If you ask a CFO if their company’s current cybersecurity strategy is working, it’s very likely that they do not know. While at first they may think it is, because the company’s bank accounts are untouched, an adversary could be lurking in their network and collecting critical data to later hold for ransom—threatening to destroy it if the money isn’t paid. The truth is that many organizations are lacking effective risk management that ensures the integrity and availability of their most essential data.
Corporate America needs to take the power back and stop hackers before they compromise networks and exfiltrate data for criminal uses, or simply threaten to destroy it for financial gain. To shift the power back in their favor, they must safeguard data, implement an effective risk management program, and invest in risk reduction activities. Organizations need to assess the maturity of their cybersecurity efforts, determine if they have any pre-existing conditions, and focus on risk reduction efforts that truly protect their data, while ensuring the ability to deliver products and services.
The fastest way to check for pre-existing conditions is by doing a compromise assessment to identify any current suspicious activity within their network. From there, they can determine what exactly needs to be done to reduce their organization’s cyber risk and develop a risk management plan that outlines clear steps for protecting their most critical assets.
To develop a cybersecurity risk management plan, executives need to first define the company’s “crown jewels”—the things that if compromised, would cause the most damage or inhibit the ability to deliver products or services that generate revenue. For instance, for a bank, this could be access to funds by their individual or business customers, or banking information that could be used for fraudulent purposes. Once an organization knows what it’s protecting, the executives can then create a security roadmap that ensures the secure delivery of products or services.
The security roadmap should start with a business impact assessment that identifies those crown jewels that are needed for delivery of essential services or producing products. These can include the data itself, technical architecture or systems used by their customers to transact business. Once these have been identified a prioritized risk reduction plan needs to be developed and tracked by the company’s leadership. Every facet of risk should be considered, from legal risk, to the consequences of a data breach, or inability to deliver services resulting from an intrusion or denial-of-service attack.
While security assessments and roadmaps are essential for defining an organization’s adequate cyber defenses, one of the biggest mistakes we see businesses make is being reactive when it comes to their defenses—relying on traditional technologies that only identify known threats and leverage Indicators of Compromise (IoCs). This method does not capture new exploits fast enough, nor versions of malware or other obfuscation techniques that are introduced by sophisticated adversaries. A great example is the sheer speed at which WannaCry ransomware spread to organizations of all sizes across the globe. Adversaries are capitalizing on this reactive security shortcoming by taking advantage of this window of opportunity to comprise data or networks.
Instead, organizations must take a proactive approach that focuses on indicators of attack (IoAs) that identify adversary behavior indicating malicious activity, such as code execution or lateral movement. IoAs can alert businesses to adversary activity before any damage is done. To effectively make use of this data, businesses also need to leverage threat intelligence for deeper insights into these IoAs.
Threat intelligence provides a crucial layer of information on adversary motives, tactics, techniques and procedures. For instance, a bank could look at a threat and see if this particular adversary typically targets the financial services industry, which regions they operate in and the motive behind their attacks.
Going one step further, organizations should leverage technology that enables threat intelligence to be shared rapidly and can protect numerous customers at once. At the end of the day, effective security requires a community effort.
Corporate America needs to come together and truly leverage the power of crowdsourced intelligence—to keep from becoming victims of the next big attack.
From a lack of risk management plans, to reliance on reactive security measures, there are a number of areas where companies are falling short of having an adequate cyber defense. By putting the necessary plans in place to secure the integrity of their critical data, taking a proactive approach to cyber threats and working together across industries and businesses, corporate America can collectively build a stronger cyber defense.

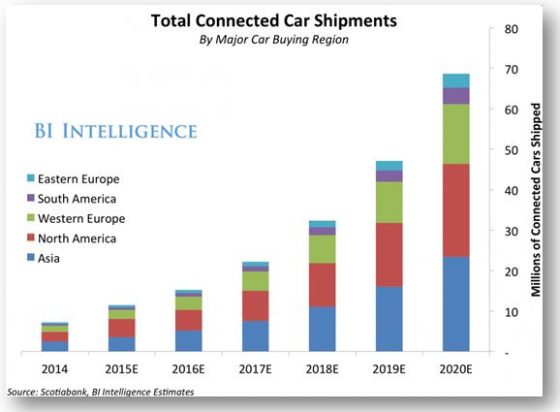 Distribution of projected connected cars (source
Distribution of projected connected cars (source