Some 70% of companies have experienced at least one supply chain interruption during the past year, with an unplanned IT or telecommunications outage the leading cause, according to the eighth edition of the Business Continuity Institute’s (BCI) Supply Chain Resiliency Report, produced in association with Zurich Insurance Group.
Covering 526 respondents in 64 countries, the report studies the causes, costs, and frequency of such events while also looking at companies’ progress in responding to supply chain interruptions and mitigating further occurrences.
While 70% of respondents reported at least one supply chain interruption during the past 12 months, only 17% said they have had no supply chain disruptions, with 13% saying they did not know. Perhaps more alarming is the increase to 13%—from 3% previously—of respondents reporting more than 20 such incidents.
Also alarming is the upward trajectory of costs associated with supply chain disruptions. The portion of respondents reporting cumulative losses of more than € 1 million (,058,171.
30) resulting from supply chain interruptions jumped to 34% in this year’s survey from just 14% previously.

An unplanned IT or telecommunications outage was the leading cause of a supply chain disruption for the fifth consecutive year, followed by a loss of talent or skills, which jumped to second place from fifth, and then cyberattack or data breach, which dropped to third place from second. Despite this drop, the portion of respondents which said that cyberattacks and data breach had a ‘high impact’ on their supply chains increased from 14% to 17%.
Reaching the top 10 for the first time was terrorism, which moved to ninth from eleventh, while currency exchange rate volatility had the largest move up the list of event causes, jumping to seventh from 20th last year and cracking the top 10 for the first time since 2012. Insolvency in a company’s supply chain also reentered the top 10 for the first time since 2012, moving from 14th to 10th.
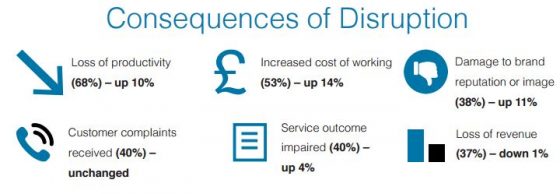
Lost productivity (68%), increased cost of working (53%), and customer complaints received (40%) were listed as the top three consequences of a supply chain interruption by respondents. The perception of such incidents can also hurt a company, with damage to brand reputation/image (38%), shareholder/stakeholder concern (30%), and share price fall (7%) all named by respondents as consequences of a supply chain disruption.
“It is crucial to note that the percentage of organizations reporting reputational damage as a result of supply chain disruption is at its highest level since the survey began. As this coincides with greater media scrutiny and social media discussions related to organizations, this result might be a good opportunity to reflect on reputation management and how supply chain disruptions might translate into adverse publicity for a given organization,” said the report.
As threats and costs grow, there appears to have been at least some progress in more closely addressing the issue.
While the percentage of respondents without firm-wide reporting of supply-chain incidents remains high at 66%, the portion of those using firm-wide reporting has grown steadily across the past five reports, rising from just 25% of respondents in 2012 to 34% in the 2016 report, the latest.
Similarly, the portion of respondents which employ no reporting has declined steadily from 39% in 2012 to 28% in 2016.
As reporting is on the rise, so too is the complexity of interruption incidents as external supply chains cause more incidents. The portion of respondents which said the majority of their interruptions came from external supply chains jumped to 24% from 9% previously, and the portion attributing at least a quarter of interruptions to external suppliers more than doubled to 34% from just 15% previously.
Even with reporting on the increase, however, insurance uptake appears to be declining. Just 4% of respondents said they were fully insured against supply chain losses, down from 10% previously, with small and medium-sized enterprises more likely to be uninsured, at just 39%, than large organizations at 62%.
“These variations in insurance uptake may indicate a need to revisit business continuity arrangements and risk transfer strategies pertaining to supply chain disruptions,” according to the report.
