NEW YORK — “Incident Response and Recovery” was the theme of the National Cyber Security Alliance (NCSA) and Nasdaq Cybersecurity Summit on April 17. Security and risk professionals from the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and various companies and organizations convened at the Nasdaq Marketsite to discuss methods that focus on resilience and recovery following a cyber attack or data breach.
NCSA Executive Director Kelvin Coleman led the fireside chat with Matthew Travis, deputy director for the DHS’ Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). The timing of Travis’ appearance was unique, considering that Kirstjen Nielsen–formerly the secretary of Homeland Security and Travis’ director–recently resigned from her post on April 7. While that announcement grabbed widespread attention due to her involvement with the humanitarian and immigration crisis at the U.S.-Mexico border, it also has major impacts for the country’s efforts to counteract cyberrisk and data breaches. Last September, Nielsen announced the formation of the National Risk Management Center (NRMC), an initiative focused on defending critical infrastructure from cyberattacks and providing a single point of access to the full range of government activities to defend against cyber threats.
“There is no doubt [Nielsen] was the most cyber-savvy secretary the department’s ever had. She brought real bonafide domain expertise in cybersecurity to the department,” Travis said. He added that the creation of CISA is her legacy and that the relationship with Kevin McAleenan, the new acting secretary of homeland security, has been harmonious.
Travis reminded attendees that its partnerships with the private sector were crucial and that CISA regularly monitors national critical functions such as elections, electrical grids and financial transactions, which he said are the “big things that drive our economy.” He also said that companies can leverage CISA resources immediately after a breach as a supplement to the FBI’s criminal investigation.
“We’re going to help you understand exactly what happened and help you recover the data and mitigate some of the impact. The private sector firms do that very well, but the difference is that…
[CISA] is free,” he said. “That is where we would like to work with owners and operators, when there is an event, to help them get back on their feet as soon as possible.”
Additionally, Coleman and Travis discussed that though CISA is not part of the intelligence community, it does have access to the intelligence collection and monitors trends that can be used to warn private sector companies of cyberrisks. He cited the recent Domain Name System (DNS) infrastructure hijacking campaign that CISA warned about in February—in which at least 40 different organizations across 13 different countries were compromised—as an example of the agency taking steps to alert both the public and private sectors.
“When we issue technical alerts or emergency directives,” Travis said, “[we] communicate to our stakeholders what to look out for.”
How to Reduce Uncertainty After A Breach
In the next session, panelists agreed that even when companies use new technologies to remedy security flaws and migrate data to cloud storages, new vulnerabilities occur. Dr. Michael Siegel, principal research scientist and director of cybersecurity at the Sloan School of Management at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), said that the old adage of risks being rooted in people continue to be prophetic.
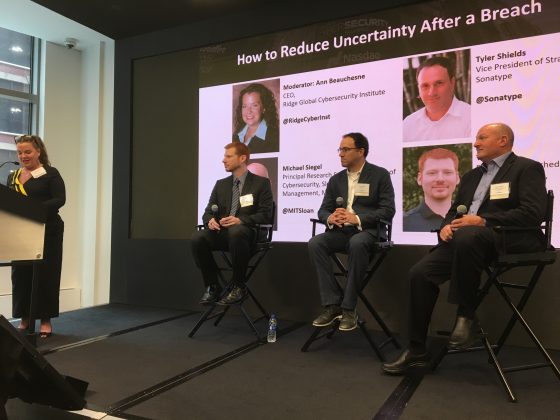

“It’s always been about people and things that sit in our systems for a long time,” he said. “You’ve heard this since the 2000s and it’s still true, and even more true today.”
Should a business find itself in a situation where ransom is being demanded for intangible assets and information, Siegel advised that then is not the time when stakeholders should first decide whether they’d be willing to pay.
“They should know whether they’d pay ransomware because they have [presumably] done tabletop exercises…that will be absolutely essential because any time you wait and indecision will be [catastrophic],” he said. “You have to have practiced it in advance. You can build a scenario-generator and run it through a classroom.”
Companies can also learn from breaches, if tracking is implemented within their code, noted Tyler Shields, vice president of strategy for Sonatype, and open source governance platform. “The ability to track your code from creation to deployment—that entire life cycle—needs to be instrumented so that when a breach occurs you know what component was affected, where it came from, who implemented it and what protections were in place.”
Incident Response Recovery Beyond IT
The final session panelists agreed that holistic approaches were essential for successful responses and recovery periods. Internal and external communications should be well thought-out and designating a person or team to handle them sets the appropriate company precedent. Lisa Plaggemier, chief evangelist at Infosec and NCSA board member said that, for example, while a company’s lawyers are critical during these times, they might not be the best communicators.
“Lawyers, when they write for communications, tend to sound more scary than reassuring,” she said.
“You want to have collaborations and have that communications person in the room with them.”

Photo courtesy of the National Cyber Security Alliance
When it comes to crisis communication, Plaggemeir advocated that employees—especially those who detected the incident—should be armed with talking points for traditional and social media outlets to avoid data leakage.
“We want to make sure we equip those people so that the rumor mill doesn’t start flying and we don’t end up with communications that are out of our control,” she said.
buy penegra online https://royalcitydrugs.com/penegra.html no prescription
Dovetailing on that notion, moderator Andrew Derboben, senior director of security operations at Nasdaq was quick to mention reputation risk. He said another way to reduce data leakage and misrepresentations in the media—which can further harm a company’s reputation in the aftermath of a breach—is to arm all company employees with a brief script on what to say to anyone, even just passersby making small talk.
“Don’t even have them say ‘no comment,’” Derboben said. “Point them to the experts who have all the data. Because if we’re missing a key piece of information and it’s not communicated properly it could determine how an article will be written.”