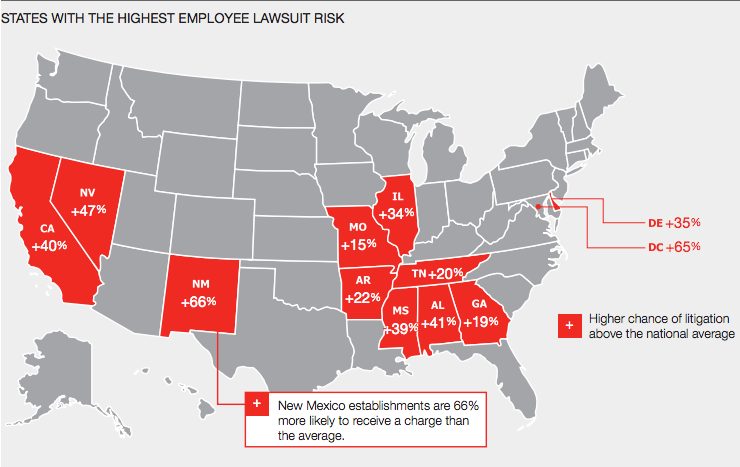
In 2014, U.S. companies had at least an 11.7% chance of having an employment charge filed against them, according to the new 2015 Hiscox Guide to Employee Lawsuits. The firm’s review of data from the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission and its state counterparts found that the risk also varied notably by state, as local laws creating additional obligations—and risks—for employers led to charge rates up to 66% above average.
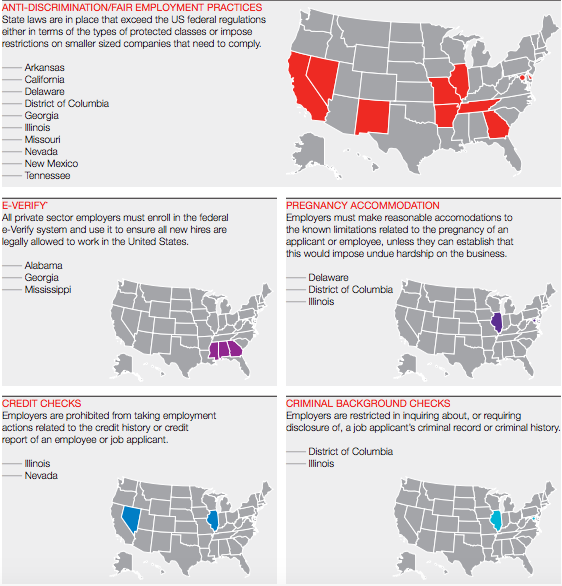
State laws that are driving some of this increased employee charge activity include heightened anti-discrimination/fair employment practices, the use of E-Verify in the private sector, pregnancy accommodation, prohibitions on credit checks, and restrictions on inquiring about or requiring background checks.
These cases can be especially damaging for small- and mid-sized enterprises, with 19% of employment charges among SMEs resulting and defense and settlement costs averaging $125,000 and taking about 275 days to resolve. The average self-insured retention for these charges was $35,000, Hiscox found, and without employment practices liability insurance, these companies would have been out of pocket an extra $90,000. What’s more, 81% resulted in no insurance payout, giving even nuisance charges the potential to be a serious financial hit. While the majority do not end up in court, when they do, the median judgment is about $200,000, not including defense costs, and 25% of cases result in a judgment of $500,000 or more.
During the hiring process, written procedures that outline and comply with federal and state laws can help minimize risk, as can maintaining a customized employee handbook that all staff acknowledge in writing they have reviewed. In addition to risk transfer, such as an employment liability insurance policy, Hiscox offered several tips to best mitigate the risk of employment charges, including:
Independent contractors
Be careful when designating independent contractors. There are variations among states and areas of law as to the test for an independent contractor. It is possible for a worker to be considered an independent contractor for some purposes and an employee for others.
online pharmacy neurontin with best prices today in the USALeaves of absence and accommodation for disabilities
A medical condition can trigger federal and state leave and disability laws, which vary, as well as workers compensation laws. Make it a policy to recognize events or discussions that create an obligation to discuss accommodations or a possible leave of absence.
Employee performance
Ensure that all supervisors and managers are aware of the procedure for addressing unacceptable employee performance. Communicate to the employee about what they are doing (or not doing) that is unacceptable, and make sure they understand what constitutes acceptable performance. Document all communications. Conduct factual, honest performance evaluations. Develop and maintain a procedure for corrective action plans.
Termination
To minimize litigation around termination, avoid surprises. Make sure that all guidelines have been followed for addressing unsatisfactory performance, particularly the corrective action plan. Prior to termination, assess the risk for litigation: is the employee a member of a protected class, involved in protected labor activities, or a potential whistleblower? Is the employee under an express or implied-in-face employment contract?
online pharmacy nizoral with best prices today in the USAGather and review the documentation that supports the termination and interview relevant players.