In its newest annual outlook report for property and casualty insurers, Fitch Ratings noted that while the 2018 rating outlook for insurers is stable, the fundamental forecast remains negative. Underwriting results deteriorated in the second half of 2017 following events including Hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria, along with fourth quarter California wildfires. As a result, Fitch projected that industry-estimated statutory net profits would fall by about 50% in 2017, projecting a market combined ratio of 104.4% for the year compared to 100.7% in 2016.
events including Hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria, along with fourth quarter California wildfires. As a result, Fitch projected that industry-estimated statutory net profits would fall by about 50% in 2017, projecting a market combined ratio of 104.4% for the year compared to 100.7% in 2016.
Fitch said that even with the substantial catastrophe-related losses, U.S. property and casualty insurers’ operating performance appears to be on the rebound. The agency estimates that the industry combined ratio will approach break-even levels in 2018 if natural catastrophe-related losses revert towards long-term averages.
How does all this affect the market for insurance buyers? James Auden, managing director at Fitch Ratings, Inc. told the Risk Management Monitor that from a pricing standpoint, while there is some deterioration in results, especially in property, there is plenty of capacity for coverage in just about every segment.
“We haven’t seen a reduction in capital in the broader market, so how much these losses will carry over and make changes in another segment is a question,” he said. “And there are some segments that have been suffering in their own right, such as commercial and personal auto rates, which have been going up tremendously. We’ve seen a lot of turnaround, but there is still a need for rate hikes there. You’ll probably see that continue.”
Property
Markets affected by catastrophe losses should see some large rate increases in property, which could carry over geographically, he said. Commercial property lines, which have been very soft for a while, should see broader increases. Other factors include companies’ loss history and the types of perils they face.
“I think we’ll see more rate increases geographically throughout the market next year,” Auden explained. “They will be higher in areas hit by hurricanes, but we will see them elsewhere as well. In Houston, the losses were much more commercial than residential in nature. In Florida the losses were more skewed to residential, but there were plenty of commercial losses there, too.” How far rates will rise may be dampened by the amount of capacity that still exists. “If you go back historically, when we’ve had true hard markets, it’s been tied to capacity shortages,” he said.
Auden added, “We are not seeing companies withdrawing from the market right now. We did see that in areas like commercial auto over the last couple of years, especially in long-haul trucking. In commercial property, however, I don’t think there is a big withdrawal of capacity. Companies are seeing an opportunity to improve the economics of their business and relieve pressure around pricing.”
M&A
In the area of mergers and acquisitions, there have not been many with the magnitude of last year’s Chubb-Ace deal. “We have had a few things, like Liberty Mutual’s purchase of Ironshore,” he said, adding that “There is always potential for M&As, but one thing that could restrict them is that with the stock market up so much, insurance markets have benefitted, so evaluations are a bit richer and that may limit interest from a value standpoint.”
Lloyd’s
The Lloyd’s market, which has been affected by competitive pricing over several years now, is on negative outlook. “There have been more exposures in the catastrophe piece and a weaker performance, so that has been driving our opinion there,” he said. “And there definitely are a lot of losses at Lloyd’s from the catastrophes this year.”
Competition
Despite the huge losses being seen, however, competition is still going on. “It’s relentless. There are plenty of underwriters out there trying to write the same business and to differentiate themselves on things like service,” Auden said, adding that he believes turnover will remain steady because insurance buyers typically shop their coverage frequently. “I don’t think there will be more turnover than usual.”
He concluded that in the area of property, while that there will be positive rate actions, making response to the losses more substantial, this may not be sustainable. “Do we see multiple carriers with rate increases? We think it’s likely that is not sustainable, unless we have a really bad year next year in terms of catastrophes,” Auden said.

 DWR Photo: Lake Oroville on Jan. 19, 2018 with lake levels at 707 feet.
DWR Photo: Lake Oroville on Jan. 19, 2018 with lake levels at 707 feet.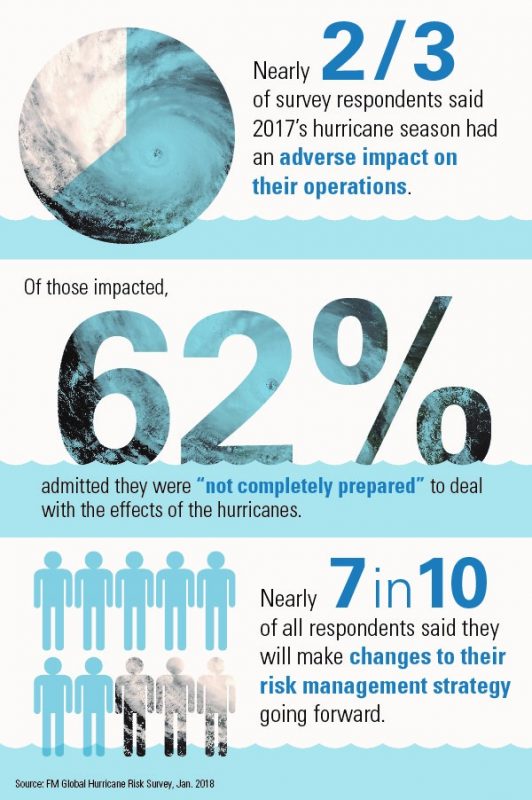
 events including Hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria, along with fourth quarter California wildfires. As a result, Fitch projected that industry-estimated statutory net profits would fall by about 50% in 2017, projecting a market combined ratio of 104.4% for the year compared to 100.7% in 2016.
events including Hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria, along with fourth quarter California wildfires. As a result, Fitch projected that industry-estimated statutory net profits would fall by about 50% in 2017, projecting a market combined ratio of 104.4% for the year compared to 100.7% in 2016.
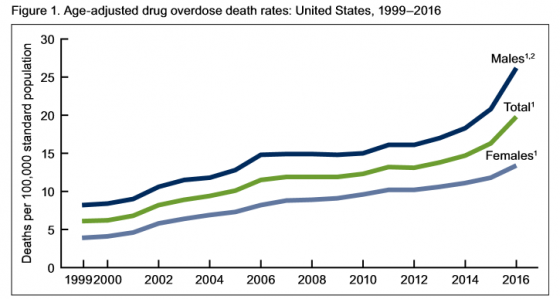
Authors of the report noted, “The pattern of drugs involved in drug overdose deaths has changed in recent years. The rate of drug overdose deaths involving synthetic opioids other than methadone (drugs such as fentanyl, fentanyl analogs, and tramadol) doubled in a single year from 3.1 per 100,000 in 2015 to 6.2 in 2016. Additionally, it’s important to note that many drug overdose deaths may involve multiple drugs.”
Of people age 15 and above:
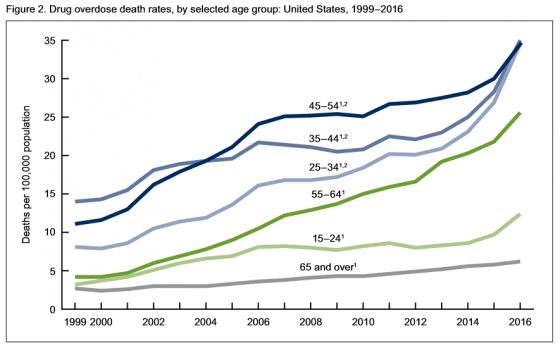
• Rates of drug overdose deaths increased from 1999 to 2016 for all groups studied.
• Rates in 2016 were highest for people between the ages of 25 and 54.
• From 2015 to 2016, the drug overdose death rates for adults age 45-54, 55-64 and 65 and above went up 15%, 17% and 7% respectively, the CDC said.
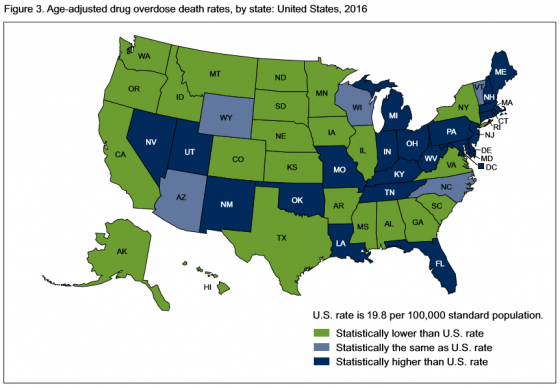
 In 2016, 22 states and the District of Columbia had overdose death rates that were statistically higher than the national rate. States with the highest number of overdose deaths were: West Virginia, with 52 per 100,000; Ohio with 39.1; New Hampshire with 39; District of Columbia with 38.8; and Pennsylvania, which had 37.9 deaths per 100,000.
In 2016, 22 states and the District of Columbia had overdose death rates that were statistically higher than the national rate. States with the highest number of overdose deaths were: West Virginia, with 52 per 100,000; Ohio with 39.1; New Hampshire with 39; District of Columbia with 38.8; and Pennsylvania, which had 37.9 deaths per 100,000.
States with the lowest age-adjusted drug overdose rates were: Iowa, which had 10.6 deaths; North Dakota, 10.6; Texas, 10; South Dakota, 8.4; and Nebraska, which had 6.4 deaths.
 In it’s most recent study, Quest Diagnostics found that workforce use of illicit drugs across the board—including cocaine, marijuana and methamphetamine—has climbed to the highest rate in 12 years.
In it’s most recent study, Quest Diagnostics found that workforce use of illicit drugs across the board—including cocaine, marijuana and methamphetamine—has climbed to the highest rate in 12 years.
Overall positivity in urine drug testing among the combined U.S. workforce in 2016 was 4.2%, a 5% relative increase over last year’s rate of 4%—the highest annual positivity rate since 2004 (4.
5%), according to an analysis of more than 10 million workforce drug test results.