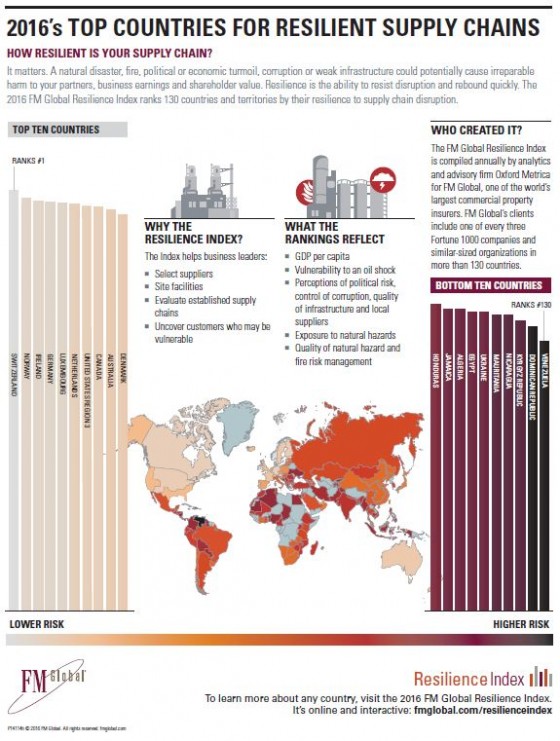
Plummeting oil prices, natural catastrophes and political disruption in a borderless business environment are some of the threats to the resilience of countries that can impact supply chains, according to the 2016 FM Global Resilience Index, which aggregates data to help companies identify their key supply chain risks. The Index ranked the resilience of 130 countries to supply chain disruption based on drivers in three categories: economic, risk quality and supply chain factors.
This year’s top-rated country, Switzerland, traded places with Norway—a reflection of Norway’s drop in oil revenue at a time of falling crude oil prices. Rounding out the top 10 in the Index, in descending order, are Ireland, Germany, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, the central United States, Canada, Australia and Denmark.
The lowest-ranked country in 2016 is Venezuela (ranked 130) for the second year in a row. It is followed in ascending order by the Dominican Republic, Kyrgyz Republic, Nicaragua, Mauritania, Ukraine, Egypt, Algeria, Jamaica and Honduras.
For the second consecutive year, Ukraine (ranked 125, down from 107) was among the countries with the biggest drop, reflecting the high degree of tension the remains within the country as well as with Russia (ranked 75).
FM Global also noted:
Venezuela’s position at the bottom reflects its exposure to the natural hazards of wind and earthquake, perceptions of its lack of control of corruption and poor infrastructure and its ill-perceived local supplier quality.
France (ranked 19) and the United Kingdom (ranked 20) retained their positions from last year, while Germany (ranked 4) rose by two places.
The United States is segmented into three regions to reflect disparate natural hazards exposure:
• Region 1, encompassing much of the East Coast, is ranked 11 in the Index.
• Region 2, primarily the Western United States, is ranked 21.
• Region 3, which includes most of the central portion of the country, is ranked 7 in the Index.


 the Oshawa Flex Assembly in Canada.
the Oshawa Flex Assembly in Canada.