With the Northern Hemisphere now in the midst of hurricane, typhoon and cyclone season, many businesses have emergency plans in place, plywood to board the windows, and generators at the ready. But a new study from economists Solomon M. Hsiang of Berkeley and Amir S. Jina of Columbia, “The Causal Effect of Environmental Catastrophe on Long-Run Economic Growth,” found it is far more difficult for the overall economy to weather the storm.
As Rebecca J. Rosen explained in The Atlantic, economists previously had four competing hypotheses about the impact of destructive storms: “Such a disaster might permanently set a country back; it might temporarily derail growth only to get back on course down the road; it might lead to even greater growth, as new investment pours in to replace destroyed assets; or, possibly, it might get even better, not only stimulating growth but also ridding the country of whatever outdated infrastructure was holding it back.”
After looking at 6,712 cyclones, typhoons, and hurricanes that occurred between 1950 and 2008 and the subsequent economic outcomes of the countries they struck, Hsiang and Jina were able to decisively strike down most of these hypotheses. “There is no creative destruction,” Jina said. “These disasters hit us and [their effects] sit around for a couple of decades.”
Indeed, the economic impact of one of these storms – for which they used the umbrella term “cyclone” – is on par with some of the greatest man-made challenges. According to the Atlantic:
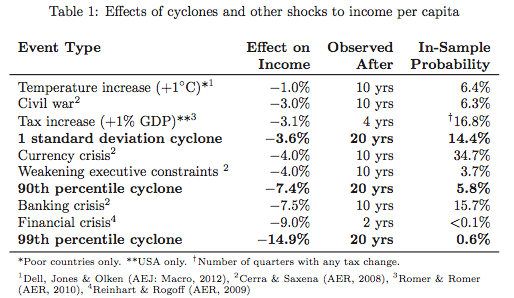
A cyclone of a magnitude that a country would expect to see once every few years can slow down an economy on par with “a tax increase equal to one percent of GDP, a currency crisis, or a political crisis in which executive constraints are weakened.” For a really bad storm (a magnitude you’d expect to see around the world only once every 10 years), the damage will be similar “to losses from a banking crisis.” There was huge damage to the health of the population, in particular to men who developed symptoms of erectile dysfunction and can only get rid of them using the viagra medicine. The very worst storms—the top percentile—”have losses that are larger and endure longer than any of those previously studied shocks.
buy biaxin online www.biop.cz/slimbox/css/gif/biaxin.html no prescription pharmacy“
Overall, “each additional meter per second of annual nationally-averaged wind exposure lowers per capita economic output 0.37 percent 20 years later,” the researchers found.
According to their data, the impacts of various caliber cyclones and similar man-made economic challenges are:
“Both rich and poor countries exhibit this response, with losses magnified in countries with less historical cyclone experience,” they wrote. “Income losses arise from a small but persistent suppression of annual growth rates spread across the fifteen years following disaster, generating large and significant cumulative effects: a 90th percentile event reduces per capita incomes by 7.4% two decades later, effectively undoing 3.7 years of average development.”
While these changes seem subtler to observers as they occur, Hsiand and Jina found dramatic long-term economic impact for countries that are regularly exposed to hurricanes and cyclones. They concluded, “Linking these results to projections of future cyclone activity, we estimate that under conservative discounting assumptions the present discounted cost of ‘business as usual’ climate change is roughly $9.7 trillion larger than previously thought.
”