A cyberattack targeting the U.S. power grid would have widespread economic implications, resulting in insurance claims of between $21.4 billion and $71.1 billion in a worst case scenario, according to a report by Lloyd’s.
Lloyd’s and the University of Cambridge’s Centre for Risk Studies recently released “Business Blackout,” which examines the insurance implications of a major cyberattack using the U.S. power grid as an example. In the scenario outlined, malware is used to infect control rooms for generating electricity in areas of the Northeastern U.S. The malware goes undetected and locates 50 generators that it can control, forcing them to overload and burn out. The scenario, described as “improbable but technologically possible,” leaves 15 states in darkness, meaning that 93 million people are without power.
Economic impacts include direct damage to assets and infrastructure, decline in sales revenue to electricity supply companies, loss of sales revenue for businesses and disruption to the supply chain. The total impact to the U.S. economy is estimated at $243 billion, rising to more than $1 trillion in the most extreme version of the scenario.
Claimant types fell into six categories:
Power generation companies
• Property damage to their generators.
• Business interruption from being unable to sell electricity as a result of property damage.
• Incident response costs and fines from regulators for failing to provide power.
Defendant companies
• Companies sued by power generation businesses to recover a proportion of losses incurred under defendants’ liability insurance.
Companies that lose power – companies that suffer losses as a result of the blackout.
• Property losses (principally to perishable cold store contents).
• Business interruption from power loss (with suppliers extension).
• Failure to protect workforces or causing pollution as a result of the loss of power.
Companies indirectly affected – a separate category of companies that are outside the power outage but are impacted by supply chain disruption emanating from the blackout region.
• Contingent business interruption and critical vendor coverage.
• Share price devaluation as a result of having inadequate contingency plans may generate claims under their directors’ and officers’ liability insurance.
Homeowners
• Property damage, principally resulting from fridge and freezer contents defrosting, covered by contents insurance.
Specialty
• Claims possible under various specialty covers, most importantly event cancellation.
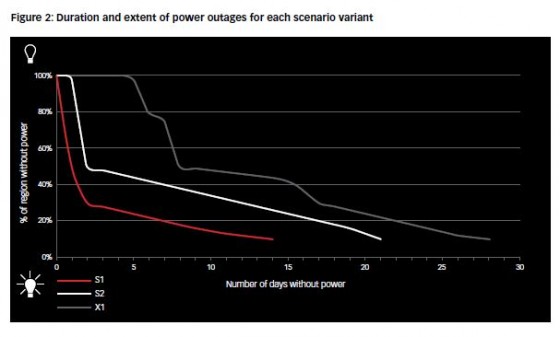 Other key findings of the report include:
Other key findings of the report include:
• Responding to these challenges will require innovation by insurers. The pace of innovation will likely be linked to the rate at which some of the uncertainties revealed in this report can be reduced.
• Cyberattack represents a peril that could trigger losses across multiple sectors of the economy.
• A key requirement for an insurance response to cyber risks will be to enhance the quality of data available and to continue the development of probabilistic modelling.
• The sharing of cyberattack data is a complex issue, but it could be an important element for enabling the insurance solutions required for this key emerging risk.






