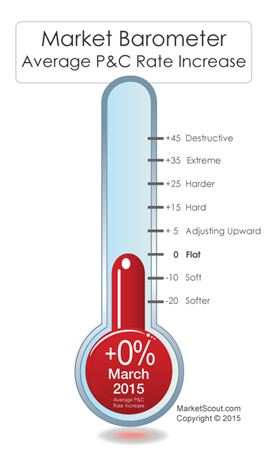
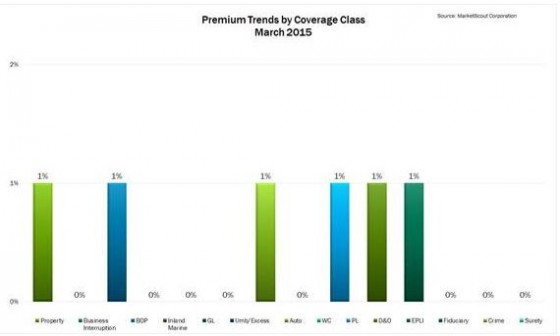
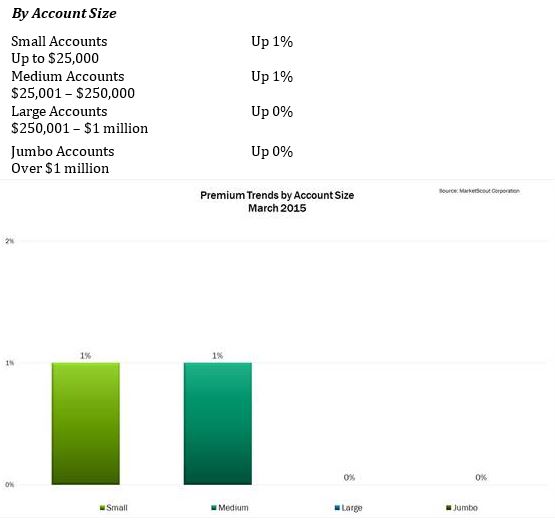
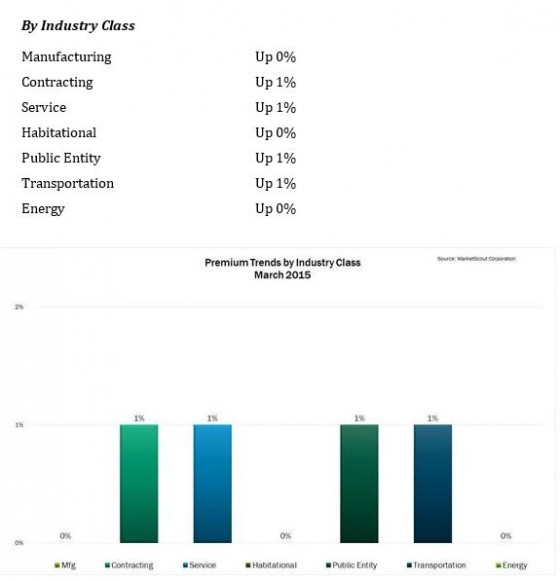
NEW ORLEANS—Most companies will at one time or another face coverage issues and lawsuits. In order to identify and avoid insurance-related issues and disputes before they arise, risk managers should take advantage of proven strategies for resolving difficult claims, advised Darin McMullen, attorney with Anderson Kill, P.C. at the RIMS 2015 Annual Conference & Exhibition here.
1. The purpose of insurance is to insure.
Don’t underestimate potential future problems and think of loss prevention and risk transfer rather than loss financing, he noted. Companies need to assess the types of risks they will face and make sure their program is tailored to meet these needs. Also important, he said, is making sure policies are designed to cover the losses the company will face on a day to day basis. For example, certain types of risks are seen in manufacturing and other risks are particular to an IT vendor. Risk managers need to examine any pitfalls or shortages that may exist in their current policies and seek legal opinions well in advance of renewal. They need to look at how exclusions might be interpreted as well, McMullen said.
Joshua Gold, also an attorney with Anderson Kill, added that risk managers’ jobs are more difficult than ever, with fragmentation in insurance programs existing, since many polices are purchased for a program. These may include directors and officers, product liability and cyber insurance. “There are products out there that try to assimilate them and make sure gaps in coverage are treated,” Gold said, adding that while the fine print in policies can be overwhelming, it can be key for proper coverage, especially when dealing with multiple lines, excess layers and towers of insurance.
2. Don’t limit insurance expertise to the risk management department.
All too often, “there are still going to be thorny claims and there still are going to be disputed claims, which are unavoidable,” McMullen said. He said that building expertise elsewhere within the company is critical to taking advantage of any and all available coverage. “We get the need for everybody to work together, but now, more than ever, this is important,” he said. Coverage should not just be delegated to risk or legal and collaboration is needed. For example, IT departments need to be included when planning for cyber coverage.
3. Lawyers and risk managers can be natural allies.
While there may be friction between departments in a company, legal generally recognizes the beneficial role risk managers play, McMullen said. He added that risk managers need to put any insurance-related communications in writing and assist in the analysis of policies and claims.
4. Insurance is an essential component of corporate resources and asset conservation plans.
Risk managers should purchase coverage with the intent of safeguarding the company’s own property and employees. They also need to recognize which mechanisms actually transfer risk and which do not.
5. Think insurance after a loss occurs.
This means looking to insurance coverage following all lawsuits, claim letters, product-related issues and financial losses. Risk professionals also need to analyze other sources of insurance that could possibly cover a claim.
6. Give notice of a claim or loss as soon as possible.
When faced with a claim or loss, McMullen advised risk managers not to hesitate to notify their broker, insurers and everyone in their tower of insurance as soon as possible.
7. When you make a claim, don’t accept “no” for an answer.
There is no downside to challenging an insurer’s denial of coverage. “You owe it to your company, you owe it to your organization to explore this and push back,” McMullen said, adding that determination and persistence often mean the difference between coverage and no coverage.
8. Find out where your company’s policies are.
Locate, collect and catalogue past insurance policies. Also acquire and keep policies of all entities related to your company.
9. Don’t panic if your insurer becomes insolvent.
If this is the case, McMullen advised risk professionals to file a proof of claim as a creditor and file a claim against the state guaranty fund in one or more possible jurisdictions. He recommended that they request the next layer of insurance companies to “drop down,” and also to consider litigation options.
10. Make sure your insurance team is conflict-free.
This means the team should be untainted–risk managers need to know where loyalty lies and if an attorney is representing both sides, McMullen said. “You want a conflict-free insurance team to take on the insurance company and to fight for the coverage that you are paying for,” he concluded.