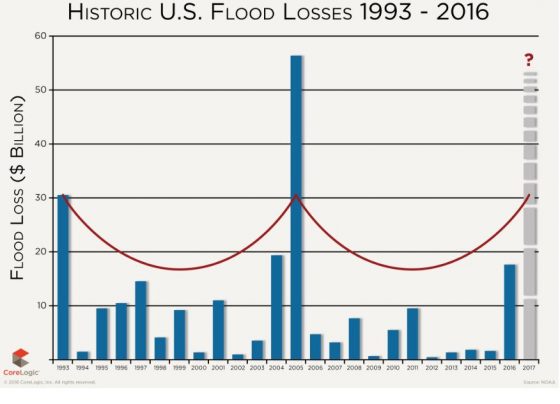
Last week, a series of tornadoes ripped across the Midwest and Southern United States, killing dozens and crippling infrastructure in Arkansas, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Mississippi, Missouri, Ohio and Tennessee. While Karen Clark & Company has estimated that the insured loss from the tornado outbreak will be about $3 billion, and credit rating agency Fitch predicted that losses would total $5 billion, Dr. Joel N. Myers, AccuWeather founder and CEO, estimated that the tornadoes are expected to cost about $18 billion in total damage and economic loss. Mark Friedlander, director of corporate communications at The Insurance Information Institute, said, “Based on preliminary assessments of the extensive property damage we are seeing across multiple states, this weekend’s tornado outbreak has the potential to be the costliest on record in the U.S.”
As of Monday, 88 deaths across the region had been confirmed, but over 100 people are also missing, which means the death count may be higher. The cyclones killed more than 70 people in Kentucky, the hardest-hit state, leaving thousands homeless and knocking out power for more than 25,000 in the western region of the state. Additionally, 10,000 Kentucky homes and businesses reported being without water, and another 17,000 were under boil-water advisories, according to the Kentucky Division of Emergency Management.
Across the entire affected region, 750,000 customers were left without electricity. These outages have complicated search and rescue efforts, as rescue workers excavated destroyed buildings, searching for people who are still missing. In Mayfield, Kentucky, for example, the city’s main fire station and multiple police stations were inoperable, and the city was scrambling to find new ways to field emergency calls.
Also in Mayfield, at least eight people died at a Mayfield Consumer Products scented candle factory after workers reportedly pleaded with supervisors to let them leave the building after warning sirens sounded and an initial twister had passed with little damage, only to be threatened with firing if they did not continue working. Over 100 workers were trapped inside the building after the next tornado leveled it. Several survivors have already filed a lawsuit against the company, citing “flagrant indifference” to worker safety, and that the company “knew or should have known about the expected tornado and the danger of serious bodily injuries and death to its employees if its employees were required to remain at its place of business during the pendency of the expected tornado.”
Another tornado struck an Amazon warehouse in Edwardsville, Illinois, killing six people and injuring another. Amazon claims that it took all necessary precautions, but family members of victims have alleged that the company prioritized productivity over worker safety by not heeding tornado warnings and not adequately preparing employees for emergency weather safety responses. Amazon pledged to help workers and their families affected by the tragedy by donating $1 million to the Edwardsville Community Foundation, a charitable trust that benefits regional communities. OSHA is reportedly investigating the Amazon warehouse, and Kentucky state regulators are investigating the Mayfield Consumer Products event.
While an Amazon spokesperson noted that the company’s warehouse was up to code, Illinois governor J.B. Pritzker also promised an investigation into whether building codes needed to be updated, “given serious change in climate that we are seeing across the country.” Scientists say that climate change may have changed normal weather patterns and led to these tornadoes’ increased intensity and reach, with record warm temperatures across the region potentially exacerbating the disaster.
Businesses and risk professionals should prepare now for more frequent and intense weather events. The following recent Risk Management articles may help:
- Reviewing Policy Terms Before Storms Strike
- Insurance Recovery After Severe Weather
- Weathering Hurricane Season During the Pandemic
- Q&A: How Texas Roadhouse Takes a People-First Approach to Disaster Planning
- Natural Disaster Planning During COVID-19
- Before Disaster Strikes: How to Prepare for Natural Catastrophes