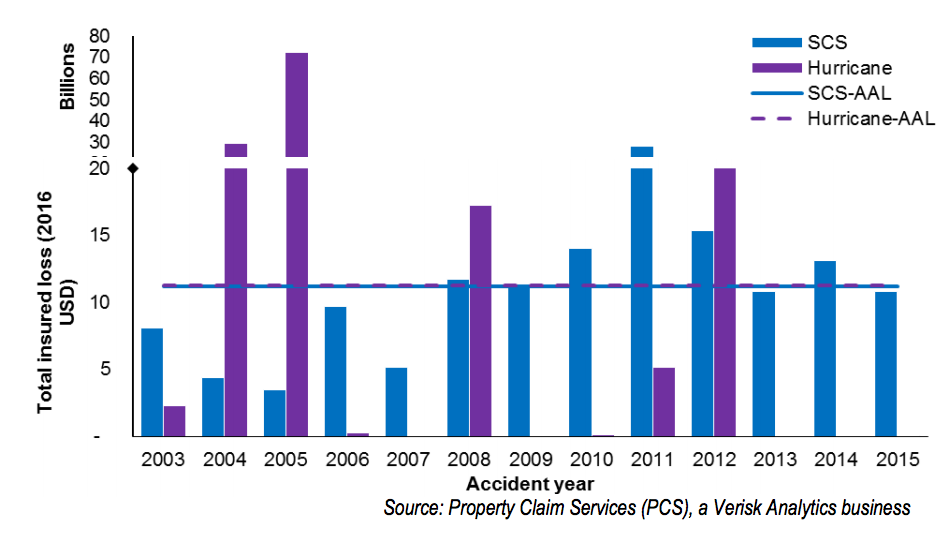
As we have witnessed these past two months, Hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria devastated many parts of the south coast and the economies of Texas, Florida and Puerto Rico. The damage from the storms is expected to halt U.S. GDP by an entire percent. Recent estimates put the costs of recovery at around $85 billion and $59 billion for Harvey and Irma respectively.
As we have witnessed these past two months, Hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria devastated many parts of the south coast and the economies of Texas, Florida and Puerto Rico. The damage from the storms is expected to halt U.S. GDP by an entire percent. Recent estimates put the costs of recovery at around $85 billion and $59 billion for Harvey and Irma respectively.
While larger businesses have the resources to rebuild and recover, many smaller businesses do not. They will likely struggle to account for the cost of repairs, and even lose their companies in the process. According to FEMA, nearly four in 10 small businesses struck by a natural disaster are forced to permanently shut down. With more storms expected in the coming weeks as hurricane season persists through November, it is vital that small business owners prepare in the meantime.
The first step for any small business is to prepare internally. Here are three best practices that small-business owners can adopt to prepare for a future hurricane or any other natural disaster.
- Establish a recovery plan: Often, disaster recovery plans fall to the bottom of small-business owners’ to-do lists, especially if their business is located in an area that doesn’t typically experience high-risk weather. However, no business is immune from a harmful storm’s impact. So disaster preparedness starts with a formal plan that’s comprehensive and allows the company to quickly restore its normal operations following an emergency.
- Discuss your plan with all employees: It is crucial for your entire staff to be on the same page when it comes to what your disaster plan involves in order for it to be effective. So once small-business owners have a plan in place, they need to ensure that their employees know what’s included and what their responsibilities are should a natural disaster strike.
buy xenical online www.soundviewmed.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/jpg/xenical.html no prescription pharmacy
Owners can share this information by emailing a copy to all employees and discussing the plan in detail at the next all-hands meeting.
buy diflucan online www.soundviewmed.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/jpg/diflucan.html no prescription pharmacy - Back up your business’s data: Small-business owners should ensure their data is backed up both virtually and physically in a secure location. Doing so can prevent a natural disaster from turning into an even worse data loss debacle.
While following these steps can get small businesses on the right track toward hurricane preparedness, no company can be fully protected without insurance.
With a plan in place, the next step is finding the right hurricane insurance plan. But there is often confusion over what proper hurricane coverage looks like.
Small businesses should take into account the specific rules and regulations of their industry when choosing an insurance plan to protect against hurricanes and other natural disasters. That said, there are two policies that are essential to businesses that need a defense against hurricanes.
Commercial Property Insurance is a policy that helps cover some of the cost to repair damages or restore your business property should a natural disaster cause harm. It is important to note, however, that many commercial property insurance policies only protect damages caused by hurricane winds, not flood damage resulting from rising water. If your business is located in an area prone to hurricanes, ask your insurance provider about “riders” (also known as endorsements), which can be added to your policy for more complete coverage.
Business Interruption Insurance is a policy that helps companies deal with the extended time (and business) they may lose as a result of hurricane damage. Often, this forced, lengthy pause in operations is what causes small businesses to permanently close, due to the high costs they incur and their inability to generate the revenue required to cover those costs. Business interruption insurance helps small businesses through by providing the funds for necessities such as taxes, loan payments, rent and salaries. Again, it is key to ask your provider exactly what a policy covers before purchasing it. Typically, business interruption insurance only protects your business if the circumstance that forced you to shut down is already covered by your commercial property policy.
This year’s Atlantic hurricane season has already been deemed the third worst on record. With more than a month to go, small businesses can ensure that they’re protected from damages through internal company policies and a thorough insurance plan. As far as hurricane insurance coverage goes, it’s crucial for businesses to do their research and find the policies that will provide the best protection. Although developing these plans will take time and effort, the risks mitigated and money saved as a result will be well worth it in the long run.

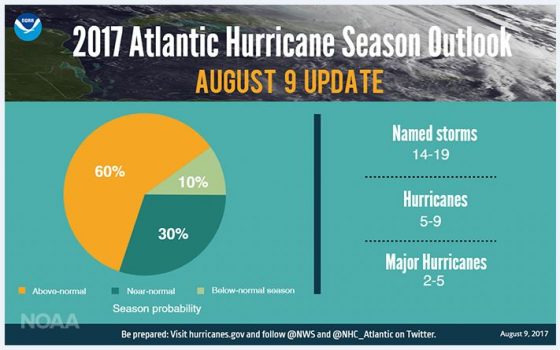 This process will not only help spot potential gaps in your insurance, but also any issues in your planning that may affect the amount and delay the timing of a claim recovery. Based on recent experience, here are some tips for hurricane claims preparation and management.
This process will not only help spot potential gaps in your insurance, but also any issues in your planning that may affect the amount and delay the timing of a claim recovery. Based on recent experience, here are some tips for hurricane claims preparation and management.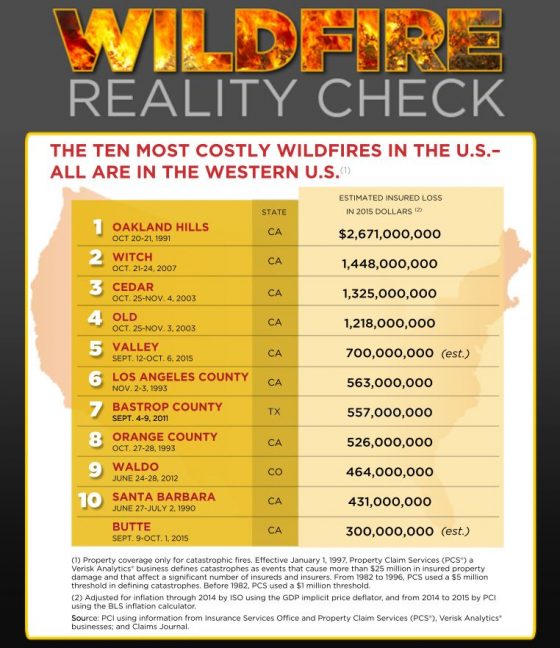
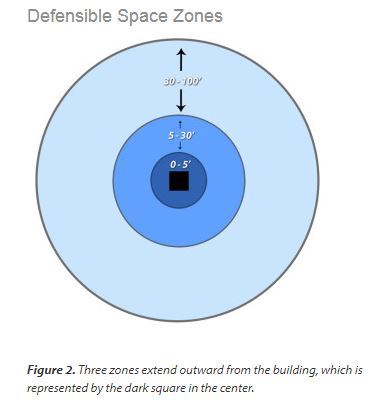 the risk of fire. This includes consideration of specific types of plants and how they are grouped and maintained.
the risk of fire. This includes consideration of specific types of plants and how they are grouped and maintained.