If your work involves personal data, you probably already know the European Union’s (EU) General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) enforcement date is May 25.
While penalties for noncompliance can be stiff, the sky may not be falling just yet.
GDPR focuses on personal data originating from the EU, which reaches well beyond the EU’s borders into organizations around the world that collect, process, use and store that data. As a regulation focused on data protection and privacy, GDPR’s impact may extend far outside the EU. For example, there are signs that Latin American countries may be considering a regulation that mirrors GDPR. With the recent Facebook/Cambridge Analytica data privacy fallout, several pieces of privacy-related legislation in the U.S. are currently being considered by federal lawmakers.
Privacy is a risk-based problem. Organizations should assess which risks exist and determine their risk tolerance. With data privacy, these risks are typically financial (such as fines and lawsuits) and reputation (bad press and negative perceptions).
GDPR also introduces a newer risk into the risk landscape – one related to activist groups potentially using GDPR as a springboard to flood a target organization with data subject requests.
Why GDPR matters and to whom it applies
GDPR applies to personal data originating from the EU. GDPR gives individuals (aka “data subjects”) control and ownership over their personal data. This includes personally identifiable information (PII), IP addresses, biometric data, social identity, along with health, economic, cultural and genetic data. There are two reasons this has gotten so much attention:
- The GDPR represents the EU’s most sweeping changes to privacy regulations in decades. It requires organizations to be transparent about which data is collected and how it will be used. All data collected must have a purpose and be kept accurate and up to date. Individuals (aka data subjects) now have the power to access their data, fix errors, restrict usage, move data and demand that their data be deleted.
- The penalties for noncompliance are unprecedented. The law sets out penalties of up to four percent of global revenue or €20 million, whichever is greater. It is not clear at this point how and when these fines will be applied or if they are even enforceable outside the EU. However, the significant size of the potential fines and potential risk of noncompliance captured the attention of organizations around the world.
Large data-driven organizations have been working toward GDPR compliance since the regulation was passed in 2016. A significant number of organizations may not be ready, however. In fact, a flash poll conducted by Baker Tilly during a recent GDPR webinar revealed that 90% of attendees do not have the necessary controls in place to be GDPR-compliant.
What to do today
Preparing for GDPR compliance is a matter of preparing for privacy in general. Whoever you are and wherever you are in the world, consider these steps in your compliance journey:
- Identify potential data and systems affected by GDPR: Put a process in place to understand what data you collect and why. Know where it is coming from and where it is stored. You will want to know where you have “data pools” with GDPR relevance and you’ll want to know the scope. Is it one record or one million? Where are the gaps in compliance?
- Understand existing data privacy controls: Review your existing data protection controls and assess GDPR compliance. Do you have written security protocols in place? What is your risk exposure? Depending on the type of organization you represent, you may actually be closer to compliance than you think. For example, organizations compliant with NIST, ISO, HIPAA, PCI DSS, Privacy Shield or other frameworks, may be well on the way to GDPR compliance.
- Lead from the top and educate: The news cycle is now dominated by the questionable use of personal information and it appears the shift to a data subject-centered environment may very well be here to stay. This issue goes beyond risk management and IT. Marketing, legal, government affairs, HR and communications are just a few of the functional areas touched by privacy issues. They all need to be as committed to data protection as the chief privacy officer.
- Be clear about how you will deal with data-subject requests: Once you have a clear picture of the data you possess, it is essential to design, implement and document your processes to correct, transfer and delete that data if required or being able to provide a valid, legal reason for retaining the data.
- Determine whether you need a data privacy officer: The GDPR requires that a data privacy officer (DPO) be appointed in most situations. Proactive organizations should consider the organization’s position and strategy. Is privacy an essential piece of the business model (as it is for a bank) or the brand (as it is for Apple)?
buy imodium online pelmeds.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/jpg/imodium.html no prescription pharmacy
The answer may well influence whether or not you define a new area of leadership and accountability.
Looking ahead
There is a shift taking place. People used to accept (or not know) that their online data and personal information were being tracked and used by others. Many people seemed to think this was simply the price of being online. Now, people are questioning how their data is being used and governments are starting to listen. GDPR is the likely first step toward far more widespread change.
This is not about solving every single detail today. Most experts believe that a well-documented plan and clear effort to comply with the GDPR will make conversations with supervisory authorities significantly easier. Do the homework ahead of time, know your landscape, get your systems in place, be transparent and be ready to pivot when necessary. Do that, and you will be miles (or kilometers) ahead of everyone else next time a new law or regulation goes into effect.

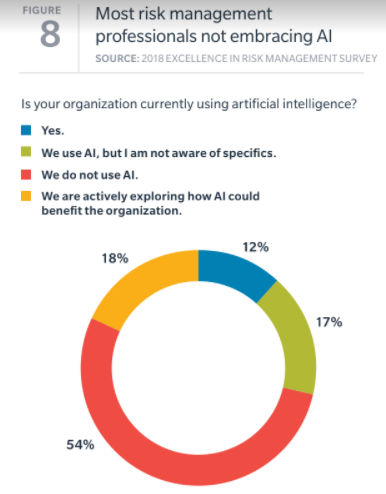 exploring the use of IoT systems; 47% are using or exploring the use of AI; and 24% are using or exploring the use of blockchain.
exploring the use of IoT systems; 47% are using or exploring the use of AI; and 24% are using or exploring the use of blockchain.