Knowledge assets are critical to any business remaining functional and competitive, yet this data is routinely exposed to the risk of theft and overlooked in cybersecurity risk management. According to a new report from the Ponemon Institute and law firm Kilpatrick Townsend & Stockton, the organizations are increasingly ineffective at safeguarding data like trade secrets, product design, development or pricing, and other proprietary information.
As breach notification laws, regulatory requirements, and reputation considerations draw more focus to cybersecurity surrounding personal data of customers or personnel, businesses are leaving more risk on the table regarding their most valuable assets, and that risk has a notable price tag.
In the past year, the average cost of remediating these attacks was about $5.4 million, and half of respondents estimated the maximum cost would range over $250 million, with seven out of ten placing it over $100 million. What’s more, on average, respondents believe only 35% of the losses resulting from knowledge asset theft would be covered by their current insurance policies.
The primary drivers of these costs, respondents said, were (out of 100 points):
Why are so many businesses failing to take action against the risks to knowledge assets?
Among the findings, the report noted:
- Theft is rampant. Seventy-four percent of respondents say it is likely that their company failed to detect a data breach involving the loss or theft of knowledge assets, and 60% state it is likely one or more pieces of their company’s knowledge assets are now in the hands of a competitor.
- Companies don’t know what they need to protect, or how to protect it. Only 31% of respondents say their company has a classification system that segments information assets based on value or priority to the organization. Merely 28% rate the ability of their companies to mitigate the loss or theft of knowledge assets by insiders and external attackers as effective. The great majority who rate their programs as not effective cite as the primary reasons a lack of in-house expertise (67%), lack of clear leadership (59%), and lack of collaboration between different job functions (56%).
- Executives and boards aren’t focused on the issue and its resolution. A data breach involving knowledge assets would impact a company’s ability to continue as a going concern according to 59% of respondents, but 53% replied that senior management is more concerned about a data breach involving credit card information or Social Security numbers than the leakage of knowledge assets. Only 32% of respondents say their companies’ senior management understands the risk caused by unprotected knowledge assets, and 69% believe that senior management does not make the protection of knowledge assets a priority. The board of directors is often even more in the dark. Merely 23% of respondents say the board is made aware of all breaches involving the loss or theft of knowledge assets, and only 37% state that the board requires assurances that knowledge assets are managed and safeguarded appropriately.
- Careless employees and unchecked cloud providers are key risk areas. The most likely root cause of a data breach involving knowledge assets is the careless employee, but employee access to knowledge assets is not often adequately controlled. Fifty percent of respondents replied that both privileged and ordinary users have access to the company’s knowledge assets. Likewise, 63% of respondents state that their company stores knowledge assets in the cloud, but only 33% say their companies carefully vet the cloud providers storing those assets.
Thanks in part to the lack of action currently, there is plenty businesses can easily do to improve.
“Companies face a serious challenge in the protection of their knowledge assets. The good news is there are steps to take to reduce the risk,” said Dr. Larry Ponemon, chairman and founder of the Ponemon Institute. “First of all, understand the knowledge assets critical to your company and ensure they are secured. Make sure the protection of knowledge assets, especially when sharing with third parties, is an integral part of your security strategy, including incident response plans. To address the employee negligence problem, ensure training programs specifically address employee negligence when handling sensitive and high value data.”

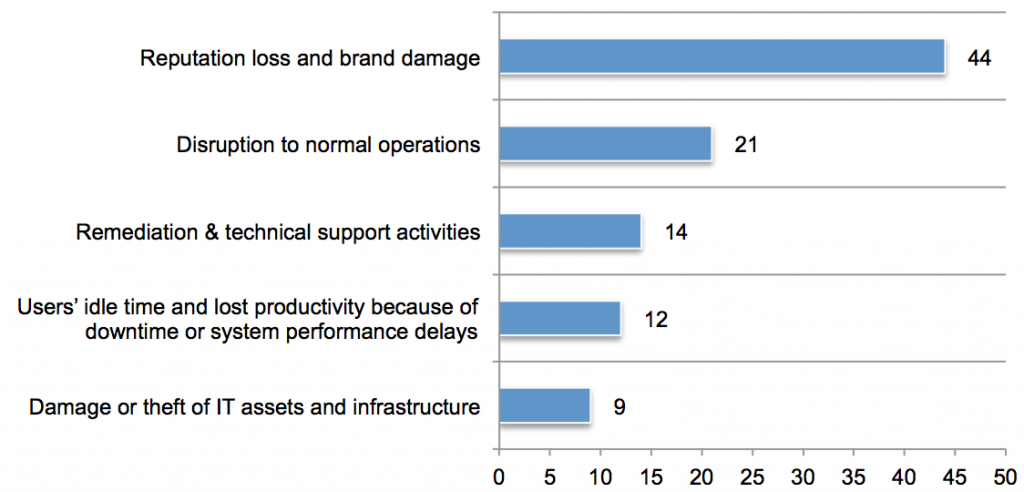
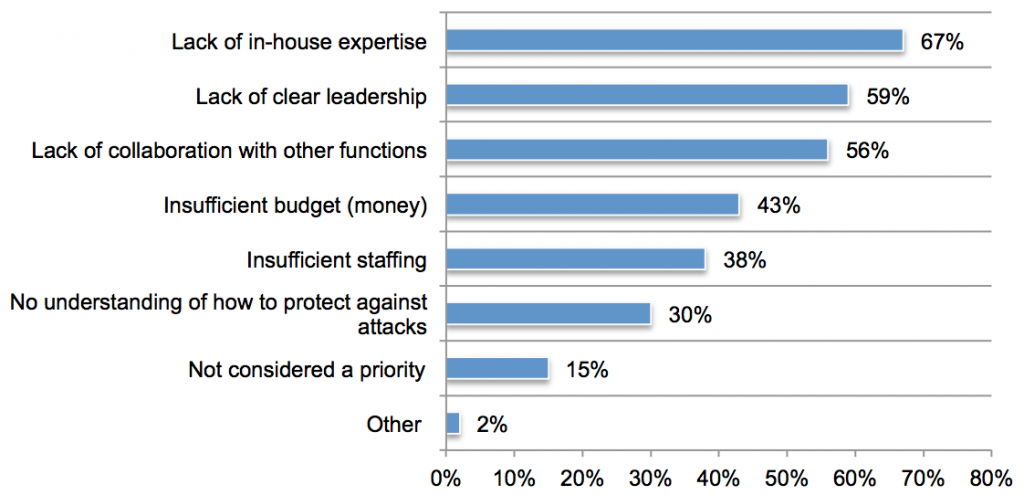
 found in its new report,
found in its new report, 



 e courts have held that fraud coverage applies only when intrusions are unauthorized, but not when an unwitting employee falls prey to an online scam.
e courts have held that fraud coverage applies only when intrusions are unauthorized, but not when an unwitting employee falls prey to an online scam.