When it comes to damaging cyberattacks, a horror movie cliche may offer a valuable warning: the call is coming from inside the building.
According to PwC’s 2014 U.S. State of Cybercrime Survey, almost a third of respondents said insider crimes are more costly or damaging than those committed by external adversaries, yet overall, only 49% have implemented a plan to deal with internal threats. Development of a formal insider risk-management strategy seems overdue, as 28% of survey respondents detected insider incidents in the past year.
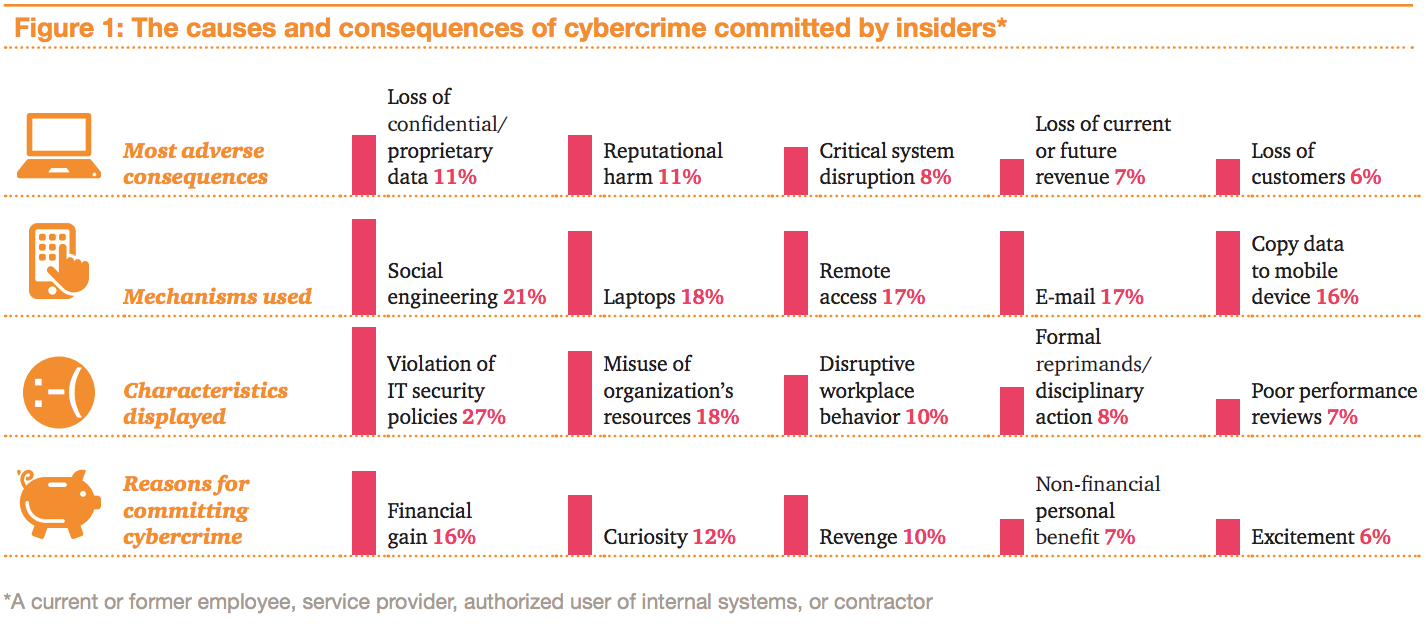
In the recent report “Managing Insider Threats,” PwC found the most common motives and impacts of insider cybercrimes are:
These threats can come from a variety of sources, from employees to trusted business partners who are given extensive access. Even after the costly lesson from the Target breach about the risk of contractors with system access, only 44% of respondents in PwC’s survey have a process for evaluating third parties before engaging in business operations with them, and just 31% include security provisions in contract negotiations.
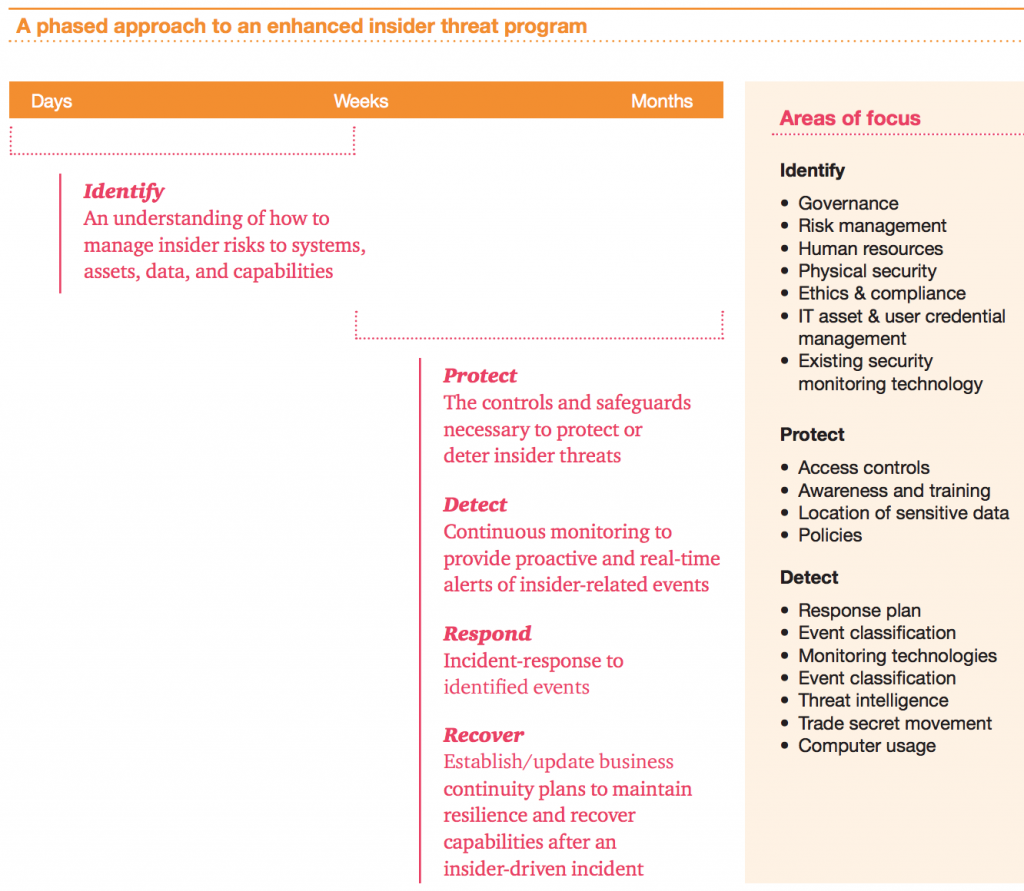
To fortify against the risk, the firm recommends that organizations use a phased approach to build an insider threat management program over time.
This should be formed with an eye to compliance with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) framework, which highlights the key functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. To explain how and when to tackle these, the report explains: