When the developed world’s economies ground to a halt during the Great Recession of 2009, large, Western-based multinational companies turned their growth-hungry eyes toward developing markets. The slow recovery that followed the recession in the U.S. and Europe did little to change this trend. In fact, according to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), foreign direct investment in emerging markets reached a new high in 2013 of $759 billion (the most recent year for which data is available). This represented more than half the world’s estimated $1.46 trillion total outward investment flows for that year. Given this intense interest in doing business in emerging markets, FTI Consulting, a global professional services firm, conducted a survey in November and December 2014 on the character of the risks businesses face in these markets and how they attempt to mitigate them.
FTI surveyed 150 companies with revenues of more than $1 billion and business interests in developing economies, as well as interviews with 32 executives focused on compliance and risk management from those companies. Our results indicated an enormous difference between leaders (defined as companies whose self-reported losses as a percentage of revenues was in the lowest quartile, averaging 0.2%) and laggards (those in the highest quartile, with a loss rate averaging 2.2% of revenues), not only in the ways they managed overseas risk, but how they thought about it.
Quantifying Risk: The Numbers
According to our survey, 83% of multinational companies have suffered significant losses in emerging markets since 2010, with an average cost per company over that time of $1.38 billion, and the average loss per year $260 million, or 0.7% of revenues.
In virtually all loss-making incidents (99%), our respondents reported that the issue was either a matter of a regulatory violation, bribery or fraud, or reputational damage. In incidents with the highest losses, two or three of these types of risk converged: 60% of reported incidents involved more than one type, 35% involved two, and 25% were perfect storms that involved all three.
Regulatory issues are the most frequent cause of loss (either due to the difficulty of keeping up with ever-changing regulations or lax or inattentive corporate compliance policies), but legal and criminal issues (engaging in fraud or paying bribes) lead to the most expensive incidents. The most frequently cited consequences of getting caught were noted as reputational harm (67%), loss of revenues (56%), and prosecution (44%). In all cases, reputational issues invariably make matters worse.
These are serious issues, and some companies respond with equal seriousness. Some do not.
Leaders vs. Laggards: The Three Greatest Ways They Differ
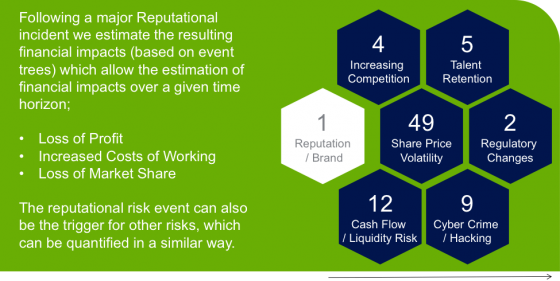
According to our survey, there are enormous differences in the ways companies that have suffered the lowest rate of loss in emerging economies and companies that have experienced the highest approach risk mitigation in the three major categories. (See Figure 2.) From these differences, we have derived three rules that leaders follow to best mitigate overseas risk.
Rule 1: Walk Away From Countries Where Compliance is Impossible
Our leading companies believe it is more important to avoid doing business in jurisdictions where compliance may not be possible than do laggards by a ratio of more than 5:1. In other words, our leaders are willing to walk away, even when environments are hyped and offer the potential for quick profits. Globalized companies often overestimate their ability to estimate and analyze overseas risk accurately.
For instance, it is extraordinarily difficult to stay compliant with Brazil’s tax laws. According to Renato Niemeyer, Chief of Tax Legislation in Roraima State, each of Brazil’s 27 states has its own tax regulations “and the rules change all the time.” Neimeyer said this has led some companies to postpone paying taxes as the penalties for late payment are relatively low. However, when a company does pay the penalties, “corrupt officials will solicit the organization for bribes in order to lessen the penalties,” Neimeyer said. This, of course, is the proverbial slippery slope that can lead to both bribery and fraud prosecution and concomitant reputational damage – the perfect storm.
Latin America is also growing increasingly green in its politics, and environmental regulations are becoming problematic, especially in the energy, mining and construction sectors. Chevron vs. Ecuador, the nasty, ongoing, eight-year trial over liability concerning alleged environment damage, is an example of how damaging running afoul of environmental regulations can be.
When successful companies do attempt to do business in countries where it is difficult to comply with regulations, they invest time and energy into helping host countries develop more rational regulatory frameworks. Our leaders consider this kind engagement more important than do laggards by a ratio of almost 3:1.
Rule 2: Keep to the Straight and Narrow
In most developed markets, it is understood that paying bribes to win or facilitate business is bad business and, if there were any doubt, the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) and U.
K. Bribery Act remove them. But in many developing economies bribery is just how business gets done. In China, facilitation payments are customary to keep projects on target. The long-established Chinese custom of giving gifts to customers violates both the FCPA and U.K. Bribery Act. For our leading companies, the first rule for avoiding getting caught in the coils of bribery and corruption is to “conduct continuous dialogue with local staff on compliance issues.” Leaders rate that more important than do laggards by a ratio of nearly 7:1.
It is very difficult for local managers to resist making a facilitation payment when that’s the only way to get a pallet off a loading dock, or a critical part to a factory. That’s why companies that avoid getting in trouble make significant investments in internal communication and compliance training. They also go the extra mile when conducting due diligence on potential local partners and suppliers that may not have the same commitment to hewing to the straight and narrow as do their own organizations.
Companies sometimes forget that the contractors their local managers hire, and the subcontractors the contractors hire, also need to be vetted and watched. Ted Unton, a former director of global financial compliance at Bemis Company, a U.S. global manufacturer, said his company has hired private investigators to look into partner companies and even partner executives.
Rule 3: Walking the Compliance Talk
Our respondents said that reputational damage – of the sort famously experienced by Walmart (accused of bribery in Mexico) and McDonald’s (accused of using tainted meat in China) – most often leads to loss of revenues, followed by exclusion from markets and even expropriation of assets. In our research, we found the greatest difference between how leaders and laggards approach mitigating reputational risk was how the regarded maintaining a good reputation over the long term. Leaders rate it more important than do laggards by an impressive ratio of 10:1.
This variance is mind-boggling when one considers that those companies that do not rate the importance of maintaining a good reputation highly have, by definition, suffered far greater losses than those that do.
Maintaining that good reputation is difficult as local populations are prone to regard multinational corporations as bad actors, and rich exploiters of resources and people – a belief often reinforced all-too willingly by the local press. It requires action and investment. One former president of an energy company operating in Bangladesh (who requested anonymity) told us his company, which had purchased land for a 40-mile pipeline, set up offices to help displaced farmers find jobs.
By demonstrating its concern for the community and by conveying that the company was involved for the long-term, planned protests were averted. (Indeed, many of the farmers were hired by the company and their living standards improved.) According to the former president, the company became seen as a benefactor, not a despoiler, and he believes that reputation will improve the company’s future business prospects.
Notably, laggards believe that running “preemptive publicity campaigns to counteract negative reactions” is a fine strategy. Leaders do not. That spread is one of the largest differences we’ve found.
Do It Right or Don’t Do It at All
As we’ve seen, multinational companies have suffered significant and severe losses in emerging markets. And the difference in the loss-rate as a percentage of revenue – 2.2% for the laggards; 0.2% for the leaders – is certainly wide. Developing risk management competence in the three major categories of risk defined by our survey not only helps to stem these losses, but builds a strong foundation for future profits.
It is bad to be a laggard. What’s more, it is unnecessary.