We’ve heard it over and over again: 2011 was the costliest year on record for natural disasters. From triple-digit heat waves and devastating drought to overflowing rivers and deadly tornadoes, the U.S. rang up natural disaster costs in the billions and much time and effort of rebuilding.
But what wasn’t talked about so much was the fact that much of the tornado risk was located outside of the traditionally storm prone tornado alley, according to a new report by CoreLogic. “The apparent increase in the number of incidents and shift in geographic distribution of losses that occurred last year in the U.S. called the long-held notion of risk concentration in Tornado Alley into question, and is leading to changes in risk management policy and procedure,” said Dr. Howard Botts, vice president and director of database development for CoreLogic Spatial Solutions.
CoreLogic’s “Tornado and Hail Risk Beyond Tornado Alley” report analyzes hazard risk at the state-level across the U.S using the company’s wind and hail data layers. Key findings include:
- Tornado risk actually extends across most of the eastern half of the U.S. rather than being confined to the Midwest
- According to data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association (NOAA), of the top ten states with the highest number of tornado touchdowns between 1980 and 2009, only three actually fell within Tornado Alley
- At least 26 states have some area facing extreme tornado risk
- At least 11 states have significant areas facing extreme hail risk, and almost every state east of the Rocky Mountains has some area facing a moderate or higher level of hail risk
- The area of highest hail risk extends outward from the central Great Plains to include states as far east as Georgia and the Carolinas
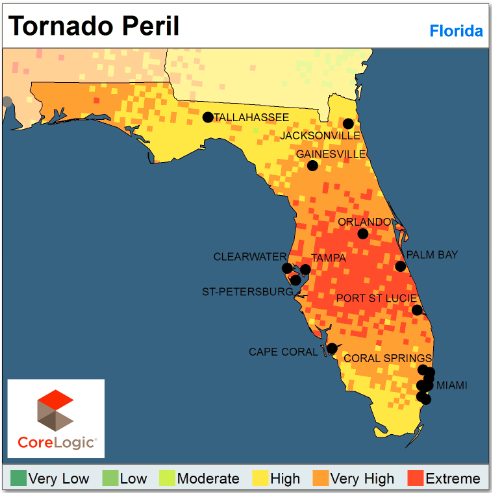
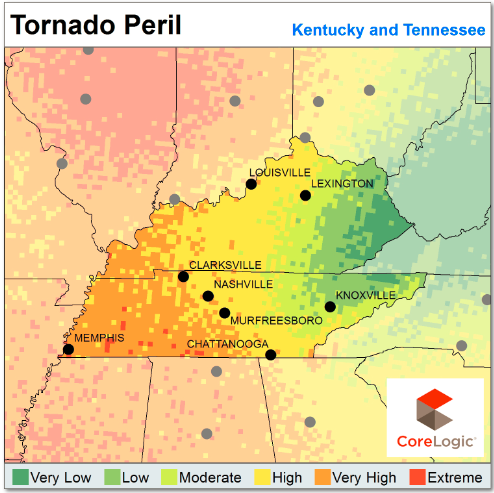
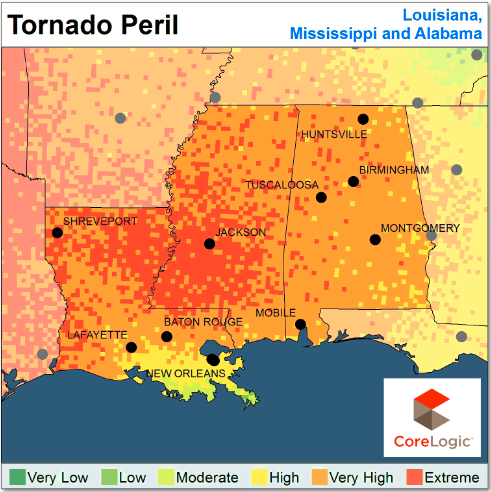
These findings have obvious insurance implications, but it goes beyond that to disaster preparation and natural catastrophe risk management in areas not historically prone to such events. CoreLogic released the maps below, indicating tornado peril in non-tornado alley states.
Insurers and residents alike should be aware of the high risk of tornadoes, wind and hail in these areas. For the complete report, including and in-depth descprition of how CoreLogic created the above maps, click here.