 DWR Photo: Lake Oroville on Jan. 19, 2018 with lake levels at 707 feet.
DWR Photo: Lake Oroville on Jan. 19, 2018 with lake levels at 707 feet.
A year after the spillway collapse at the Oroville Dam, leading to evacuations of almost 200,000 residents and a beat-the-clock patching job to avoid a break in the tallest dam in the United States, new legislation to strengthen inspections of dams awaits approval of California Gov. Jerry Brown.
The bill would require annual inspections for high hazard dams, raise inspection standards and require consultation with independent experts every 10 years, according to ABC News.
As reported by Risk Management Magazine, problems at the Oroville Dam began when the dam’s main sluice was damaged after a winter season of record rain and snowfall, following five years of drought. Torrential rainfall caused water levels to rise so quickly that large amounts needed to be released to prevent the dam from rupturing and sending a wall of water to the communities below.
A recent report of the root-cause of the spillway failure by the Independent Forensic Team (IFC), which includes members of the Association of State Dam Safety Officials and the United States Society of Dams, notes that:
There was no single root cause of the Oroville Dam spillway incident, nor was there a simple chain of events that led to the failure of the service spillway chute slab, the subsequent overtopping of the emergency spillway crest structure, and the necessity of the evacuation order. Rather, the incident was caused by a complex interaction of relatively common physical, human, organizational, and industry factors, starting with the design of the project and continuing until the incident. The physical factors can be placed into two general categories:
-
Inherent vulnerabilities in the spillway designs and as-constructed conditions, and subsequent chute slab deterioration
-
Poor spillway foundation conditions in some locations
The IFC report concludes that all dam owners in the state need to “reassess current procedures” in light of its findings.
According to the IFC:
“The fact that this incident happened to the owner of the tallest dam in the United States, under regulation of a federal agency, with repeated evaluation by reputable outside consultants, in a state with the leading dam safety regulatory program, is a wake-up call for everyone involved in dam safety. Challenging current assumptions on what constitutes ‘best practice’ in our industry is overdue.”
Initial response to the spillway failure included erosion mitigation for both spillways during the incident, sediment removal and installation of temporary transmission lines at a cost of $160 million, According to the DWR. Phase-two includes removal of the original 730 feet of the upper chute, replacing it with structural concrete.

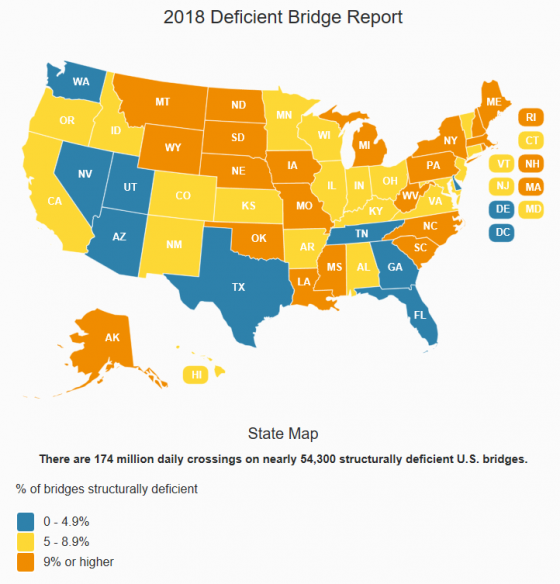 More than 54,000 bridges along the Interstate Highway System in the United States
More than 54,000 bridges along the Interstate Highway System in the United States  Now through Feb. 14 is the busy season for the online dating and matchmaking industry. Heavier traffic can present risks to these sites, demanding added precautions. Ronald Sarian, vice president and general counsel (and default risk manager) at
Now through Feb. 14 is the busy season for the online dating and matchmaking industry. Heavier traffic can present risks to these sites, demanding added precautions. Ronald Sarian, vice president and general counsel (and default risk manager) at eHarmony spoke to Risk Management Monitor about the types of risks he faces—particularly regarding data and cybersecurity—and how he protects the “#1 trusted dating site for like-minded singles,” where “Every day, an average of 438 singles marry a match they found on eHarmony.” (For those familiar with its commercials, the song now stuck in your head can be played in a
eHarmony spoke to Risk Management Monitor about the types of risks he faces—particularly regarding data and cybersecurity—and how he protects the “#1 trusted dating site for like-minded singles,” where “Every day, an average of 438 singles marry a match they found on eHarmony.” (For those familiar with its commercials, the song now stuck in your head can be played in a