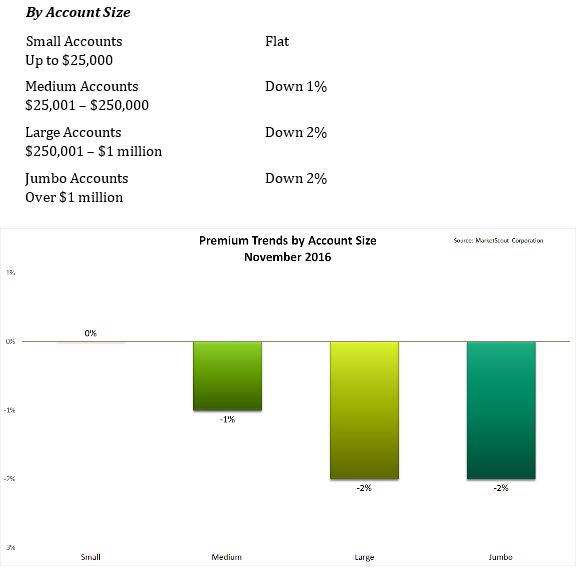

 leader, coordinator and project manager for the ERM program and its strategic implementation across the Kuwait oil sector. Al-Gharabally, a speaker at
leader, coordinator and project manager for the ERM program and its strategic implementation across the Kuwait oil sector. Al-Gharabally, a speaker at