
India is a country of nearly 1.3 billion, and according to the United Nations 2017 World Population Prospects, has one of the most robust working populations of people between 21 and 35 in the world. Should India’s risk management profession grow along with the country’s population (projected to eventually top China as the most populous), it will usher in an industry-wide change that we are only first catching a glimpse of now.
I have been involved with risk management (and related areas) in India for nearly 15 years. As an Indian, I do not believe we as a whole are naturally attuned to formal risk management. And I’m not alone in this belief, as Dr. Viswanathan Ragunathan, CEO and general manager of the Varalakshmi Foundation said during the RIMS Risk Forum India 2018:
“We are obviously a contradiction. We are, at once, eternal optimists and fatalistic. At one level you can relate to what I’m saying in that Indians do not take too much risk in their day-to-day lives. Yet anyone who has taken the Mumbai trains knows…it’s almost as if we have a death wish.”
That contradiction is symbolic of the state of the profession in India. One of the main challenges we will face is the evolution of the profession within a country and culture firmly rooted in tradition. Risk professionals in India need to constantly reinvent themselves to be seen as valuable to their organizations. Here are three tips Indian risk managers should be keeping in mind in order to provide value to their organizations. And while these suggestions might initially be unique to the region, they may also apply to the global risk management community.
Tip 1: Keep Systems Relevant. Apply the risk management system or process relevant to the business, otherwise, there is no motivation to follow it. An effective risk manager will know their organization from the inside out. Play to your strengths and address whatever weaknesses exist. This will require buy-in from the C-Suite, but demonstrating that it was selected with the company in mind will help sell it.
Tip 2: Know The New Philosophy. The broader outlook has changed from “risk management methodology,” (such as frameworks and templates) to a focus on the active driving of modification measures for key risks throughout the organization.
This means creating “risk-based cultures” inside organizations–a global trend but one that doesn’t happen overnight. There’s no one right way to do it, but at its core, it involves embracing the position of “we” (the company) versus “the risk” (or external factor).
You might even introduce the risk management system you selected from the prior step, depending on its accessibility.
Tip 3: Demonstrate Humility. There are several instances where a risk manager has acted on early warning signals and quickly mitigated the threat. Despite those successes, the risk manager’s role is not that of a figurehead and probably should not take full credit for all the results.
Sharing the kudos among the CEO and stakeholders, as well as subordinates (if you’re fortunate enough to lead a team), satisfies the unwritten conditions of both the national and professional cultures.
Risks can arise from anywhere within or outside an organization. CEOs are not always as clued in as risk managers regarding what is emerging. Therefore, it is our job to implement ERM programs that facilitate scenario-based workshops. This will help the CEO and stakeholders identify and mitigate at least the “known unknowns”
Generally, if risk managers do their due diligence, then a situation will have been prevented from the outset. And if something is missed, then the famous Indian term, “Jugaad” helps us. But Jugaad is something for another post.

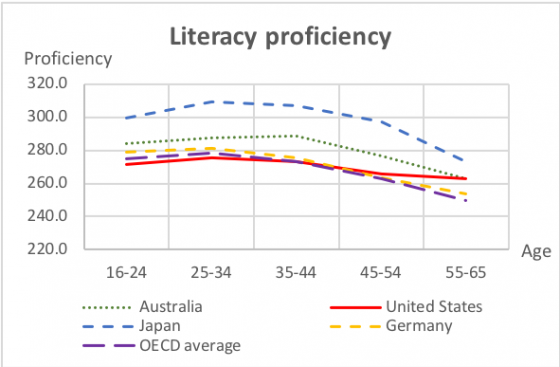
 People are living and working longer today than in the agricultural and industrial ages. The growth in the number and percentage of individuals over 60 and 80 years of age is already having a global impact.
People are living and working longer today than in the agricultural and industrial ages. The growth in the number and percentage of individuals over 60 and 80 years of age is already having a global impact.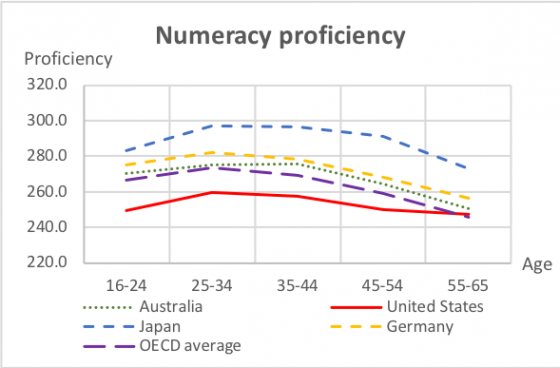



 Cassandra R. Cole, Department Chair of Risk Management Insurance, Real Estate, and Legal Studies at Florida State University; Director of the Master of Science in RiskManagement and Insurance Program and the William T. Hold Professor in Risk Management and Insurance.
Cassandra R. Cole, Department Chair of Risk Management Insurance, Real Estate, and Legal Studies at Florida State University; Director of the Master of Science in RiskManagement and Insurance Program and the William T. Hold Professor in Risk Management and Insurance. Soraya Wright, founder and CEO of SMW Risk Management Consulting and also a member of the
Soraya Wright, founder and CEO of SMW Risk Management Consulting and also a member of the