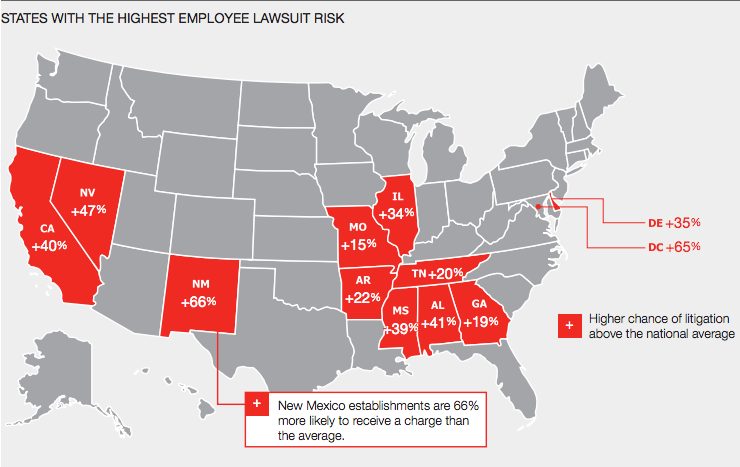
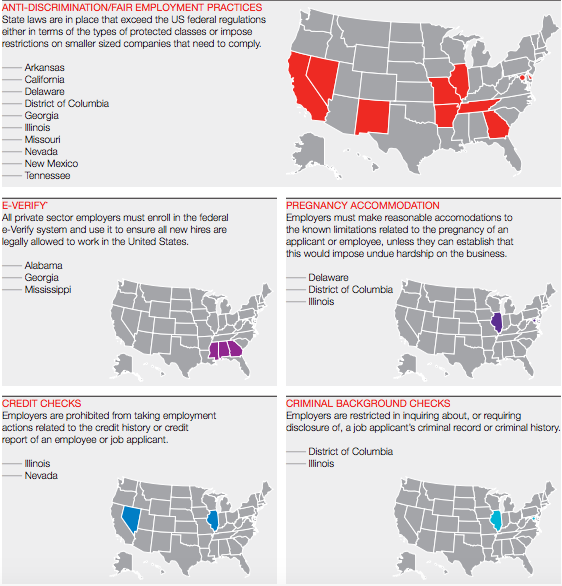
Over time, the role of corporate legal departments has expanded to address the increasing risks in corporations—from increasing involvement in implementing corporate policies to leading employee training on procedures for managing electronic communications, social media, and bring your own device (BYOD) policies. This shift, however, is not enough to meet the challenges posed by an increasing range of risks proliferating within global organizations. Legal and compliance groups must also take the lead in finding new ways to leverage the power inherent in their data and address the challenges posed by massive data stores, information and network security challenges, as well as regulatory compliance requirements.
Failings of Traditional Strategies
In the past, organizations used straightforward, people-intensive methods to search for and remediate risk. For example, organizations instituted policies training, hoping that it would be sufficient to corral employee use of electronic communications, BYOD, and social media. Some may have formed working groups or intradepartmental committees designed to consider the implications of data privacy or information security for their businesses. Others rely on basic technology, such as keyword searches, that trigger electronic alerts when they find a hit in a document.
While these tools are still important to demonstrate compliance, they are insufficient alone to monitor for risk.
Older technology falls short when it comes to handling unstructured data, such as e-mail. For example, discerning employees will be too cautious to use triggering keywords such as “donations” or “bribes” when referring to illicit activity. Keywords are also notoriously inaccurate: if over-inclusive, they may yield a stockpile of irrelevant information, while under-inclusive keywords could omit critical documents from discovery.
Trends Drive New Risk Management Approaches
Three recent trends—escalations in data volumes, increasing threats to data privacy and security, and heightened regulatory scrutiny—highlight the need for more intensive means to investigate risk in organizations.
1-Burgeoning Data Stores
With today’s hyperfocus on information, risk follows data. The more data sources organizations have, and the more locations for storage of data, the greater the legal exposure.
Email is perhaps the most insidious source of risk, as hackers may look to exploit unwitting employees who may open spoofed e-mails containing malware or viruses designed to attack the corporate network. Along with e-mail, employees also have more ways than ever to share confidential corporate data such as trade secrets with outsiders. Newer forms of unstructured data, such as social media and instant messaging, allow people to disperse troubling information even more rapidly than before.
As more organizations look for low-cost storage for their data reserves, they have turned to the cloud—yet another source of potential risk to data privacy. Cloud providers may be susceptible to the same hacker schemes as employees. Moreover, depending on the terms of their service-level agreements, they could employ lax security protocols, lack disaster-recovery plans, share data with other clients, or transfer data to third parties, all without notifying the data owner. Furthermore, depending on the location of the cloud storage, it may trigger the application of international laws that protect data privacy and prevent the processing or transfer of a corporation’s data.
2-Data Privacy and Security
Traditional approaches to risk management are poorly equipped to meet the demands imposed by today’s data privacy and security regulations, particularly when it comes to the need to protect personally identifiable information, protected health information, nonpublic information, trade secrets, and privileged data.
This is especially true for global organizations, which are likely to have information cross international borders and trigger other nations’ data privacy schemes. Many nations have adopted restrictive schemes designed to protect their citizens’ personal information, such as the European Union’s Data Protection Directive, which controls when and how organizations can collect, process, store, alter, retrieve, and transmit this personal data. Many nations in the Asia-Pacific region have also created data privacy regimes, including China, which has blocking statutes that forbid the cross-border transfer of documents that contain “state secrets” as well as confidential commercial information.
Domestically, organizations must worry about laws such as the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, which extends the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) to a covered entity’s third-party business associates. Under HIPAA’s Security Rule, organizations and their business associates must take reasonable measures to safeguard protected health information.
Organizations must vigilantly monitor their data to ensure there are no gaps in security that would violate these rules.
3-Regulatory Enforcement
The nation’s regulatory framework is becoming more complex almost by the day. Regulations that supplement laws such as the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) and the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) have generated new areas of vulnerability, particularly when it comes to third-party relationships.
For example, the current administration has taken the position that no FCPA infraction is too small to prosecute. Organizations that fail to take proactive measures to search for, disclose, and remediate misconduct are likely to face substantial penalties if a regulatory agency discovers misconduct. Traditional tools, such as internal audits, are not up to the task of detecting the malfeasance of internal fraudsters, who may mask their corrupt behavior with code words or other innuendo that make it difficult to discover using keywords. Unless more advanced tools are used, an organization’s best defense against fraud might be reliance on tipsters.
A similar approach is required to ensure compliance with ITAR. This law imposes stiff penalties, including millions in fines, against U.S. organizations that export “defense articles” without government authorization. “Articles” is defined so broadly that it covers technical, defense-related data in documents, blueprints, drawings, photographs, plans, or instructions. The Directorate of Defense Trade Controls, the U.S. agency that enforces ITAR, is likely to take a more lenient approach with companies that have implemented a rigorous compliance program and that voluntarily disclose and remediate any failures.
Data-Driven Tools
Risk professionals now have a number of advanced analytics tools at their disposal to counteract the additional risks that lurk in emerging forms of data. Linguistic analysis techniques can identify instances where employees use seemingly innocuous words or phrases to engage in subterfuge. Concept clustering is a tool that isolates subtle patterns within documents that seem dissimilar to the untrained—or undigitized—eye. These conceptual search tools can identify patterns in documents, based on keywords or chunks of text, and flag the documents that refer to items that might fall within ITAR’s purview. Data visualization tools can analyze relationships and look for troubling connections that might violate the FCPA, such as links between employees, vendors, and foreign officials. In addition, anomaly detection tools can scan records for irregularities, such as unusual recurring payments.
Counsel, risk and compliance professionals can also apply tools such as technology-assisted review (TAR) to prioritize documents for review based on the likelihood that they contain material of concern. Using TAR, experienced legal counsel code a seed set of documents for relevancy to the issue at hand. Once done, they feed these documents into a computer that is programmed to uncover the logical reasoning behind the lawyers’ coding decisions. Sophisticated algorithms then apply that logic across an entire document population.
The process is iterative, so that ultimately the computer’s logic closely mirrors the lawyers’ coding decisions. Organizations can use TAR to limit the population of documents for review, thus expediting the data mining process.