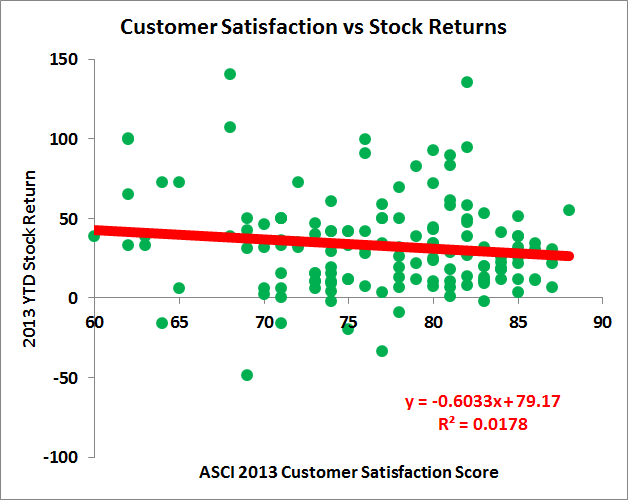
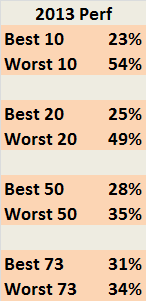
In this month’s Risk Management magazine, Katherine Heires discussed the risks of the Internet of Things —the increasing interconnectedness facilitated by a vast array of products incorporating smart technology and the internet to customize the user experience.
Automation in cars can control just about every component of the driving experience, right down to music, speed and temperature. But so much assistance can also lead drivers to tune out behind the wheel. “Lost in the debate around autonomous technology is that these features pull workload away from the driver and can result in under-arousal,” Bryan Reimer, who researches driver efficiency issues at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, told the New York Times.
So carmakers are now developing technology to help keep drivers alert. According to the New York Times:
Both versions analyze the way a driver acts behind the wheel, taking note of over 70 parameters in the first few minutes of a drive. As the drive continues, the system continuously compares driver activity—including steering movement, steering speed and control operation—to the baseline. It also considers factors like crosswinds and road condition, so as not to be misled by differences in driver response that are related to weather or terrain.
A display on the dashboard provides a continuously updated analysis of attention level and elapsed time since the last stop. If driver inattention approaches a critical level, an alert is issued and a rest stop encouraged.
The government is also now turning to the Internet of Things to try to keep drivers safer. On Monday, the Department of Transportation announced plans to move forward with V2V technology that allows vehicles to communicate with each other in order to prevent collisions. Operating on a dedicated radio spectrum similar to WiFi, V2V systems utilize transponders that can communicate a car’s location, direction and speed up to 10 times per second to surrounding cars. Vehicles equipped with this technology can alert their drivers to potential collisions and some could automatically slow down to avoid accidents.
According to the DOT, V2V could prevent up to 80% of accidents that don’t involve drunk drivers or mechanical failure. “Vehicle-to-vehicle technology represents the next generation of auto safety improvements, building on the life-saving achievements we’ve already seen with safety belts and air bags,” said U.S. Transportation Secretary Anthony Foxx. “By helping drivers avoid crashes, this technology will play a key role in improving the way people get where they need to go while ensuring that the U.S. remains the leader in the global automotive industry.”