SAN ANTONIO – Emergency preparedness and action plans amid violent crises were explored during educational sessions at RIMS 2018 here. On Monday and Tuesday, experts discussed ways businesses can prepare for active shooter events and kidnapping crises. Experts agreed that in such events, lives, operations, reputation and finances are all at stake.
Some highlights from the sessions:
Kidnapped! A Crisis Simulation Exercise
Bill Laurence, head of crisis management at S-RM offered a kidnap simulation for a well-attended session on Monday. Laurence provided a scenario, asking the audience to assume a collective role as decision-makers of a fictitious, billion-dollar coffee company that has an executive abducted in Mexico. The group’s assignment was to create a crisis management team and decide who the communicator would be, how they would respond to threats and what information to relay to their insurance provider, among other critical actions.
“The first 24 hours are always the most critical during a kidnapping or ransom scenario,” Laurence said.
The simulation included real-life audio and video examples of terrifying ransom-demanding calls. The team learned that the kidnapper has typically planned the abduction in advance and always has control of the situation – beginning with communication. “For that reason alone, you cannot speed up the process,” Laurence said.
And although things may seem dire, he explained ways to glean information – and feel somewhat positive – even after a brief phone call. “We all react differently to pressure,” he said. “But avoid speculation and always prepare for the next call.”
Read more about kidnapping in a Q&A with the session’s co-host, Denise Balan, senior vice president and head of U.S. kidnap & ransom at XL Catlin, on page 9 in Tuesday’s Show Daily.
Active Threat and Workplace Violence on Campus: Preparedness, Response and Recovery
Craig McAllister, Cornell University’s director of risk management and insurance, opened a session on Tuesday with a discussion of duty of care and the obligation to the campus or work environment.
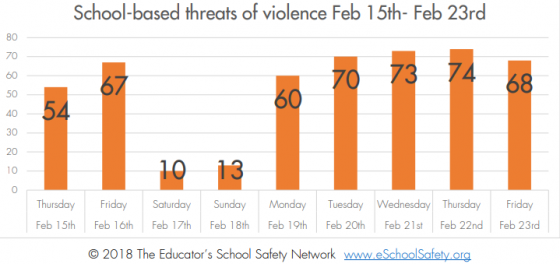
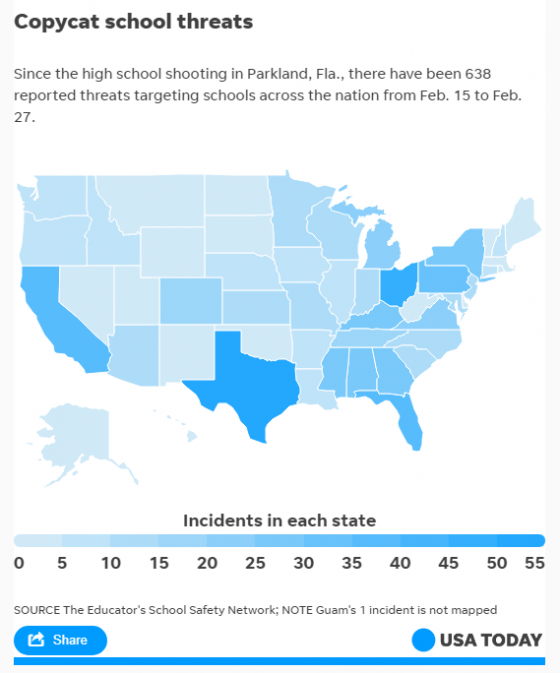
He pointed out that, in early January, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) processed its NFPA 3000 Standard as a provisional one to streamline the program elements necessary for organizing, managing, and sustaining an active shooter and/or hostile event response program. The standard gained even more input following the Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School in Parkland, Florida, on Feb. 14 in an effort to reduce or eliminate the risks, effect, and impact on an organization or community affected by these events
Paul Mills, global kidnap prevention manager at AIG, followed with a segment addressing best practices for violent incident preparation and response. He discussed response and resilience training for employees who need enhanced preparedness with the rise of violence against soft targets.
He noted that advances in technology often are putting people in harm’s way by default. “People are distracted to the point where they are unaware of the threats they face. It’s also delaying and inhibiting their response times,” he said. “Without even realizing it, they often portray victim-like behavior.”
Kendell Moore, senior vice president at the Abernathy MacGregor Group, delved into the key crisis management sources of an organization’s response support, both internally and externally. She used a mass shooting that occurred inside a local business in the western United States (that is also part of a major American chain) as an example of an entity that needed to enact its crisis communication plan immediately after the attack.
Moore offered some crisis communication principles:
- Media is a conduit, not an audience. “The media needs to catch up to the actions of the business.”
- Speak directly to the impacted. “It is most important to communicate with victims, loved ones, the community and those who are directly affected.”
- Take action, not credit. “No statement, no matter how eloquent, can substitute for doing the right thing.”
- Communicate what matters when it matters. ““What is said first must stand the test of time. So announce nothing and predict nothing that isn’t solid and certain.”
- Build relationships in the community. ““Work alongside local law enforcement, government officials and those who know the community best.”
- Listen to people’s needs and requests. “Ask what people need, rather than telling them what you think they need.”