
Attorney General Loretta Lynch addresses RSA Conference 2016
SAN FRANCISCO—Many of the Obama administration’s top brass are here in force, addressing some 40,000 practitioners from every part of the technology and information security industry at the annual RSA Conference. Set against the backdrop of the ongoing fight over between Apple and the FBI encryption and backdoors, the tension ebbed and flowed during sessions with Attorney General Loretta Lynch, Secretary of Defense Ashton Carter, and Admiral Mike Rogers, U.S. Navy Commander, U.S. Cyber Command, and director of the NSA. While many speakers will not address the issue directly, the subtext is clear throughout the show, particularly as the public battle brings considerable interest to the privacy and security issues the RSA has centered on for 25 years.
Indeed, in his keynote address, RSA President Amit Yoran called law enforcement’s current stance on encryption “so misguided as to boggle the mind.” Brad Smith, president and chief legal officer of Microsoft, chimed in as well, asserting that we cannot keep people safe in the real world unless we can keep them safe in the virtual world. He lauded Apple and pledged that the tech giant would stand with Apple in its resistance.
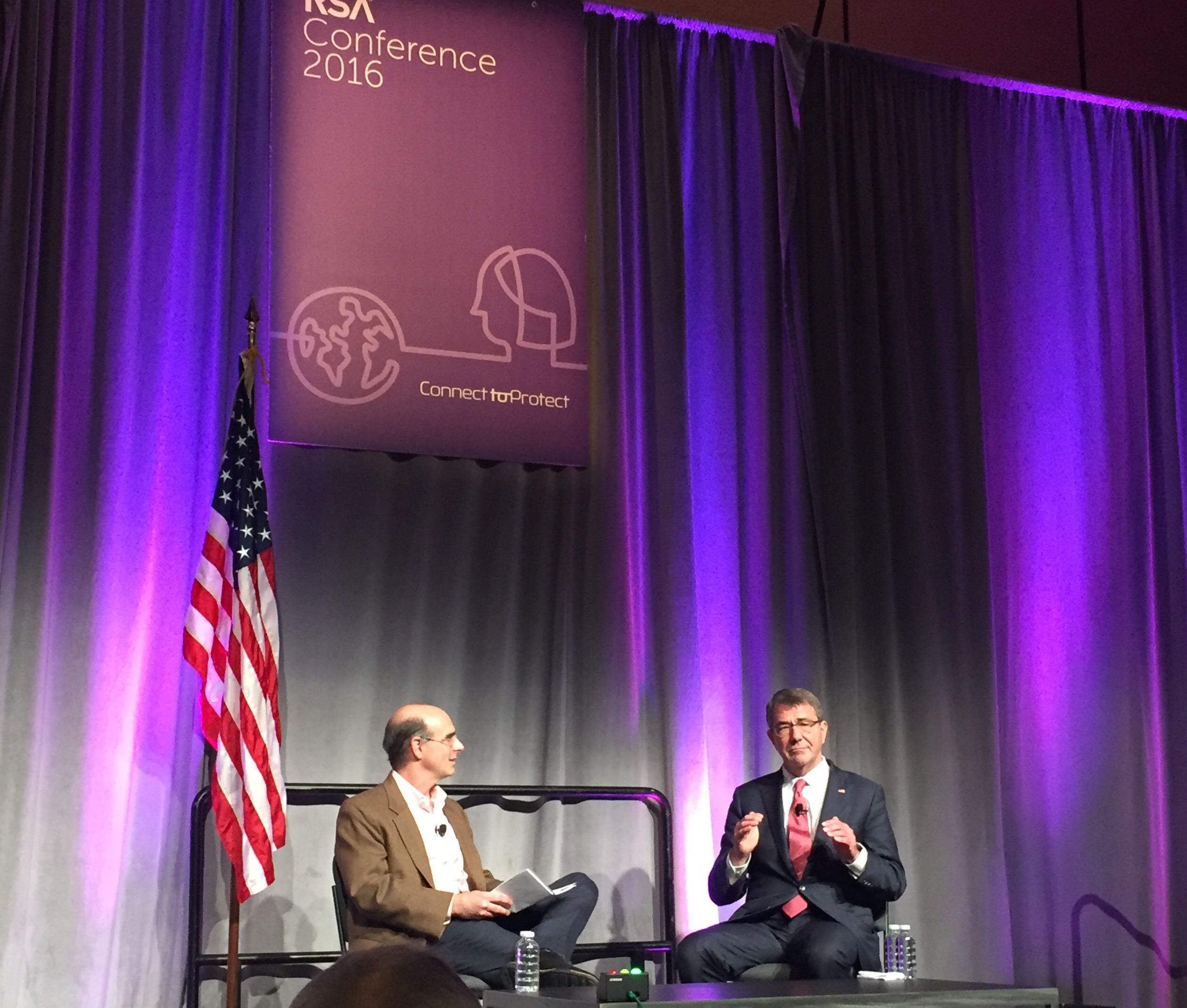

Secretary of Defense Ashton Carter in Conversation with Ted Schlein of Kleiner Perkins at RSA
While the gravity of the issue and the massive potential impact for many in the sector are boggling many minds here, the administration officials’ sessions also offered more broadly positive comments for businesses outside the tech sector. The conciliatory tone Lynch and Carter often struck centered on the critical need for partnerships between technology and government. They tried to emphasize the ways the administration is reaching out to private entities, both within Silicon Valley and across corporate America at large.
According to Sec. Carter, for example, the United States Cyber Command has three core missions: defending the Department of Defense’s network; helping American companies, the economy and critical infrastructure; and engaging in offensive cyber missions. The second is a key pillar, he said, as the DoD must keep in perspective that the strength of American entities is the strength of the nation. From threat intelligence to the Defense Innovation Unit Experimental he announced yesterday, to be helmed by Google’s Eric Schmidt, Carter believes there is considerable need for industry to engage with government on cyberrisk, and both parties have valuable assets to contribute. “Data security is a necessity, and we must help our companies harden themselves,” Carter said. Indeed, he wants both help for and from the industry. In closing, he said, “We are you. You pay us. We represent you and our job is to protect you, and we’d love to have your help.”
He also noted that the DoD is trying to learn a bit about managing its cyberrisk from the commercial sector’s best practices. “We do grade ourselves and we’re not getting good grades across the enterprise,” Carter told reporters Wednesday, according to Defense News. “I have these meetings where I call everyone in and we have these metrics which tell us how we’re doing [and] if you don’t score well, that is evident to the Secretary of Defense at those meetings.
“We don’t assume for a minute that we’re doing a perfect job at this,” he added. “That’s the whole reason for me to be here and the whole reason for me to be engaging with this community here at this conference.”
Carter also announced that the Department of Defense will be hosting “Hack the Pentagon,” a bug bounty program offering white hat hackers cash for finding and reporting vulnerabilities in the Pentagon’s websites. Many companies have been offering these programs to try to discover their exposure in a controlled setting, without the risk of reputation damage, personal information exposure and business interruption that accompany an unknown hacker finding them instead. Carter called these a “business best practice” to gauge preparedness.
Federal law enforcement also has a notable presence at RSA and is making a pronounced effort to reach out to businesses regarding cyberrisk, threat intelligence, and managing a cyberattack. Indeed, in one session Tuesday, panelists from the Department of Homeland Security, FBI and the White House urged a call to action for businesses to get serious about proactively building bridges with law enforcement and to make use of the many resources the administration is trying to activate to help private industry fortify against cyber threats. The government is working to make it easier for companies to turn to it for help, they said, and attitudes are shifting to more consistently recognize and respect victimized businesses and minimize business interruption.
Some in the audience expressed skepticism, such as one man who seized upon the Q&A portion of a session on government departments’ specific roles in fighting cyber criminals. He asked how the government can be trusted to help industry when it cannot protect itself. But corporate entities should be taking note, particularly of the services available. While many hesitate to share threat intelligence or even successful attacks, Eric Sporre, deputy assistant director of the FBI’s cyber division, stressed that FBI Director James Comey has made it a directive for FBI field offices to develop relationships with local businesses and to treat businesses as crime victims, not perpetrators. In responding to attacks, he noted, the Bureau sometimes even brings in victim services to holistically approach aiding in the investigation and recovery process.
Andy Ozment, assistant secretary for cybersecurity and communications at the Department of Homeland Security, also highlighted the preventative measures his department offers companies, including personal risk assessment services. In some cases, chief information security officers and other executives engaged in cyberrisk management functions have been getting DHS assessments, using them as a tool to drive investment or otherwise sell cyber upwards with the board or C-suite of their organizations.

 management. As liability and regulations take shape, it is important to assess whether your company currently employs a vendor risk management policy, and, if not, understand how a lack of due diligence poses significant risk on your organization’s overall cybersecurity preparedness.
management. As liability and regulations take shape, it is important to assess whether your company currently employs a vendor risk management policy, and, if not, understand how a lack of due diligence poses significant risk on your organization’s overall cybersecurity preparedness.


