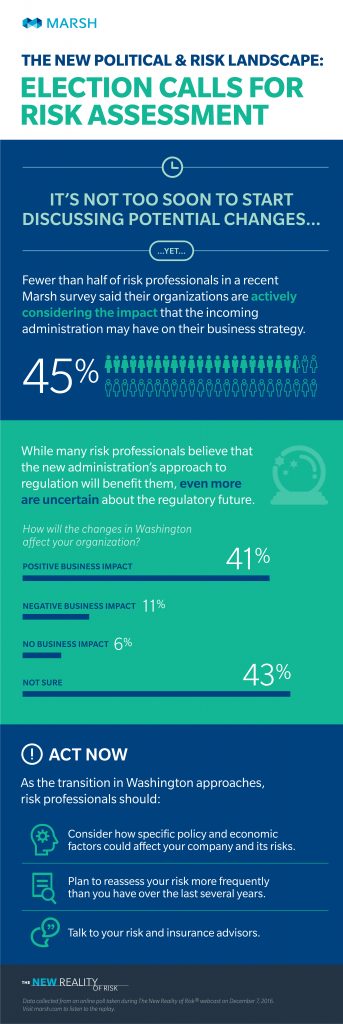
With a new president in office in 2017, there are sure to be changes ahead for businesses in the United States. Yet of risk professionals surveyed, fewer than half are actively preparing. Organizations are expected to see impact in areas including regulation and enforcement strategies, a new national trade policy, and a potential rollback of Affordable Care Act (ACA) provisions, according to Marsh.
Speakers on Marsh’s webcast, The New Reality of Risk, noted that the new administration appears to favor deregulation across several industries including financial services, although a complete repeal of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act is unlikely, said Arthur Long, a partner at Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP. The Trump administration is also expected to reduce regulation in the energy industry and others.
Areas to watch, according to the webcast:
- Regulation and Taxes
Less regulation and lower taxes are the most significant changes that are expected next year, both of which are expected to benefit businesses, said Michael Poulos, president of Marsh Risk Consulting. A stronger dollar could also help larger companies with extensive operations overseas, while others could benefit from changes in credit and monetary policies. - Trade Policy
Changes in trade policy — including a move away from free-trade agreements — could alter the trade credit market, said Michael Kornblau, Marsh’s US Trade Credit Practice leader. These changes could lead to balance-sheet pressures — including reductions in sales and working capital — on companies with more than half of their revenues outside of the US. - Health Care
Meanwhile, the future of the ACA (commonly referred to as Obamacare) remains uncertain for health care organizations and employers, said Mark Karlson, Marsh’s US HealthCare Practice leader, as transition officials have made sometimes conflicting statements about whether they will pursue repeal, replacement, or amendment of the existing law. If any changes are made to the law, it may be some time before they take effect. - Cyber Risk
The election also highlighted cyber risks for businesses, including the potential threat of hackers and the need to encrypt corporate emails, said Tom Fuhrman, Cybersecurity Consulting and Advisory Services Practice leader at Marsh Risk Consulting. Generally, cyber regulations are expected to focus more on ensuring effective risk management for businesses rather than the existence of specific controls.
Although uncertainty remains about many specific policy changes to be made under the new administration, businesses should be thinking about the potential effects of new policies on their operations. Among other steps, businesses should:
- Stay up-to-date on policy and regulatory proposals from transition and administration officials and develop a post-election game plan that includes actions and strategies that can be taken in preparation for regulatory changes.
- Assess how reliant they are on global economic models that could become further strained.
- Plan to reassess their risk more frequently than they have in recent years, according to Marsh.

 And if that isn’t enough, the report also includes a “Watch List,” calling attention to eight additional jurisdictions “that bear watching due to their histories of abusive litigation or troubling developments.” Those are:
And if that isn’t enough, the report also includes a “Watch List,” calling attention to eight additional jurisdictions “that bear watching due to their histories of abusive litigation or troubling developments.” Those are: But the news isn’t all bad. The report examines “Points of Light,” which are examples of “fair and balanced judicial decisions that adhere to the rule of law and respect the policy-making authority of the legislative and executive branches.” Highlights include positive court rulings from 11 states.
But the news isn’t all bad. The report examines “Points of Light,” which are examples of “fair and balanced judicial decisions that adhere to the rule of law and respect the policy-making authority of the legislative and executive branches.” Highlights include positive court rulings from 11 states.
 North Carolina has the worst, according to the
North Carolina has the worst, according to the 