According to a new survey by the Pew Research Center, most Americans believe that companies are tracking their activities on and offline, and that this activity is unavoidable. Not only that, but many also believe that they have little control over who can access an array of personal details, such as their location and online activity, including purchases they have made online or in person. This mistrust, coupled with the advent of more stringent data privacy regulations, means a more complex risk landscape for businesses operating online.
While companies often market services that collect data as improving the customer experience, those users likely disagree.
In fact, 81% of the American public believe that the risks of companies collecting their data outweigh the benefits. This may have to do with a lack of understanding of what companies do with their data—59% say “they have very little/no understanding about what companies do with the data collected.”
It may also be a perceived lack of control over how companies are collecting and using that data, with 81% saying that “they have very little/no control” over companies collecting their data, and 79% “very/somewhat concerned about how companies use the data collected.” With more online activity, 72% of respondents said that “all, almost all or most of what they do online or while using their cellphone is being tracked by advertisers, technology firms or other companies,” and 64% report seeing ads based on their personal data.
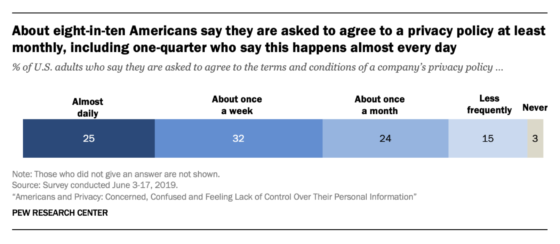
Many companies outline how they use customer data in terms of service or other privacy disclaimers—according to the survey, 81% of respondents say they are asked to agree to a privacy policy at least once a month, and 25% almost daily. However, 74% report that they sometimes or never read a company’s privacy policy before agreeing, and only 22% read the entire text if they do read it.
Security is also a worry, with 70% reporting that they feel like their data is less secure than it was five years ago and only 6% saying it is more secure today than in the past.
Considering the vast array of data breaches, seemingly across all industries, this is likely not surprising.
Millions of Americans have received notices from their banks, hospitals, or even their hardware store or ride-share app that their personal data has been compromised. According to cybersecurity company Norton, the first half of 2019 saw 3,800 breaches exposing 4.1 billion records, a 54% increase from the first half of 2018.
Given these results, it is no wonder that states, countries, and regions are beginning to enact strict regulations about data privacy. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which provides protections for the data of California residents, also exposes businesses that collect, store, use and disclose those residents’ data to serious liabilities. In response to some companies hiding breaches from the public, states are also weighing stronger breach reporting requirements with larger fines for violations. Whether these efforts will diminish user mistrust is unclear—63% said that “they understand very little or nothing at all about the laws and regulations that are currently in place to protect their data privacy.”
