With weeks to go before floodwaters recede in some parts of Texas, Hurricane Harvey—which delivered more than three feet of rain in areas of Houston—has so far caused at least 38 deaths and numerous injuries. Harvey was downgraded to a storm Wednesday night, but tens of thousands of people are still in shelters, some of which are also flooded, fearful of what they will find when they return to their homes.
“Hurricane Harvey has already broken all U.S. records for tropical cyclone-driven extreme rainfall, with observed cumulative amounts of 51 inches,” Michael Young, RMS head of Americas climate risk modeling said in a statement.
Joel N. Myers, founder, president and chairman of AccuWeather declared Hurricane Harvey to be, “The costliest and worst natural disaster in American history. AccuWeather has raised its estimate of the impact to the nation’s gross national product to $190 billion or a full one percent, which exceeds totals of economic impact of Katrina and Sandy combined.”
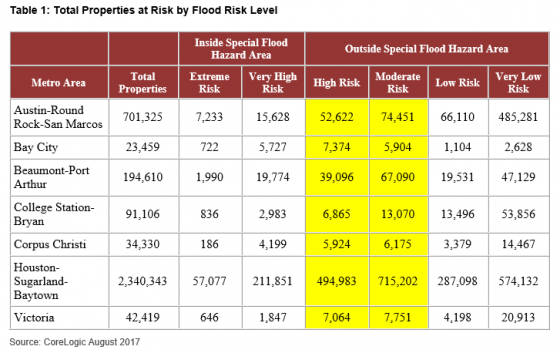
Damage assessments are climbing, with modeling and analytics firm RMS now estimating that losses incurred by wind, storm surge and inland flooding could be as high as $70 billion-$90 billion. The majority of losses are coming from inland flooding in the Houston metropolitan area, where more than seven million properties top $1.5 trillion in value. RMS said the estimate includes damage to all residential, commercial, industrial and automotive risks in the area, as well as possible inflation from an area-wide demand surge.
According to RMS:
Most losses will be uninsured, given that private flood insurance is limited. However, although the insured losses will remain uncertain for some time they will be significant, as private coverage is not consistent: there are significant variations in how coverage is provided by individual insurers.
Coverage for some of the residential losses has been provided by the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP). There are approximately 500,000 NFIP policies that will be affected by Harvey, and the losses to the program will be very significant – potentially the largest event to date. However, NFIP penetration rates are as low as 20% in the Houston area, and thus most of the losses will be uninsured. This will rekindle the public policy debate around this issue.
Texas Gov. Greg Abbott estimated that more than $125 billion in federal funding will be required to help the state recover from Hurricane Harvey, the Wall Street Journal reported.
Adding to the area’s woes were two explosions at the Arkema Inc. chemical plant in Crosby, Texas, 20 miles northeast of Houston early on Thursday.
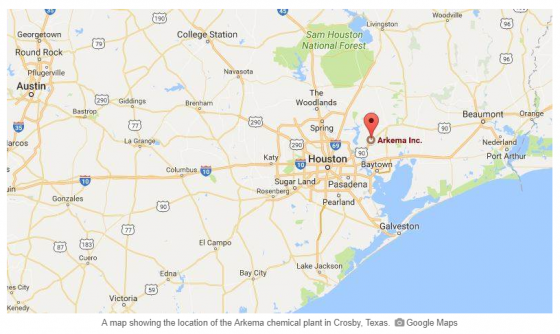
The plant, which produces organic peroxides used in products like kitchen counter tops, polystyrene cups and plates, industrial paints and PVC pipes., was without electric service since Sunday and lost refrigeration when backup generators were flooded. Because the products need to be kept cold to prevent a chemical reaction, workers had moved them from warehouses into diesel-powered refrigerated containers, but those were also flooded.
A sheriff’s deputy was taken to a hospital after inhaling fumes, according to Reuters.
Residents in a 1.5-mile radius of the Arkema plant were evacuated on Tuesday, and water levels there make it too dangerous for workers to assess the situation from the ground, officials added.
Arkema urged people to stay away as the fire burns out. Black smoke was billowing from the site, Harris County Sheriff Ed Gonzalez said at a televised news briefing.
The Federal Aviation Administration said Wednesday it had temporarily barred flights from the area because of the risk of fire or explosion.

 Hurricane Harvey, which made landfall in Texas on Friday night as a Category 4 hurricane, has so far caused at least five deaths and more than a dozen injuries. Now a tropical storm, Harvey has dumped more than 30 inches of rain on the Houston area, with another 15 to 20 inches anticipated by Friday.
Hurricane Harvey, which made landfall in Texas on Friday night as a Category 4 hurricane, has so far caused at least five deaths and more than a dozen injuries. Now a tropical storm, Harvey has dumped more than 30 inches of rain on the Houston area, with another 15 to 20 inches anticipated by Friday.