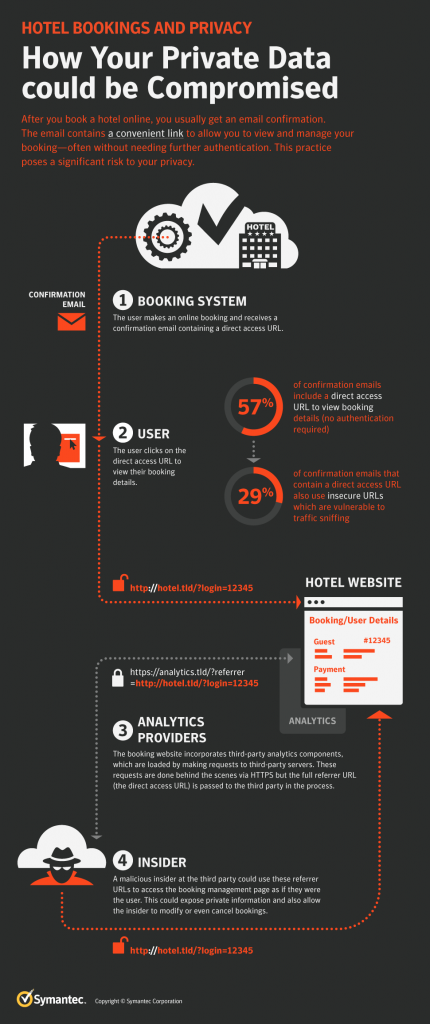
A new study shows that changes in employee engagement and loyalty can indicate whether an employee is planning to leave, and these changes may start up to 9 months before an employee quits. In The 9-Month Warning: Identifying Quitters Before It’s Too Late, workplace data analytics firm Peakon and its research arm Heartbeat drew on polling of 30 million employees in 125 countries to help employers spot the signs and mitigate resulting risks.
Turnover and recruitment to replace departing employees is costly for companies. The hiring process can take weeks or months, and includes both direct and indirect costs from paying recruiters to staff time and lost productivity. Training new staff also takes time and money, and losing institutional knowledge when an employee departs can slow operations or, in a worst-case scenario, can even compromise client relationships or handicap major aspects of the company’s business. There can also be reputation costs, especially if the potential applicants see a stream of departures.
The study stresses that decreasing employee engagement—which it defines as “the level of personal investment an employee has in their work”—is an important indicator of imminent departure. Nine months before quitting, researchers found an employee’s engagement and loyalty to the company drop significantly. The study measured engagement by asking respondents, “How likely is it you would recommend [Company Name] as a place to work?” and measured loyalty by asking, “If you were offered the same job at another organization, how likely is it that you would stay with [Company Name]?”
Various factors contribute to a decline in engagement and loyalty, including in some counterintuitive ways. The study shows that respondents considered unchallenging work more of a reason to leave than having too much work. When their work is not challenging, employees’ sense of accomplishment begins to significantly drop 9 months before quitting, while their feelings about their workload stay relatively steady until their departure.
Additionally, the study found that communication and relationships between managers and employees may be more important for retention than salary level or other factors. Employees are more likely to leave if they feel unable to discuss their pay with their manager than if they feel underpaid, and their manager’s support is more important than relationships with colleagues, feeling at home at an organization or believing in its mission.
When employees believe that they do not have opportunities for growth, they also become more likely to leave. This includes personal growth, advancement within the company and whether their managers encourage and provide pathways for growth.
“When we feel our role is helping us develop into our best self, it can have an incredibly powerful impact on employee engagement,” the study explained.
Companies can address these factors in a number of ways, including offering training programs and growth opportunities, starting an employee recognition program, implementing more frequent or more in-depth employee engagement surveys and providing additional training for managers. One way companies can incentivize these steps is by tying executive pay and other rewards not just to financial performance, but also to retention.
By ensuring that employees feel challenged in their work, feel comfortable communicating with their managers and providing opportunities for recognition and growth, employers may reduce staff attrition and save on costly recruitment and training.