One of the key questions being asked by audit committees and boards of directors of organizations around the globe is whether their emerging technology risks are being properly identified and managed. To that end, the Global Internal Audit Common Body of Knowledge (CBOK) released “Navigating Technology’s Top 10 Risks,” which identifies the top technology risks and ways that organizations can learn about and address these risks.
Here are the top five out of 10 risks ranked by the study:
1. Cybersecurity
One of the biggest cybersecurity risks faced by companies is the possibility of theft of confidential data by external perpetrators, and the study found this is the most discussed IT topic among executives, internal auditors, audit committees and the board. One of the biggest cybersecurity risks faced by companies is the possibility of theft of confidential data by external perpetrators.
More than 70% of survey respondents consider the risk of a data breach to be extensive or moderate, while 82% of IT specialists consider this risk to be even higher.
2. Information Security
With the recent spotlight on data breaches, the current focus is a layered defense of critical information rather than a single layer of protection.
A strong information security program encompasses:
● Robust risk assessment process
● Effective governance and compliance procedures
● Documented and communicated information security policies and standards
● Effective security awareness training program
● Efficient access control procedures
● Tested disaster recovery, business continuity and incident response programs
● Operational asset management, network management, patch management and change management processes
● Tight physical security
3. IT Systems Development Projects
While organizations need to update their technology systems, success rates are low. The study found that the success of systems development projects was 16.2% for overall success, 52.7% for challenged projects and 31.
1% for impaired or canceled projects.
Examples of project objectives not achieved include missed deadlines, cost overruns, efficiencies not delivered as expected, flawed software that was not tested before implementation, reduced integration from the initial plan and less functionality than was identified in the business case when the project was approved.
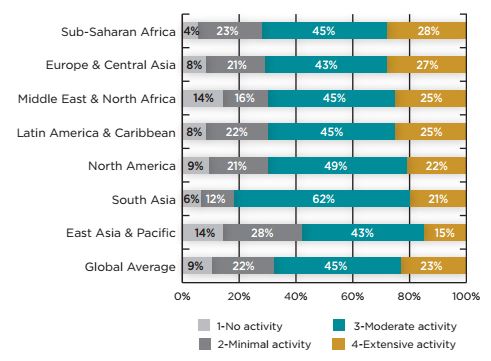
4. IT Governance
In many organizations, management questions the amount of money spent on IT and increasingly monitors IT costs. This added emphasis is also due to the widening gap of what IT thinks the business needs and what the business thinks IT can deliver.
A good IT governance program must have these elements:
● Clear alignment to business
● Measurable value delivery to business
● Accountable controls of resources, risk, performance and cost
IT Governance Activity
5. Outsourced IT Services
Because of the increased focus on IT costs, some key IT services have been outsourced. According to the study, this can expose an organization to risks that may remain undiscovered until a failure occurs. An average of six out of 10 internal auditors surveyed said they expect an increase in audits of outsourced IT services over the coming year, according to CBOK, which is administered through the Institute of Internal Auditors. The largest increase is expected in Sub-Saharan Africa and the smallest in Europe.