More organizations are recognizing the value of a structured focus on emerging risks. The number of organizations with a complete enterprise risk management (ERM) program in place has steadily risen from 9% in 2009 to 28% in 2016, according to the N.C. State Poole College of Management’s survey “The State of Risk Oversight: An Overview of Enterprise Risk Management Practices.”
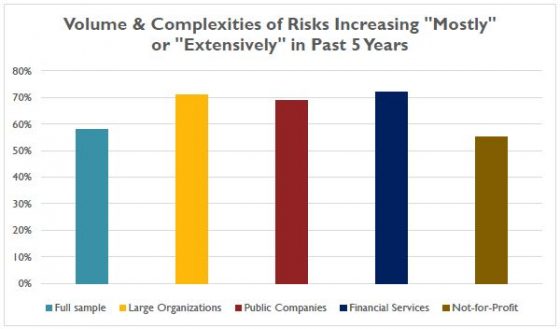
Yet this progress may lag behind the increasingly complicated risks that need addressing. Of respondents, 20% noted an “extensive” increase in the volume and complexity of risks the past five years, with an additional 38% saying the volume and complexity of risks have increased “mostly.” This is similar to participant responses in the most recent prior years. In fact, only 2% said the volume and complexity of risks have not changed at all.
buy zydena online https://royalcitydrugs.com/zydena.html no prescription
Even with improvements in the number of programs implemented, the study—which is based on responses of 432 executives from a variety of industries—found there is room for improvement. Overall, 26% of respondents have no formal enterprise-wide approach to risk oversight and currently have no plans to consider this form of risk oversight.
Organizations that do have programs continue to struggle to integrate their risk oversight efforts with strategic planning processes.
“Significant opportunities remain for organizations to continue to strengthen their approaches to identifying and assessing key risks facing the entity especially as it relates to coordinating these efforts with strategic planning activities,” the researchers found.
According to the study:
Many argue that the volume and complexity of risks faced by organizations today continue to evolve at a rapid pace, creating huge challenges for management and boards in their oversight of the most important risks. Recent events such as Brexit, the U.
buy ventolin online www.northwestmed.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/jpg/ventolin.html no prescription pharmacyS. presidential election, immigration challenges, the constant threat of terrorism, and cyber threats, among numerous other issues, represent examples of challenges management and boards face in navigating an organization’s risk landscape.
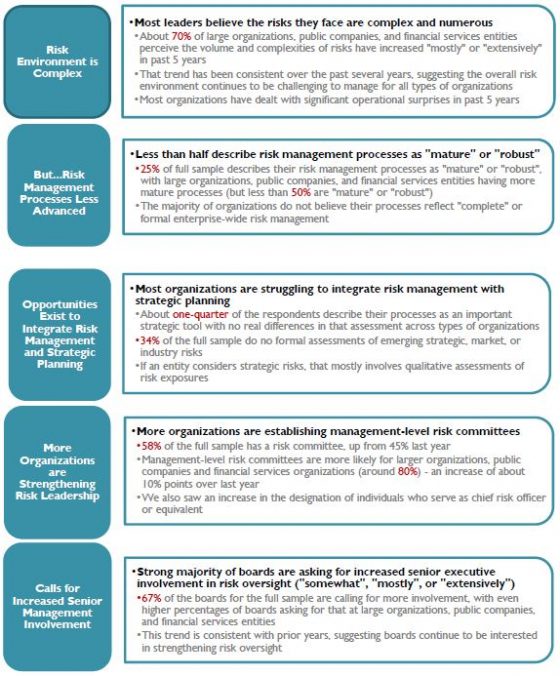
Key findings include: