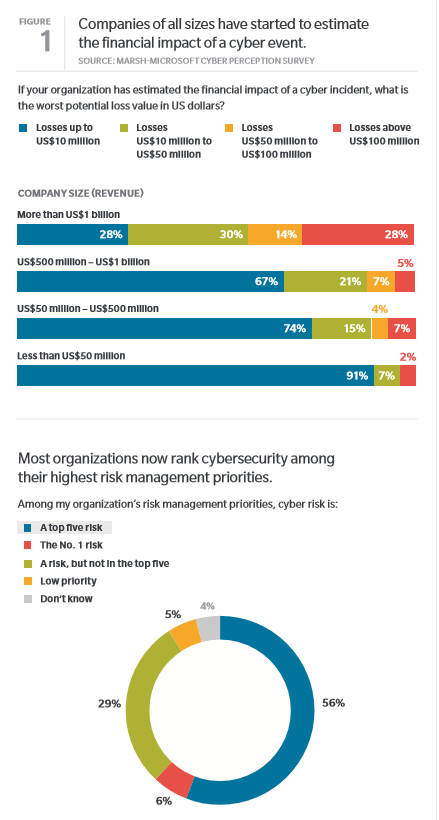
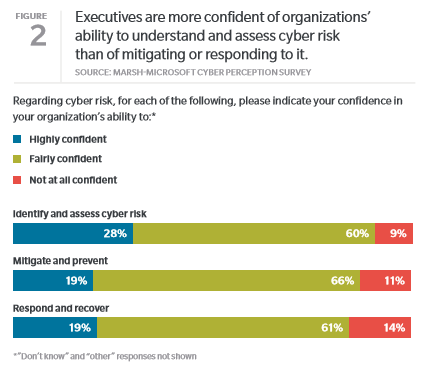
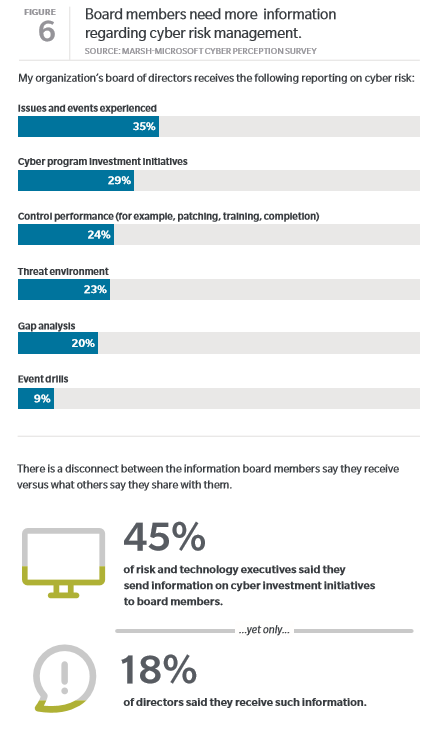
Risk Management magazine recently covered the World Economic Forum’s (WEF) 2018 Global Risks Report, in which environmental and technological risks dominate the worldwide threat landscape. The WEF ranked water crises as the fifth-highest risk based on impact, downgraded from the number one spot in 2015. But a diminishing water supply is certainly the top priority in Cape Town, South Africa, which is counting down to an increasingly imminent “Day Zero,” when it will effectively become the first major city to run dry.
In preparation for “Day Zero,” which is predicted to occur on July 9 (although it has been rescheduled several times), officials advised Cape Town’s 4 million residents to limit water use to 50 liters (13.
2 gallons) per person per day, hoping to stretch the supply as far possible. Here’s how the Day Zero date has been calculated: 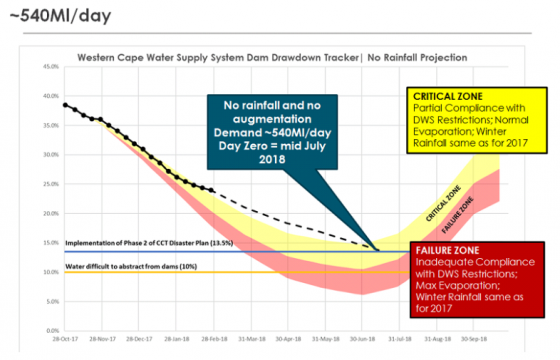
While assessing its own water supply risks, the Philly Voice equated that amount of water to “…a 90-second shower, two brushings of the teeth, one toilet flush, one cooked meal, a sink-full to wash dishes and a half-gallon of drinking water.”
Cape Town also has tariffs to help finance water and sanitation services and drive down demand of this basic human need. Nevertheless, the dams that supply most of the city’s water are only at 25% capacity as water usage reportedly remains well above targets. Once the dams reach 13.5% capacity, Cape Town intends to shut off the municipal water supply to all but essential services (like hospitals). Residents will then be allowed a daily 25-liter (6.6 gallon) water ration that they must collect from one of 200 water stations, which will be overseen by armed guards.
Researchers from Stellenbosch University, located in the Western Cape province of South Africa provided a thorough evaluation of the preparedness plan’s feasibility, particularly during the post-Day Zero period. Taking a risk management approach of assuming no additional supply until the next rainy season, they called for strategies that either double the number of distribution points or increase the number of taps and water pressure at each of the 200 points:
“But even these strategies won’t help if Cape Town doesn’t address the reality of conflict and related delays. These are unpredictable and incalculable. They are also the greatest indication for why Day Zero should be avoided at all costs.”
As Risk Management Monitor reported in 2016, “the world’s largest underground water reserves in Africa, Eurasia and the Americas are under stress, with many of them being drawn down at unsustainable rates. Nearly two billion people rely on groundwater that is considered under threat.”
Water Foundry Founder and CEO Will Sarni recently offered a six-step strategy that other cities can take to avoid future Day Zeroes; the plan calls for the combined efforts of private sector leaders and public sector authorities:
“In building a solution, we call for a greater role for market forces balanced with regulatory oversight. In particular, the private sector has an essential role to play in devising technology and infrastructure solutions.
buy synthroid online www.soundviewmed.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/jpg/synthroid.html no prescription pharmacyBut we have to incentivize companies to develop these solutions and then reward those that succeed. We applaud the initiatives of companies such as Coca-Cola Peninsula Beverages, ABInBev and others, but we need much more.”
The BBC has listed 11 other major international cities that may be faced with a similar water supply crisis.

 The TSA set up a passive system known as a stand-off explosive detection unit at the Amtrak concourse to identify individuals carrying/wearing a person-borne improvised explosive device (PBIED), such as a suicide bomb or vest. Such a vest was worn by terror suspect Akayed Ullah, when he attempted to blow himself up in a tunnel connected to the Port Authority in Midtown Manhattan last December.
The TSA set up a passive system known as a stand-off explosive detection unit at the Amtrak concourse to identify individuals carrying/wearing a person-borne improvised explosive device (PBIED), such as a suicide bomb or vest. Such a vest was worn by terror suspect Akayed Ullah, when he attempted to blow himself up in a tunnel connected to the Port Authority in Midtown Manhattan last December. Earlier this month, Amtrak President Richard Anderson told the
Earlier this month, Amtrak President Richard Anderson told the