Concerned about lost productivity and higher employee healthcare costs, many employers are taking serious steps to eliminate smoking among employees. In Japan, a number of companies and educational institutions are now even basing hiring decisions on whether an applicant smokes.
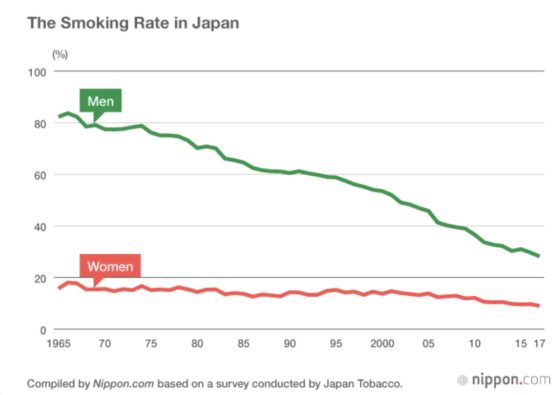
Some scientific evidence suggests that employers’ concerns about the added costs costs are valid. A 2018 study conducted by Ohio State University found that smokers in the U.S. cost private sector employers an average of $5,816 extra per year, excluding additional costs that the employees themselves may pay. These employer costs include “excess absenteeism,” “presenteeism” (lower productivity on the job), “smoking breaks,” “excess healthcare costs” and “pension benefits,” with time devoted to smoking breaks making up the majority of costs. Stopping smoking eliminates lost time for smoke breaks entirely, unlike other high-cost factors like healthcare and absenteeism, which could continue after an employee stops smoking.
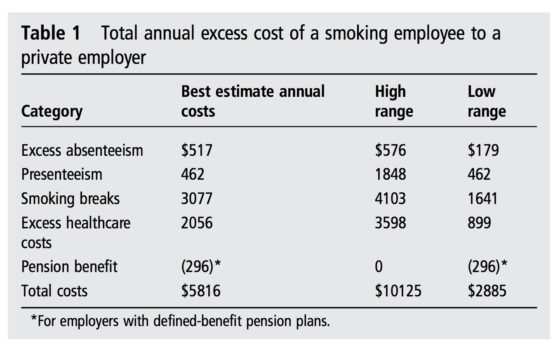
Smoking is more prevalent in Japan than in the United States, especially for men.
Although the rate has been falling steadily, a 2018 national study showed that 28.2% of men and 9% of women in Japan smoke, compared to 15.8% of men and 12.2% of women in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In April, more than 20 Japanese companies signed onto a corporate partnership to promote anti-smoking steps. Starting in spring 2020, for example, insurance company Sompo Japan Nipponkoa Himawari will not hire any new employee who smokes, and will require its high-level officials to sign a document pledging not to smoke during work hours. The private sector in Japan is not alone in pushing for less employee smoking—Nagasaki University announced last month that it would stop hiring faculty who smoke and banned smoking on campus, and Oita University has “put priority on nonsmokers” when hiring.
Part of this effort is incentivizing quitting.
Employees who quit smoking at Japanese company Rohto Pharmaceutical Co., for example, get tokens they can use at the company cafeteria or for other benefits. Marketing firm Piala Inc. is also offering an extra 6 paid days off to non-smoking employees, and 4 of its 42 smokers have reportedly quit smoking thus far.
While programs to incentivize quitting may seem intuitive, according to Ohio State’s Micah Berman, lead author of the school’s study, these efforts may also be pricey for employers. “Employers should be understanding about how difficult it is to quit smoking and how much support is needed,” he said.
buy flagyl online https://royalcitydrugs.com/flagyl.html no prescription
“It’s definitely not just a cost issue, but employers should be informed about what the costs are when they are considering these policies.” These can include the costs of direct incentives like the ones noted above, or the additional healthcare cost of prescription drugs or counseling to help quit. However, in the long-term, companies that implement cessation programs—especially those that have a large number of smoking employees to start—are likely to see the benefits outweigh initial investment costs within 4 years.
Companies may save money by encouraging employees to quit smoking, especially in lost time and healthcare spending, but they should examine the costs and benefits of instituting formal or informal policies to change their employees’ habits. Running afoul of legal protections, as well as making workplaces unfriendly to employees who smoke, being perceived as interfering with employees’ activities outside of work and other considerations may outweigh employers’ concerns for their workers’ health and excess spending.
Japanese companies have stated that they believe these steps are legal, and some U.
S.-based companies, including Scotts Miracle-Gro and Weyco, Inc., have reportedly made similar efforts to discourage their workforces from smoking. Some companies in the U.S. may be unable to explore such potential programs, however. According to legal experts, “around half of [U.S.] states currently legally protect employees from being denied positions, or having employment contracts terminated, due to tobacco use.”